Abstract
Natural flavonoids are ubiquitous in dietary plants and vegetables and have been proposed to have antiviral, antioxidant, cardiovascular protective, and anticancer effects. Volume-regulated anion channels (VRACs), which are essential for cell volume regulation, have been proposed to play a key role in cell proliferation and migration, apoptosis, transepithelial transport, and cancer development. In this study, we screened a group of 53 structurally related natural flavonoids and three synthetic flavonoids for their inhibitory activities on VRAC currents. A whole-cell patch technique was used to record VRAC currents in the human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 and human umbilical vein endothelial (HUVEC) cells. The 5′-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU) assay technique was used to investigate cell proliferation. At 100 μM, 34 of 53 compounds significantly inhibited hypotonic extrasolution-induced VRAC currents by > 50% in HEK293 cells. Among these compounds, luteolin, baicalein, eupatorin, galangin, quercetin, fisetin, karanjin, Dh-morin, genistein, irisolidone, and prunetin exhibited the highest efficacy for VRAC blockade (the mean inhibition > 80%) with IC50s of 5–13 μM and Emaxs of about 87–99%. We also studied the effects of three synthetic flavonoids on VRAC currents in HEK293 cells. Flavoxate showed high inhibition efficacy toward VRAC currents (IC50 = 2.3 ± 0.3 μM; Emax = 91.8% ± 2.7%). Finally, these flavonoids inhibited endogenous VRAC currents and cell proliferation in endothelial cells. This study demonstrates that natural and synthetic flavonoids are potent VRAC current inhibitors, and VRAC inhibition by flavonoids might be responsible for their anti-angiogenic effects.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- VRACs:
-
volume-regulated anion channels
- HEK:
-
human embryonic kidney
- DCPIB:
-
4-(2-butyl-6, 7-dichloro-2-cyclopentyl-indan-1-on-5-yl) oxobutyric acid
- HUVECs:
-
human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- EGTA:
-
ethylene glycol-O,O′-bis(2-aminoethyl)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid
- HEPES:
-
N-(hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N′-(2-ethanesulfonic acid)
- IC50 :
-
half-maximal concentrations
- E max :
-
maximum effect
References
Bhat TA, Nambiar D, Pal A, Agarwal R, Singh RP (2012) Fisetin inhibits various attributes of angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo--implications for angioprevention. Carcinogenesis 33:385–393
Cho H, Lee HY, Ahn DR, Kim SY, Kim S, Lee KB, Lee YM, Park H, Yang EG (2008) Baicalein induces functional hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and angiogenesis. Mol Pharmacol 74:70–81
Decher N, Lang HJ, Nilius B, Bruggemann A, Busch AE, Steinmeyer K (2001) DCPIB is a novel selective blocker of I(Cl,swell) and prevents swelling-induced shortening of Guinea-pig atrial action potential duration. Br J Pharmacol 134:1467–1479
Dick GM, Kong ID, Sanders KM (1999) Effects of anion channel antagonists in canine colonic myocytes: comparative pharmacology of Cl-, Ca2+ and K+ currents. Br J Pharmacol 127:1819–1831
Doleckova I, Rarova L, Gruz J, Vondrusova M, Strnad M, Krystof V (2012) Antiproliferative and antiangiogenic effects of flavone eupatorin, an active constituent of chloroform extract of Orthosiphon stamineus leaves. Fitoterapia 83:1000–1007
Graefe EU, Derendorf H, Veit M (1999) Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of the flavonol quercetin in humans. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 37:219–233
Guarneri L, Ibba M, Angelico P, Colombo D, Fredella B, Testa R (1993) Effects of drugs used in the therapy of detrusor hyperactivity on the volume-induced contractions of the rat urinary bladder. Pharmacol Res 27:173–187
