Abstract
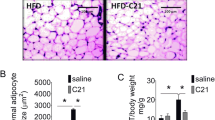
Obesity is a global health problem and treatment options are still insufficient. When chronically treated with the angiotensin II receptor blocker telmisartan (TEL), rodents do not develop diet-induced obesity (DIO). However, the underlying mechanism for this is still unclear. Here we investigated whether TEL prevents leptin resistance by enhancing leptin uptake across the blood-brain barrier (BBB). To address this question, we fed C57BL/6 mice a high-fat diet (HFD) and treated them daily with TEL by oral gavage. In addition to broadly characterizing the metabolism of leptin, we determined leptin uptake into the brain by measuring BBB transport of radioactively labeled leptin after long-term and short-term TEL treatment. Additionally, we assessed BBB integrity in response to angiotensin II in vitro and in vivo. We found that HFD markedly increased body weight, energy intake, and leptin concentration but that this effect was abolished under TEL treatment. Furthermore, glucose control and, most importantly, leptin uptake across the BBB were impaired in mice on HFD, but, again, both were preserved under TEL treatment. BBB integrity was not impaired due to angiotensin II or blocking of angiotensin II receptors. However, TEL did not exhibit an acute effect on leptin uptake across the BBB. Our results confirm that TEL prevents DIO and show that TEL preserves leptin transport and thereby prevents leptin resistance. We conclude that the preservation of leptin sensitivity is, however, more a consequence than the cause of TEL preventing body weight gain.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AngII:
-
Angiotensin II
- ARB:
-
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- BBB:
-
Blood-brain barrier
- DIO:
-
Diet-induced obesity
- HFD:
-
High-fat diet
- ITT:
-
Insulin tolerance test
- NFD:
-
Normal-fat diet
- RAS:
-
Renin-angiotensin system
- RER:
-
Respiratory exchange rate
- TEER:
-
Transendothelial electrical resistance
- TEL:
-
Telmisartan
References
Afshin A, Forouzanfar MH, Reitsma MB, Sur P, Estep K, Lee A, Marczak L, Mokdad AH, Moradi-Lakeh M, Naghavi M, Salama JS, Vos T, Abate KH, Abbafati C, Ahmed MB, Al-Aly Z, Alkerwi A, Al-Raddadi R, Amare AT, Amberbir A, Amegah AK, Amini E, Amrock SM, Anjana RM, Arnlov J, Asayesh H, Banerjee A, Barac A, Baye E, Bennett DA, Beyene AS, Biadgilign S, Biryukov S, Bjertness E, Boneya DJ, Campos-Nonato I, Carrero JJ, Cecilio P, Cercy K, Ciobanu LG, Cornaby L, Damtew SA, Dandona L, Dandona R, Dharmaratne SD, Duncan BB, Eshrati B, Esteghamati A, Feigin VL, Fernandes JC, Furst T, Gebrehiwot TT, Gold A, Gona PN, Goto A, Habtewold TD, Hadush KT, Hafezi-Nejad N, Hay SI, Horino M, Islami F, Kamal R, Kasaeian A, Katikireddi SV, Kengne AP, Kesavachandran CN, Khader YS, Khang YH, Khubchandani J, Kim D, Kim YJ, Kinfu Y, Kosen S, Ku T, Defo BK, Kumar GA, Larson HJ, Leinsalu M, Liang X, Lim SS, Liu P, Lopez AD, Lozano R, Majeed A, Malekzadeh R, Malta DC, Mazidi M, McAlinden C, McGarvey ST, Mengistu DT, Mensah GA, Mensink GBM, Mezgebe HB, Mirrakhimov EM, Mueller UO, Noubiap JJ, Obermeyer CM, Ogbo FA, Owolabi MO, Patton GC, Pourmalek F, Qorbani M, Rafay A, Rai RK, Ranabhat CL, Reinig N, Safiri S, Salomon JA, Sanabria JR, Santos IS, Sartorius B, Sawhney M, Schmidhuber J, Schutte AE, Schmidt MI, Sepanlou SG, Shamsizadeh M, Sheikhbahaei S, Shin MJ, Shiri R, Shiue I, Roba HS, Silva DAS, Silverberg JI, Singh JA, Stranges S, Swaminathan S, Tabares-Seisdedos R, Tadese F, Tedla BA, Tegegne BS, Terkawi AS, Thakur JS, Tonelli M, Topor-Madry R, Tyrovolas S, Ukwaja KN, Uthman OA, Vaezghasemi M, Vasankari T, Vlassov VV, Vollset SE, Weiderpass E, Werdecker A, Wesana J, Westerman R, Yano Y, Yonemoto N, Yonga G, Zaidi Z, Zenebe ZM, Zipkin B, Murray CJL (2017) Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med 377:13–27. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1614362
