Abstract
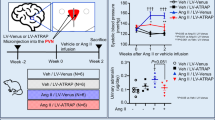
Blood pressure is controlled by tonic sympathetic activities, excessive activation of which contributes to the pathogenesis and progression of hypertension. Interleukin (IL)-1β in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) is involved in sympathetic overdrive and hypertension. Here, we investigated the therapeutic effects of IL-1 receptor type I (IL-1R1) gene silencing in the PVN on hypertension. Recombinant lentivirus vectors expressing a short hairpin RNA (shRNA) targeting IL-1R1 (Lv-shR-IL-1R1) or a control shRNA were microinjected into PVN of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) and normotensive WKY rats. The fluorescence of green fluorescent protein-labelled vectors appeared at 2 weeks after injection and persisted for at least 8 weeks. IL-1R1 protein expression in the PVN was reduced 4 weeks after Lv-shR-IL-1R1 injection in SHRs. IL-1R1 interference also reduced basal sympathetic activity, cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in SHRs. Depressor effects were observed from week 2 to 10 after Lv-shR-IL-1R1 treatment in SHRs, with the most prominent effects seen at the end of week 4. Furthermore, Lv-shR-IL-1R1 treatment decreased the ratio of left ventricular weight to body weight and cross-sectional areas of myocardial cells in SHRs. Additionally, Lv-shR-IL-1R1 treatment prevented an increase in superoxide anion and pro-inflammatory cytokines (PICs, TNF-α and IL-1β) in the PVN of SHR, and upregulated anti-inflammatory cytokine (AIC, IL-10) expression. These results indicate that shRNA interference targeting IL-1R1 in the PVN decreases arterial blood pressure, attenuates excessive sympathetic activity and cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex, and improves myocardial remodelling in SHRs by restoring the balance between PICs and AICs to attenuate oxidative stress.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal D, Haque M, Sriramula S, Mariappan N, Pariaut R, Francis J (2009) Role of proinflammatory cytokines and redox homeostasis in exercise-induced delayed progression of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 54:1393–1400. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.135459
Agarwal D, Welsch MA, Keller JN, Francis J (2011) Chronic exercise modulates RAS components and improves balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the brain of SHR. Basic Res Cardiol 106:1069–1085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-011-0231-7
Allen AM (2002) Inhibition of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in spontaneously hypertensive rats dramatically reduces sympathetic vasomotor tone. Hypertension 39:275–280
Badoer E (2010) Role of the hypothalamic PVN in the regulation of renal sympathetic nerve activity and blood flow during hyperthermia and in heart failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298:F839–F846. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00734.2009
Bagnost T, Ma L, da Silva RF, Rezakhaniha R, Houdayer C, Stergiopulos N, Andre C, Guillaume Y, Berthelot A, Demougeot C (2010) Cardiovascular effects of arginase inhibition in spontaneously hypertensive rats with fully developed hypertension. Cardiovasc Res 87:569–577. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvq081
Bhaskar V, Yin J, Mirza AM, Phan D, Vanegas S, Issafras H, Michelson K, Hunter JJ, Kantak SS (2011) Monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-1 beta reduce biomarkers of atherosclerosis in vitro and inhibit atherosclerotic plaque formation in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis 216:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.02.026
Burns J, Sivananthan MU, Ball SG, Mackintosh AF, Mary DA, Greenwood JP (2007) Relationship between central sympathetic drive and magnetic resonance imaging-determined left ventricular mass in essential hypertension. Circulation 115:1999–2005. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.668863
Cardinale JP, Sriramula S, Mariappan N, Agarwal D, Francis J (2012) Angiotensin II-induced hypertension is modulated by nuclear factor-kB in the paraventricular nucleus. Hypertension 59:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.182154
Chen AD, Zhang SJ, Yuan N, Xu Y, De W, Gao XY, Zhu GQ (2011) Angiotensin AT1 receptors in paraventricular nucleus contribute to sympathetic activation and enhanced cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in renovascular hypertensive rats. Exp Physiol 96:94–103. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2010.054353
Chi H, Messas E, Levine RA, Graves DT, Amar S (2004) Interleukin-1 receptor signaling mediates atherosclerosis associated with bacterial exposure and/or a high-fat diet in a murine apolipoprotein E heterozygote model: pharmacotherapeutic implications. Circulation 110:1678–1685. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000142085.39015.31
