Abstract
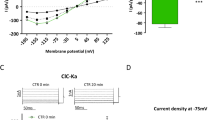
The renal collecting duct contains two distinct cell types, principal and intercalated cells, expressing potassium Kir4.1/5.1 (KCNJ10/16) and chloride ClC-K2 (ClC-Kb in humans) channels on their basolateral membrane, respectively. Both channels are thought to play important roles in controlling systemic water-electrolyte balance and blood pressure. However, little is known about mechanisms regulating activity of Kir4.1/5.1 and ClC-K2/b. Here, we employed patch clamp analysis at the single channel and whole cell levels in freshly isolated mouse collecting ducts to investigate regulation of Kir4.1/5.1 and ClC-K2/b by dietary K+ and Cl− intake. Treatment of mice with high K+ and high Cl− diet (6% K+, 5% Cl−) for 1 week significantly increased basolateral K+-selective current, single channel Kir4.1/5.1 activity and induced hyperpolarization of basolateral membrane potential in principal cells when compared to values in mice on a regular diet (0.9% K+, 0.5% Cl−). In contrast, basolateral Cl−-selective current and single channel ClC-K2/b activity was markedly decreased in intercalated cells under this condition. Substitution of dietary K+ to Na+ in the presence of high Cl− exerted a similar inhibiting action of ClC-K2/b suggesting that the channel is sensitive to variations in dietary Cl− per se. Cl−-sensitive with-no-lysine kinase (WNK) cascade has been recently proposed to orchestrate electrolyte transport in the distal tubule during variations of dietary K+. However, co-expression of WNK1 or its major downstream effector Ste20-related proline-alanine-rich kinase (SPAK) had no effect on ClC-Kb over-expressed in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. Treatment of mice with high K+ diet without concomitant elevations in dietary Cl− (6% K+, 0.5% Cl−) elicited a comparable increase in basolateral K+-selective current, single channel Kir4.1/5.1 activity in principal cells, but had no significant effect on ClC-K2/b activity in intercalated cells. Furthermore, stimulation of aldosterone signaling by Deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA) recapitulated the stimulatory actions of high K+ intake on Kir4.1/5.1 channels in principal cells but was ineffective to alter ClC-K2/b activity and basolateral Cl− conductance in intercalated cells. In summary, we report that variations of dietary K+ and Cl− independently regulate basolateral potassium and chloride conductance in principal and intercalated cells. We propose that such discrete mechanism might contribute to fine-tuning of urinary excretion of electrolytes depending on dietary intake.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrini O, Keck M, Briones R, Lourdel S, Vargas-Poussou R, Teulon J (2015) ClC-K chloride channels: emerging pathophysiology of Bartter syndrome type 3. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 308:F1324–F1334
Arroyo JP, Ronzaud C, Lagnaz D, Staub O, Gamba G (2011) Aldosterone paradox: differential regulation of ion transport in distal nephron. Physiology (Bethesda) 26:115–123
Beutler KT, Masilamani S, Turban S, Nielsen J, Brooks HL, Ageloff S, Fenton RA, Packer RK, Knepper MA (2003) Long-term regulation of ENaC expression in kidney by angiotensin II. Hypertension 41:1143–1150
Birkenhager R, Otto E, Schurmann MJ, Vollmer M, Ruf EM, Maier-Lutz I, Beekmann F, Fekete A, Omran H, Feldmann D, Milford DV, Jeck N, Konrad M, Landau D, Knoers NV, Antignac C, Sudbrak R, Kispert A, Hildebrandt F (2001) Mutation of BSND causes Bartter syndrome with sensorineural deafness and kidney failure. Nat Genet 29:310–314
Bockenhauer D, Feather S, Stanescu HC, Bandulik S, Zdebik AA, Reichold M, Tobin J, Lieberer E, Sterner C, Landoure G, Arora R, Sirimanna T, Thompson D, Cross JH, van’t Hoff W, Al Masri O, Tullus K, Yeung S, Anikster Y, Klootwijk E, Hubank M, Dillon MJ, Heitzmann D, Arcos-Burgos M, Knepper MA, Dobbie A, Gahl WA, Warth R, Sheridan E, Kleta R (2009) Epilepsy, ataxia, sensorineural deafness, tubulopathy, and KCNJ10 mutations. N Engl J Med 360:1960–1970