Albers JJ, Pitman W, Wolfbauer G, Cheung MC, Kennedy H, Tu AY, Marcovina SM, Paigen B (1999) Relationship between phospholipid transfer protein activity and HDL level and size among inbred mouse strains. J Lipid Res 40:295–301
Assmann JC, Muller K, Wenzel J, Walther T, Brands J, Thornton P, Allan SM, Schwaninger M (2017) Isolation and cultivation of primary brain endothelial cells from adult mice. Bio Protoc 7. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.2294
Banks WA (2008) The blood-brain barrier as a cause of obesity. Curr Pharm Des 14:1606–1614
Banks WA (2001) Enhanced leptin transport across the blood-brain barrier by alpha 1-adrenergic agents. Brain Res 899:209–217
Banks WA, Clever CM, Farrell CL (2000) Partial saturation and regional variation in the blood-to-brain transport of leptin in normal weight mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:E1158–E1165
Banks WA, Coon AB, Robinson SM, Moinuddin A, Shultz JM, Nakaoke R, Morley JE (2004) Triglycerides induce leptin resistance at the blood-brain barrier. Diabetes 53:1253–1260
Banks WA, DiPalma CR, Farrell CL (1999) Impaired transport of leptin across the blood-brain barrier in obesity. Peptides 20:1341–1345
Banks WA, Farrell CL (2003) Impaired transport of leptin across the blood-brain barrier in obesity is acquired and reversible. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:E10–E15. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00468.2002
Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Huang W, Jaspan JB, Maness LM (1996) Leptin enters the brain by a saturable system independent of insulin. Peptides 17:305–311
Black MH, Shu YH, Wu J, Koebnick C, MacKay A, Watanabe RM, Buchanan TA, Xiang AH (2018) Longitudinal increases in adiposity contribute to worsening adipokine profile over time in Mexican Americans. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md) 26:703–712. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22128
Cagnoni F, Njwe CA, Zaninelli A, Ricci AR, Daffra D, D'Ospina A, Preti P, Destro M (2010) Blocking the RAAS at different levels: an update on the use of the direct renin inhibitors alone and in combination. Vasc Health Risk Manag 6:549–559
Curtis MJ, Bond RA, Spina D, Ahluwalia A, Alexander SP, Giembycz MA, Gilchrist A, Hoyer D, Insel PA, Izzo AA, Lawrence AJ, MacEwan DJ, Moon LD, Wonnacott S, Weston AH, McGrath JC (2015) Experimental design and analysis and their reporting: new guidance for publication in BJP. Br J Pharmacol 172:3461–3471. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12856
de Souza CJ, Eckhardt M, Gagen K, Dong M, Chen W, Laurent D, Burkey BF (2001) Effects of pioglitazone on adipose tissue remodeling within the setting of obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 50:1863–1871
Eisinger K, Liebisch G, Schmitz G, Aslanidis C, Krautbauer S, Buechler C (2014) Lipidomic analysis of serum from high fat diet induced obese mice. Int J Mol Sci 15:2991–3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15022991
Engeli S, Bohnke J, Gorzelniak K, Janke J, Schling P, Bader M, Luft FC, and Sharma AM (2005) Weight loss and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex : 1979) 45: 356–362. doi:https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000154361.47683.d3.
Engin A (2017) The pathogenesis of obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation. Adv Exp Med Biol 960:221–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_9.