Coote JH (2005) A role for the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in the autonomic control of heart and kidney. Exp Physiol 90:169–173. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2004.029041
Duan YC, Xu B, Shi Z, Gao J, Zhang SJ, Wang W, Chen Q, Zhu GQ (2009) Nucleus of solitary tract mediates cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in rats. Pflugers Arch 459:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-009-0699-2
Fan ZD, Zhang L, Shi Z, Gan XB, Gao XY, Zhu GQ (2012) Artificial microRNA interference targeting AT(1a) receptors in paraventricular nucleus attenuates hypertension in rats. Gene Ther 19:810–817. https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.145
Fisher JP, Fadel PJ (2010) Therapeutic strategies for targeting excessive central sympathetic activation in human hypertension. Exp Physiol 95:572–580. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2009.047332
Fujita M, Ando K, Nagae A, Fujita T (2007) Sympathoexcitation by oxidative stress in the brain mediates arterial pressure elevation in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension 50:360–367. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.091009
Goldstein DS (1983) Plasma catecholamines and essential hypertension: an analytical review. Hypertension 5:86–99
Grassi G, Seravalle G, Quarti-Trevano F (2010) The ‘neuroadrenergic hypothesis’ in hypertension: current evidence. Exp Physiol 95:581–586. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2009.047381
Han Y, Shi Z, Zhang F, Yu Y, Zhong MK, Gao XY, Wang W, Zhu GQ (2007) Reactive oxygen species in the paraventricular nucleus mediate the cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in chronic heart failure rats. Eur J Heart Fail 9:967–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejheart.2007.07.004
Han Y, Yuan N, Zhang SJ, Gao J, Shi Z, Zhou YB, Gao XY, Zhu GQ (2011) C-Src in paraventricular nucleus modulates sympathetic activity and cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in renovascular hypertensive rats. Pflugers Arch 461:437–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-011-0932-7
Hu J, Lang Y, Zhang T, Ni S, Lu H (2016) Lentivirus-mediated PGC-1alpha overexpression protects against traumatic spinal cord injury in rats. Neuroscience 328:40–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.04.031
Kang YM, He RL, Yang LM, Qin DN, Guggilam A, Elks C, Yan N, Guo Z, Francis J (2009) Brain tumour necrosis factor-alpha modulates neurotransmitters in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in heart failure. Cardiovasc Res 83:737–746. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvp160
Kang YM, Zhang AQ, Zhao XF, Cardinale JP, Elks C, Cao XM, Zhang ZW, Francis J (2011) Paraventricular nucleus corticotrophin releasing hormone contributes to sympathoexcitation via interaction with neurotransmitters in heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol 106:473–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-011-0155-2
Li DP, Pan HL (2007) Glutamatergic inputs in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus maintain sympathetic vasomotor tone in hypertension. Hypertension 49:916–925. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000259666.99449.74
Li DP, Zhou JJ, Pan HL (2015) Endogenous casein kinase-1 modulates NMDA receptor activity of hypothalamic presympathetic neurons and sympathetic outflow in hypertension. J Physiol 593:4439–4452. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP270831
Li HB, Qin DN, Cheng K, Su Q, Miao YW, Guo J, Zhang M, Zhu GQ, Kang YM (2015) Central blockade of salusin beta attenuates hypertension and hypothalamic inflammation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci Rep 5:11162. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11162
Mancia G, Grassi G, Giannattasio C, Seravalle G (1999) Sympathetic activation in the pathogenesis of hypertension and progression of organ damage. Hypertension 34:724–728
Messerli FH, Williams B, Ritz E (2007) Essential hypertension. Lancet 370:591–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61299-9
Nagae A, Fujita M, Kawarazaki H, Matsui H, Ando K, Fujita T (2009) Sympathoexcitation by oxidative stress in the brain mediates arterial pressure elevation in obesity-induced hypertension. Circulation 119:978–986. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.824730
Nguyen KT, Deak T, Will MJ, Hansen MK, Hunsaker BN, Fleshner M, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2000) Timecourse and corticosterone sensitivity of the brain, pituitary, and serum interleukin-1beta protein response to acute stress. Brain Res 859:193–201
Oliveira-Sales EB, Colombari E, Abdala AP, Campos RR, Paton JF (2016) Sympathetic overactivity occurs before hypertension in the two-kidney, one-clip model. Exp Physiol 101:67–80. https://doi.org/10.1113/EP085390