Boettger T, Hubner CA, Maier H, Rust MB, Beck FX, Jentsch TJ (2002) Deafness and renal tubular acidosis in mice lacking the K-cl co-transporter KCC4. Nature 416:874–878
Cuevas CA, Su XT, Wang MX, Terker AS, Lin DH, McCormick JA, Yang CL, Ellison DH, Wang WH (2017) Potassium sensing by renal distal tubules requires Kir4.1. J Am Soc Nephrol : JASN 28:1814–1825
Estevez R, Boettger T, Stein V, Birkenhager R, Otto E, Hildebrandt F, Jentsch TJ (2001) Barttin is a cl− channel beta-subunit crucial for renal cl− reabsorption and inner ear K+ secretion. Nature 414:558–561
Gray DA, Frindt G, Zhang YY, Palmer LG, Basolateral K (2005) + conductance in principal cells of rat CCD. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 288:F493–F504
Hennings JC, Andrini O, Picard N, Paulais M, Huebner AK, Cayuqueo IK, Bignon Y, Keck M, Corniere N, Bohm D, Jentsch TJ, Chambrey R, Teulon J, Hubner CA, Eladari D (2017) The ClC-K2 Chloride Channel is critical for salt handling in the distal nephron. J Am Soc Nephrol: JASN 28:209–217
Hoekstra M, Yeh L, Lansink AO, Vogelzang M, Stegeman CA, Rodgers MG, van der Horst IC, Wietasch G, Zijlstra F, Nijsten MW (2012) Determinants of renal potassium excretion in critically ill patients: the role of insulin therapy. Crit Care Med 40:762–765
Kahle KT, Rinehart J, de Los Heros P, Louvi A, Meade P, Vazquez N, Hebert SC, Gamba G, Gimenez I, Lifton RP (2005) WNK3 modulates transport of Cl− in and out of cells: implications for control of cell volume and neuronal excitability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:16783–16788
Kamenicky P, Blanchard A, Frank M, Salenave S, Letierce A, Azizi M, Lombes M, Chanson P (2011) Body fluid expansion in acromegaly is related to enhanced epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:2127–2135
Kamenicky P, Viengchareun S, Blanchard A, Meduri G, Zizzari P, Imbert-Teboul M, Doucet A, Chanson P, Lombes M (2008) Epithelial sodium channel is a key mediator of growth hormone-induced sodium retention in acromegaly. Endocrinology 149:3294–3305
Khawaja Z, Wilcox CS (2011) Role of the kidneys in resistant hypertension. Int J Hypertens 2011:143471
Kobayashi K, Uchida S, Mizutani S, Sasaki S, Marumo F (2001) Intrarenal and cellular localization of CLC-K2 protein in the mouse kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol: JASN 12:1327–1334
Lachheb S, Cluzeaud F, Bens M, Genete M, Hibino H, Lourdel S, Kurachi Y, Vandewalle A, Teulon J, Paulais M (2008) Kir4.1/Kir5.1 channel forms the major K+ channel in the basolateral membrane of mouse renal collecting duct principal cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 294:F1398–F1407
Lourdel S, Paulais M, Cluzeaud F, Bens M, Tanemoto M, Kurachi Y, Vandewalle A, Teulon J (2002) An inward rectifier K+ channel at the basolateral membrane of the mouse distal convoluted tubule: similarities with Kir4-Kir5.1 heteromeric channels. J Physiol 538:391–404
Makhanova N, Lee G, Takahashi N, Sequeira Lopez ML, Gomez RA, Kim HS, Smithies O (2006) Kidney function in mice lacking aldosterone. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 290:F61–F69
Mamenko M, Zaika O, Prieto MC, Jensen VB, Doris PA, Navar LG, Pochynyuk O, Chronic Angiotensin II (2013) Infusion drives extensive aldosterone-independent epithelial Na+ channel activation. Hypertension 62:1111–1122
Mamenko MV, Boukelmoune N, Tomilin VN, Zaika OL, Jensen VB, O'Neil RG, Pochynyuk OM (2017) The renal TRPV4 channel is essential for adaptation to increased dietary potassium. Kidney Int 91:1398–1409