Fleegal-DeMotta MA, Doghu S, Banks WA (2009) Angiotensin II modulates BBB permeability via activation of the AT(1) receptor in brain endothelial cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:640–647. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2008.158
Frederich RC, Hamann A, Anderson S, Lollmann B, Lowell BB, Flier JS (1995) Leptin levels reflect body lipid content in mice: evidence for diet-induced resistance to leptin action. Nat Med 1:1311–1314
Friedman JM, Halaas JL (1998) Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 395:763–770. https://doi.org/10.1038/27376
Fujisaka S, Usui I, Kanatani Y, Ikutani M, Takasaki I, Tsuneyama K, Tabuchi Y, Bukhari A, Yamazaki Y, Suzuki H, Senda S, Aminuddin A, Nagai Y, Takatsu K, Kobayashi M, Tobe K (2011) Telmisartan improves insulin resistance and modulates adipose tissue macrophage polarization in high-fat-fed mice. Endocrinology 152:1789–1799. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2010-1312
Gohlke P, Von Kugelgen S, Jurgensen T, Kox T, Rascher W, Culman J, Unger T (2002) Effects of orally applied candesartan cilexetil on central responses to angiotensin II in conscious rats. J Hypertens 20:909–918
Gohlke P, Weiss S, Jansen A, Wienen W, Stangier J, Rascher W, Culman J, Unger T (2001) AT1 receptor antagonist telmisartan administered peripherally inhibits central responses to angiotensin II in conscious rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:62–70
Guillemot-Legris O, Muccioli GG (2017) Obesity-induced neuroinflammation: beyond the hypothalamus. Trends Neurosci 40:237–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2017.02.005
He H, Yang D, Ma L, Luo Z, Ma S, Feng X, Cao T, Yan Z, Liu D, Tepel M, and Zhu Z (2010) Telmisartan prevents weight gain and obesity through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta-dependent pathways. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex : 1979) 55: 869–879. doi:https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.109.143958.
Hohle S, Blume A, Lebrun C, Culman J, Unger T (1995) Angiotensin receptors in the brain. Pharmacology & toxicology 77:306–315
Kabir SM, Lee ES, Son DS (2014) Chemokine network during adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells: differential response between growth and proinflammatory factor in preadipocytes vs. adipocytes. Adipocyte 3:97–106. https://doi.org/10.4161/adip.28110
Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM (2006) Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 444:840–846. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05482
Keane KN, Calton EK, Carlessi R, Hart PH, Newsholme P (2017) The bioenergetics of inflammation: insights into obesity and type 2 diabetes. Eur J Clin Nutr 71:904–912. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2017.45
Kilkenny C, Browne W, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2010) Animal research: reporting in vivo experiments: the ARRIVE guidelines. Br J Pharmacol 160:1577–1579. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00872.x
Kintscher U, Bramlage P, Paar WD, Thoenes M, Unger T (2007) Irbesartan for the treatment of hypertension in patients with the metabolic syndrome: a sub analysis of the Treat to Target post authorization survey. Prospective observational, two armed study in 14,200 patients. Cardiovasc Diabetol 6:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2840-6-12
Larsen PJ, Jensen PB, Sorensen RV, Larsen LK, Vrang N, Wulff EM, Wassermann K (2003) Differential influences of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors gamma and -alpha on food intake and energy homeostasis. Diabetes 52:2249–2259
Lee M, Song SJ, Choi MS, Yu R, Park T (2015) IL-7 receptor deletion ameliorates diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Diabetologia 58:2361–2370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-015-3684-7
Li H, Li M, Liu P, Wang Y, Zhang H, Li H, Yang S, Song Y, Yin Y, Gao L, Cheng S, Cai J, and Tian G (2016) Telmisartan ameliorates nephropathy in metabolic syndrome by reducing leptin release from perirenal adipose tissue. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex: 1979) 68: 478–490. doi:https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.116.07008.
Michel MC, Brunner HR, Foster C, Huo Y (2016) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists in animal models of vascular, cardiac, metabolic and renal disease. Pharmacol Ther 164:1–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.03.019.