Paxinos G aWC (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. In: Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, USA
Preuss HG, Echard B, Bagchi D, Perricone NV (2010) Maitake mushroom extracts ameliorate progressive hypertension and other chronic metabolic perturbations in aging female rats. Int J Med Sci 7:169–180
Qi J, Zhao XF, XJ Y, Yi QY, Shi XL, Tan H, Fan XY, Gao HL, Yue LY, Feng ZP, Kang YM (2016) Targeting interleukin-1 beta to suppress sympathoexcitation in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. Cardiovasc Toxicol 16:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-015-9338-7
Remuzzi G (1999) Sympathetic overactivity in hypertensive patients with chronic renal disease. N Engl J Med 340:1360–1361. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199904293401711
Shi P, Diez-Freire C, Jun JY, Qi Y, Katovich MJ, Li Q, Sriramula S, Francis J, Sumners C, Raizada MK (2010) Brain microglial cytokines in neurogenic hypertension. Hypertension 56:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.150409
Shi Z, Chen AD, Xu Y, Chen Q, Gao XY, Wang W, Zhu GQ (2009) Long-term administration of tempol attenuates postinfarct ventricular dysfunction and sympathetic activity in rats. Pflugers Arch 458:247–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0627-x
Shi Z, Gan XB, Fan ZD, Zhang F, Zhou YB, Gao XY, De W, Zhu GQ (2011) Inflammatory cytokines in paraventricular nucleus modulate sympathetic activity and cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in rats. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 203:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02313.x
Shi Z, Jiang SJ, Wang GH, AL X, Guo L (2014) Pro-inflammatory cytokines in paraventricular nucleus mediate the cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in hypertension. Auton Neurosci 186:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autneu.2014.10.001
Smith SH, Bishop SP (1986) Selection criteria for drug-treated animals in two-kidney, one clip renal hypertension. Hypertension 8:700–705
Song XA, Jia LL, Cui W, Zhang M, Chen W, Yuan ZY, Guo J, Li HH, Zhu GQ, Liu H, Kang YM (2014) Inhibition of TNF-alpha in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting neurohormonal excitation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 281:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2014.09.004
Toscano MG, Romero Z, Munoz P, Cobo M, Benabdellah K, Martin F (2011) Physiological and tissue-specific vectors for treatment of inherited diseases. Gene Ther 18:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2010.138
Wei SG, Yu Y, Zhang ZH, Felder RB (2015) Proinflammatory cytokines upregulate sympathoexcitatory mechanisms in the subfornical organ of the rat. Hypertension 65:1126–1133. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.05112
Yuan N, Zhang F, Zhang LL, Gao J, Zhou YB, Han Y, Zhu GQ (2013) SOD1 gene transfer into paraventricular nucleus attenuates hypertension and sympathetic activity in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Pflugers Arch 465:261–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1173-0
Zhou LM, Shi Z, Gao J, Han Y, Yuan N, Gao XY, Zhu GQ (2010) Angiotensin-(1-7) and angiotension II in the rostral ventrolateral medulla modulate the cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex and sympathetic activity in rats. Pflugers Arch 459:681–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-010-0793-5
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Professor Guo-qing Zhu, Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Disease and Molecular Intervention, Department of Physiology, Nanjing Medical University, for his technical assistance. They are also grateful to Zhi-dan Fan, Lei Zhang, and Peng Li for their help with experiments.
Funding
This project was supported by funding under the International Cooperation Program for Excellent Lectures of 2015 by Shandong Provincial Education Department, P.R. China, grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81200186), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (BS2015YY036), and Shandong Provincial Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Plan (2016WS0051). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal work in this study was approved and performed in accordance with the Home Office UK Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 under the regulations and policies laid out by the Medical Ethics Committee of Binzhou Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, P., Jiang, Sj., Pan, H. et al. Short hairpin RNA interference targeting interleukin 1 receptor type I in the paraventricular nucleus attenuates hypertension in rats. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 470, 439–448 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-2081-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-2081-0