Muto S, Yasoshima K, Yoshitomi K, Imai M, Asano Y (1990) Electrophysiological identification of alpha- and beta-intercalated cells and their distribution along the rabbit distal nephron segments. J Clin Invest 86:1829–1839
Nissant A, Paulais M, Lachheb S, Lourdel S, Teulon J (2006) Similar chloride channels in the connecting tubule and cortical collecting duct of the mouse kidney. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 290:F1421–F1429
Ohno Y, Hibino H, Lossin C, Inanobe A, Kurachi Y (2007) Inhibition of astroglial Kir4.1 channels by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Brain Res 1178:44–51
Pearce D, Soundararajan R, Trimpert C, Kashlan OB, Deen PM, Kohan DE (2014) Collecting duct principal cell transport processes and their regulation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol: CJASN
Piala AT, Moon TM, Akella R, He H, Cobb MH, Goldsmith EJ (2014) Chloride sensing by WNK1 involves inhibition of autophosphorylation. Science Signaling 7:ra41
Pochynyuk O, Kucher V, Boiko N, Mironova E, Staruschenko A, Karpushev AV, Tong Q, Hendron E, and Stockand J (2009) Intrinsic voltage-dependence of the epithelial Na+ channel is masked by a conserved transmembrane domain tryptophan. J Biol Chem
Pochynyuk O, Tong Q, Medina J, Vandewalle A, Staruschenko A, Bugaj V, Stockand JD (2007) Molecular determinants of PI(4,5)P2 and PI(3,4,5)P3 regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel. J Gen Physiol 130:399–413
Rossetti L, Klein-Robbenhaar G, Giebisch G, Smith D, DeFronzo R (1987) Effect of insulin on renal potassium metabolism. Am J Phys 252:F60–F64
Roy A, Al-bataineh MM, Pastor-Soler NM (2015) Collecting duct intercalated cell function and regulation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol: CJASN 10:305–324
Roy A, Al-Qusairi L, Donnelly BF, Ronzaud C, Marciszyn AL, Gong F, Chang YP, Butterworth MB, Pastor-Soler NM, Hallows KR, Staub O, Subramanya AR (2015) Alternatively spliced proline-rich cassettes link WNK1 to aldosterone action. J Clin Invest 125:3433–3448
Scholl U, Hebeisen S, Janssen AG, Muller-Newen G, Alekov A, Fahlke C (2006) Barttin modulates trafficking and function of ClC-K channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:11411–11416
Scholl UI, Choi M, Liu T, Ramaekers VT, Hausler MG, Grimmer J, Tobe SW, Farhi A, Nelson-Williams C, Lifton RP (2009) Seizures, sensorineural deafness, ataxia, mental retardation, and electrolyte imbalance (SeSAME syndrome) caused by mutations in KCNJ10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:5842–5847
Shibata S, Rinehart J, Zhang J, Moeckel G, Castaneda-Bueno M, Stiegler AL, Boggon TJ, Gamba G, Lifton RP (2013) Mineralocorticoid receptor phosphorylation regulates ligand binding and renal response to volume depletion and hyperkalemia. Cell Metab 18:660–671
Simon DB, Bindra RS, Mansfield TA, Nelson-Williams C, Mendonca E, Stone R, Schurman S, Nayir A, Alpay H, Bakkaloglu A, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Morales JM, Sanjad SA, Taylor CM, Pilz D, Brem A, Trachtman H, Griswold W, Richard GA, John E, Lifton RP (1997) Mutations in the chloride channel gene, CLCNKB, cause Bartter's syndrome type III. Nat Genet 17:171–178
Staruschenko A (2012) Regulation of transport in the connecting tubule and cortical collecting duct. Compr Physiol 2:1541–1584
Su S, Ohno Y, Lossin C, Hibino H, Inanobe A, Kurachi Y (2007) Inhibition of astroglial inwardly rectifying Kir4.1 channels by a tricyclic antidepressant, nortriptyline. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:573–580
Terker AS, Zhang C, Erspamer KJ, Gamba G, Yang CL, Ellison DH (2016) Unique chloride-sensing properties of WNK4 permit the distal nephron to modulate potassium homeostasis. Kidney Int 89:127–134
Terker AS, Zhang C, McCormick JA, Lazelle RA, Zhang C, Meermeier NP, Siler DA, Park HJ, Fu Y, Cohen DM, Weinstein AM, Wang WH, Yang CL, Ellison DH (2015) Potassium modulates electrolyte balance and blood pressure through effects on distal cell voltage and chloride. Cell Metab 21:39–50