Miesel A, Muller-Fielitz H, Johren O, Vogt FM, Raasch W (2012) Double blockade of angiotensin II (AT(1) )-receptors and ACE does not improve weight gain and glucose homeostasis better than single-drug treatments in obese rats. Br J Pharmacol 165:2721–2735. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01726.x
Morton GJ, Cummings DE, Baskin DG, Barsh GS, Schwartz MW (2006) Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature 443:289–295. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05026
Muller-Fielitz H, Hubel N, Mildner M, Vogt FM, Barkhausen J, Raasch W (2014) Chronic blockade of angiotensin AT(1) receptors improves cardinal symptoms of metabolic syndrome in diet-induced obesity in rats. Br J Pharmacol 171:746–760. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12510
Muller-Fielitz H, Landolt J, Heidbreder M, Werth S, Vogt FM, Johren O, Raasch W (2012) Improved insulin sensitivity after long-term treatment with AT1 blockers is not associated with PPARgamma target gene regulation. Endocrinology 153:1103–1115. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2011-0183
Muller-Fielitz H, Lau M, Geissler C, Werner L, Winkler M, Raasch W (2015) Preventing leptin resistance by blocking angiotensin II AT1 receptors in diet-induced obese rats. Br J Pharmacol 172:857–868. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12949
Muller-Fielitz H, Markert A, Wittmershaus C, Pahlke F, Johren O, Raasch W (2011) Weight loss and hypophagia after high-dose AT1-blockade is only observed after high dosing and depends on regular leptin signalling but not blood pressure. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 383:373–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-011-0602-5
Munzberg H (2010) Leptin-signaling pathways and leptin resistance. Forum Nutr 63:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1159/000264400.
Munzberg H, Morrison CD (2015) Structure, production and signaling of leptin. Metabolism 64:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.09.010
Myers MG, Cowley MA, Munzberg H (2008) Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol 70:537–556. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.70.113006.100707
Myers MG Jr, Leibel RL, Seeley RJ, Schwartz MW (2010) Obesity and leptin resistance: distinguishing cause from effect. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21:643–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2010.08.002
Nonaka N, Hileman SM, Shioda S, Vo TQ, Banks WA (2004) Effects of lipopolysaccharide on leptin transport across the blood-brain barrier. Brain Res 1016:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2004.04.066
Park HK, Ahima RS (2013) Resistin in rodents and humans. Diabetes Metab J 37:404–414. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.6.404
Patlak CS, Blasberg RG, Fenstermacher JD (1983) Graphical evaluation of blood-to-brain transfer constants from multiple-time uptake data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 3:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.1983.1.
Pelisch N, Hosomi N, Ueno M, Masugata H, Murao K, Hitomi H, Nakano D, Kobori H, Nishiyama A, Kohno M (2010) Systemic candesartan reduces brain angiotensin II via downregulation of brain renin-angiotensin system. Hypertens Res 33:161–164. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2009.200
Pelisch N, Hosomi N, Ueno M, Nakano D, Hitomi H, Mogi M, Shimada K, Kobori H, Horiuchi M, Sakamoto H, Matsumoto M, Kohno M, Nishiyama A (2011) Blockade of AT1 receptors protects the blood-brain barrier and improves cognition in Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens 24:362–368. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajh.2010.241
Sainz N, Barrenetxe J, Moreno-Aliaga MJ, Martinez JA (2015) Leptin resistance and diet-induced obesity: central and peripheral actions of leptin. Metabolism 64:35–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.10.015
Schuchard J, Winkler M, Stolting I, Schuster F, Vogt FM, Barkhausen J, Thorns C, Santos RA, Bader M, Raasch W (2015) Lack of weight gain after angiotensin AT1 receptor blockade in diet-induced obesity is partly mediated by an angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas-dependent pathway. Br J Pharmacol 172:3764–3778. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13172.