Helix N, Strobaek D, Dahl BH, Christophersen P (2003) Inhibition of the endogenous volume-regulated anion channel (VRAC) in HEK293 cells by acidic di-aryl-ureas. J Membr Biol 196:83–94
Hoffmann EK, Holm NB, Lambert IH (2014) Functions of volume-sensitive and calcium-activated chloride channels. IUBMB Life 66:257–267
Huang H, Chen AY, Rojanasakul Y, Ye X, Rankin GO, Chen YC (2015) Dietary compounds galangin and myricetin suppress ovarian cancer cell angiogenesis. J Funct Foods 15:464–475
Kim JD, Liu L, Guo W, Meydani M (2006) Chemical structure of flavonols in relation to modulation of angiogenesis and immune-endothelial cell adhesion. J Nutr Biochem 17:165–176
Klausen TK, Bergdahl A, Hougaard C, Christophersen P, Pedersen SF, Hoffmann EK (2007) Cell cycle-dependent activity of the volume- and Ca2+-activated anion currents in Ehrlich lettre ascites cells. J Cell Physiol 210:831–842
Liantonio A, Pusch M, Picollo A, Guida P, De Luca A, Pierno S, Fracchiolla G, Loiodice F, Tortorella P, Conte Camerino D (2004) Investigations of pharmacologic properties of the renal CLC-K1 chloride channel co-expressed with barttin by the use of 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)propionic acid derivatives and other structurally unrelated chloride channels blockers. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:13–20
Liu Y, Zhang H, Huang D, Qi J, Xu J, Gao H, Du X, Gamper N (2014) Characterization of the effects of Cl(−) channel modulators on TMEM16A and bestrophin-1 Ca(2)(+) activated Cl(−) channels. Pflugers Arch 467:1417–1430
Maertens C, Droogmans G, Chakraborty P, Nilius B (2001) Inhibition of volume-regulated anion channels in cultured endothelial cells by the anti-oestrogens clomiphene and nafoxidine. Br J Pharmacol 132:135–142
Manolopoulos VG, Liekens S, Koolwijk P, Voets T, Peters E, Droogmans G, Lelkes PI, De Clercq E, Nilius B (2000) Inhibition of angiogenesis by blockers of volume-regulated anion channels. Gen Pharmacol 34:107–116
Pedersen SF, Okada Y, Nilius B (2016) Biophysics and physiology of the volume-regulated anion channel (VRAC)/volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion channel (VSOR). Pflugers Arch 468:371–383
Picollo A, Liantonio A, Didonna MP, Elia L, Camerino DC, Pusch M (2004) Molecular determinants of differential pore blocking of kidney CLC-K chloride channels. EMBO Rep 5:584–589
Planells-Cases R, Lutter D, Guyader C, Gerhards NM, Ullrich F, Elger DA, Kucukosmanoglu A, Xu G, Voss FK, Reincke SM, Stauber T, Blomen VA, Vis DJ, Wessels LF, Brummelkamp TR, Borst P, Rottenberg S, Jentsch TJ (2015) Subunit composition of VRAC channels determines substrate specificity and cellular resistance to Pt-based anti-cancer drugs. EMBO J 34:2993–3008
Pratheeshkumar P, Budhraja A, Son YO, Wang X, Zhang Z, Ding S, Wang L, Hitron A, Lee JC, Xu M, Chen G, Luo J, Shi X (2012) Quercetin inhibits angiogenesis mediated human prostate tumor growth by targeting VEGFR- 2 regulated AKT/mTOR/P70S6K signaling pathways. PLoS One 7:e47516
Pratheeshkumar P, Son YO, Budhraja A, Wang X, Ding S, Wang L, Hitron A, Lee JC, Kim D, Divya SP, Chen G, Zhang Z, Luo J, Shi X (2012) Luteolin inhibits human prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis. PLoS One 7:e52279
Qiu Z, Dubin AE, Mathur J, Tu B, Reddy K, Miraglia LJ, Reinhardt J, Orth AP, Patapoutian A (2014) SWELL1, a plasma membrane protein, is an essential component of volume-regulated anion channel. Cell 157:447–458
Tomoda T, Aishima M, Takano N, Nakano T, Seki N, Yonemitsu Y, Sueishi K, Naito S, Ito Y, Teramoto N (2005) The effects of flavoxate hydrochloride on voltage-dependent L-type Ca2+ currents in human urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol 146:25–32