Uchida S, Sasaki S (2005) Function of chloride channels in the kidney. Annu Rev Physiol 67:759–778
Wall SM, Weinstein AM (2013) Cortical distal nephron cl− transport in volume homeostasis and blood pressure regulation. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 305:F427–F438
Wang WH, Giebisch G (2009) Regulation of potassium handling in the renal collecting duct. Pflugers Archiv : Eur J Physiol 458:157–168
Wang WH, Yue P, Sun P, Lin DH (2010) Regulation and function of potassium channels in aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 19:463–470
Watanabe M, Fukuda A (2015) Development and regulation of chloride homeostasis in the central nervous system. Front Cell Neurosci 9:371
Wilson FH, Disse-Nicodeme S, Choate KA, Ishikawa K, Nelson-Williams C, Desitter I, Gunel M, Milford DV, Lipkin GW, Achard JM, Feely MP, Dussol B, Berland Y, Unwin RJ, Mayan H, Simon DB, Farfel Z, Jeunemaitre X, Lifton RP (2001) Human hypertension caused by mutations in WNK kinases. Science 293:1107–1112
Woda CB, Leite M Jr, Rohatgi R, Satlin LM (2002) Effects of luminal flow and nucleotides on [Ca2+]i in rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 283:F437–F446
Xu J, Barone S, Li H, Holiday S, Zahedi K, Soleimani M (2011) Slc26a11, a chloride transporter, localizes with the vacuolar H+-ATPase of a-intercalated cells of the kidney. Kidney Int 80:926–937
Zaika O, Mamenko M, Boukelmoune N, Pochynyuk O (2015) IGF-1 and insulin exert opposite actions on ClC-K2 activity in the cortical collecting ducts. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 308:F39–F48
Zaika O, Palygin O, Tomilin V, Mamenko M, Staruschenko A, Pochynyuk O (2016) Insulin and IGF-1 activate Kir4.1/5.1 channels in cortical collecting duct principal cells to control basolateral membrane voltage. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 310:F311–F321
Zaika O, Tomilin V, Mamenko M, Bhalla V, Pochynyuk O (2016) New perspective of ClC-kb/2 cl- channel physiology in the distal renal tubule. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 310:F923–F930
Zaika OL, Mamenko M, Palygin O, Boukelmoune N, Staruschenko A, Pochynyuk O (2013) Direct inhibition of basolateral Kir4.1/5.1 and Kir4.1 channels in the cortical collecting duct by dopamine. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 305:F1277–F1287
Zhang C, Wang L, Su XT, Zhang J, Lin DH, Wang WH (2017) ENaC and ROMK activity are inhibited in the DCT2/CNT of TgWnk4PHAII mice. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 312:F682–F688
Zhang C, Wang L, Zhang J, Su XT, Lin DH, Scholl UI, Giebisch G, Lifton RP, Wang WH (2014) KCNJ10 determines the expression of the apical Na-Cl cotransporter (NCC) in the early distal convoluted tubule (DCT1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:11864–11869
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by NIH-NIDDK DK095029 (to O. P.), AHA 17GRNT33660488 (to O. P.), NIH-NIDDK DK098145 (to A.R.S.), and ASN Ben J. Lipps Research Fellowship (to V. T.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Animal use and welfare adhered to the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals following protocols reviewed and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committees of the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Topical Collection on Ion channels, receptors and transporters
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomilin, V.N., Zaika, O., Subramanya, A.R. et al. Dietary K+ and Cl− independently regulate basolateral conductance in principal and intercalated cells of the collecting duct. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 470, 339–353 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-2084-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-2084-x