Schulte L, Schulz A, Unland J, Schulz H, Hubner N, Schmidt-Ott KM, Kreutz R (2012) MWF rats with spontaneous albuminuria inherit a reduced efficiency of nephron induction during early nephrogenesis in comparison to SHR rats. J Hypertens 30:2031–2038. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e328356a60a
Schupp M, Clemenz M, Gineste R, Witt H, Janke J, Helleboid S, Hennuyer N, Ruiz P, Unger T, Staels B, Kintscher U (2005) Molecular characterization of new selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulators with angiotensin receptor blocking activity. Diabetes 54:3442–3452
Smith PM, Hindmarch CC, Murphy D, Ferguson AV (2014) AT1 receptor blockade alters nutritional and biometric development in obesity-resistant and obesity-prone rats submitted to a high fat diet. Front Psychol 5:832. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00832
Soronen J, Laurila PP, Naukkarinen J, Surakka I, Ripatti S, Jauhiainen M, Olkkonen VM, Yki-Jarvinen H (2012) Adipose tissue gene expression analysis reveals changes in inflammatory, mitochondrial respiratory and lipid metabolic pathways in obese insulin-resistant subjects. BMC Med Genet 5:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-8794-5-9
Souza-Mello V, Gregorio BM, Cardoso-de-Lemos FS, de Carvalho L, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2010) Comparative effects of telmisartan, sitagliptin and metformin alone or in combination on obesity, insulin resistance, and liver and pancreas remodelling in C57BL/6 mice fed on a very high-fat diet. Clin Sci (Lond) 119:239–250. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs20100061
Vital SA, Terao S, Nagai M, Granger DN (2010) Mechanisms underlying the cerebral microvascular responses to angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Microcirculation 17:641–649. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1549-8719.2010.00060.x
Winkler M, Schuchard J, Stolting I, Vogt FM, Barkhausen J, Thorns C, Bader M, Raasch W (2016) The brain renin-angiotensin system plays a crucial role in regulating body weight in diet-induced obesity in rats. Br J Pharmacol 173:1602–1617. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13461
Wosik K, Cayrol R, Dodelet-Devillers A, Berthelet F, Bernard M, Moumdjian R, Bouthillier A, Reudelhuber TL, Prat A (2007) Angiotensin II controls occludin function and is required for blood-brain barrier maintenance: relevance to multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci 27:9032–9042. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2088-07.2007
Zhang QZ, Liu YL, Wang YR, Fu LN, Zhang J, Wang XR, Wang BM (2017) Effects of telmisartan on improving leptin resistance and inhibiting hepatic fibrosis in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Experimental and therapeutic medicine 14:2689–2694. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4809
Zorad S, Dou JT, Benicky J, Hutanu D, Tybitanclova K, Zhou J, Saavedra JM (2006) Long-term angiotensin II AT1 receptor inhibition produces adipose tissue hypotrophy accompanied by increased expression of adiponectin and PPARgamma. Eur J Pharmacol 552:112–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.08.062.
Acknowledgments
This publication was supported by a grant of the German Research Foundation to the Graduiertenkolleg 1957 “Adipocyte-Brain Crosstalk,” University of Lübeck, by a grant (81X2700128F) of the German Centre for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK) and by the Robert Pflüger Stiftung.
We thank Prof. Marcus Altfeld and Urte Matschl from the Heinrich Pette Institute, Hamburg, for the measurements with the luminex system, and Prof. Jens Mittag from the Center of Brain, Behavior and Metabolism, Lübeck, who provided the blood pressure measurement system.
The authors gratefully acknowledge Sherryl Sundell for improving the English style.
Parts of the work presented in the article were presented at the 2nd Pharm-Tox Summit in Heidelberg, Germany, 2017 (Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archives of Pharmacology, 390 (Suppl. 1, 39).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FS, GH, IS, KS, NH, and EEW performed the research; FS, WR, and WAB designed the research study; FS, WR, and WAB analyzed the data; and FS and WR wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 255 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuster, F., Huber, G., Stölting, I. et al. Telmisartan prevents diet-induced obesity and preserves leptin transport across the blood-brain barrier in high-fat diet-fed mice. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 470, 1673–1689 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-018-2178-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-018-2178-0