Tomoda T, Zhu HL, Iwasa K, Aishima M, Shibata A, Seki N, Naito S, Teramoto N (2007) Effects of flavoxate hydrochloride on voltage-dependent Ba2+ currents in human detrusor myocytes at different experimental temperatures. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 376:195–203
Voets T, Szucs G, Droogmans G, Nilius B (1995) Blockers of volume-activated Cl- currents inhibit endothelial cell proliferation. Pflugers Arch 431:132–134
Voss FK, Ullrich F, Munch J, Lazarow K, Lutter D, Mah N, Andrade-Navarro MA, von Kries JP, Stauber T, Jentsch TJ (2014) Identification of LRRC8 heteromers as an essential component of the volume-regulated anion channel VRAC. Science 344:634–638
Zhang X, Li H, Zhang H, Liu Y, Huo L, Jia Z, Xue Y, Sun X, Zhang W (2017) Inhibition of transmembrane member 16A calcium-activated chloride channels by natural flavonoids contributes to flavonoid anticancer effects. Br J Pharmacol 174:2334–2345
Zhao K, Li X, Lin B, Yang D, Zhou Y, Li Z, Guo Q, Lu N (2017) Oroxyloside inhibits angiogenesis through suppressing internalization of VEGFR2/Flk-1 in endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 233:3454–3464
Zhao K, Song X, Huang Y, Yao J, Zhou M, Li Z, You Q, Guo Q, Lu N (2014) Wogonin inhibits LPS-induced tumor angiogenesis via suppressing PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signaling. Eur J Pharmacol 737:57–69
Zhou M, Song X, Huang Y, Wei L, Li Z, You Q, Guo Q, Lu N (2014) Wogonin inhibits H2O2-induced angiogenesis via suppressing PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Vasc Pharmacol 60:110–119
Ziegelhoeffer T, Scholz D, Friedrich C, Helisch A, Wagner S, Fernandez B, Schaper W (2003) Inhibition of collateral artery growth by mibefradil: possible role of volume-regulated chloride channels. Endothelium 10:237–246
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Research Foundation of Education Bureau of Hebei Province (BJ2018030 to XZ), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (H2015423014 to XZ), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31401003 to XZ, 81500057 to HZ), the project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M581313 to XZ), the Research Foundation of Education Bureau of Hebei Province (QN2017113 to PC, QN2016166 to WL), and the Research Foundation of Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Hebei Province (2017007 to YL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Participated in research design: X. Zhang, M. Zhang, J. Zhang, Xue, and Chu
Conducted experiments: Xue, H. Li, Y. Zhang, Han, G. Zhang, W. Li, Lin, H. Zhang, Chen, and Sun
Performed data analysis: Xue, G. Zhang, and Liu
Wrote or contributed to the writing of the manuscript: X. Zhang, M. Zhang, J. Zhang, and Xue
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Ion channels, receptors and transporters
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 192 kb)
Figure S1
The effects of five natural flavonoids on VRAC currents in HUVEC cells. (PDF 309 kb)
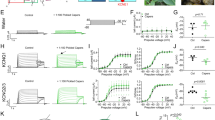
(A) Representative current traces for the effects of five natural flavonoids (100 μM) on VRAC currents tested at −100 mV in HUVEC cells.
(B) The mean inhibition of VRAC current tested at −100 mV by five natural flavonoids (100 μM) in HUVEC cells. *p < 0.05 compared with the current amplitudes in the absence of drugs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Y., Li, H., Zhang, Y. et al. Natural and synthetic flavonoids, novel blockers of the volume-regulated anion channels, inhibit endothelial cell proliferation. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 470, 1473–1483 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-018-2170-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-018-2170-8