Abstract
Purpose
The diagnosis of acute appendicitis remains a challenge in daily clinical practice. The aim of the present study was to determine clinical criteria for a careful and cost-effective integration of computed tomography (CT) scans in the clinical pathway for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis.
Methods
In this retrospective study, we analyzed all patients who were admitted to our hospital with suspected appendicitis (2008–2011). We included all patients who had an appendectomy with or without preoperative CT. Furthermore, we analyzed all patients who received a CT because of suspected appendicitis but did not have an appendectomy.
Results
A total of 367 patients were included in this study. A CT was performed in 35 % of the patients with suspected appendicitis. Women had a significantly higher rate of negative appendectomy (NA) (16.5 %) than men (5.3 %). The frequency of NA was 5.7 % in the group of patients who were imaged, whereas it was 11.8 % (p = 0.075) among those who were not imaged. Thereby, CT scans helped to reduce total hospital expenses (€1,317.44 (no CT scan) to €675.85 (CT scan and no operation). Furthermore, CT scans can be avoided in men with normal white blood cell counts who should be observed if not operated immediately.
Conclusion
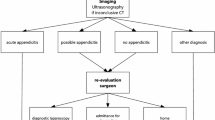
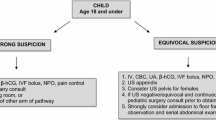
CT can be effectively applied for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. We propose a diagnostic algorithm which helps to simultaneously avoid unnecessary operations and radiation exposure.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bundesamt S (2010) Operationen und Prozeduren der vollstationären Patientinnen und Patienten in Krankenhäusern. http://www.gbe-bund.de. 2010
Addiss DG, Shaffer N, Fowler BS, Tauxe RV (1990) The epidemiology of appendicitis and appendectomy in the United States. Am J Epidemiol 132(5):910–925
Jess P, Bjerregaard B, Brynitz S, Holst-Christensen J, Kalaja E, Lund-Kristensen J (1981) Acute appendicitis. Prospective trial concerning diagnostic accuracy and complications. Am J Surg 141(2):232–234
Lewis FR, Holcroft JW, Boey J, Dunphy E (1975) Appendicitis. A critical review of diagnosis and treatment in 1,000 cases. Arch Surg 110(5):677–684, Chicago, Ill : 1960
Ma KW, Chia NH, Yeung HW, Cheung MT (2010) If not appendicitis, then what else can it be? A retrospective review of 1492 appendectomies. Hong Kong Med J=Xianggang yi xue za zhi / Hong Kong Acad Med 16(1):12–17
Pickhardt PJ, Lawrence EM, Pooler BD, Bruce RJ (2011) Diagnostic performance of multidetector computed tomography for suspected acute appendicitis. Ann Intern Med 154(12):789–796. doi:10.1059/0003-4819-154-12-201106210-00006
Bijnen CL, van den Broek WT, Bijnen AB, de Ruiter P, Gouma DJ (2003) Implications of removing a normal appendix. Dig Surg 20(3):215–219. doi:10.1159/000070388, discussion 220–211
Paulson EK, Kalady MF, Pappas TN (2003) Clinical practice. Suspected appendicitis. New Engl J Med 348(3):236–242. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp013351
Pooler BD, Lawrence EM, Pickhardt PJ (2012) MDCT for suspected appendicitis in the elderly: diagnostic performance and patient outcome. Emerg Radiol 19(1):27–33. doi:10.1007/s10140-011-1002-3
Paranjape C, Dalia S, Pan J, Horattas M (2007) Appendicitis in the elderly: a change in the laparoscopic era. Surg Endosc 21(5):777–781. doi:10.1007/s00464-006-9097-4
Storm-Dickerson TL, Horattas MC (2003) What have we learned over the past 20 years about appendicitis in the elderly? Am J Surg 185(3):198–201
Antevil J, Rivera L, Langenberg B, Brown CV (2004) The influence of age and gender on the utility of computed tomography to diagnose acute appendicitis. Am Surg 70(10):850–853
McGory ML, Zingmond DS, Nanayakkara D, Maggard MA, Ko CY (2005) Negative appendectomy rate: influence of CT scans. Am Surg 71(10):803–808
Naoum JJ, Mileski WJ, Daller JA, Gomez GA, Gore DC, Kimbrough TD, Ko TC, Sanford AP, Wolf SE (2002) The use of abdominal computed tomography scan decreases the frequency of misdiagnosis in cases of suspected appendicitis. Am J Surg 184(6):587–589, discussion 589–590
Wagner PL, Eachempati SR, Soe K, Pieracci FM, Shou J, Barie PS (2008) Defining the current negative appendectomy rate: for whom is preoperative computed tomography making an impact? Surgery 144(2):276–282. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2008.03.040
Morse BC, Roettger RH, Kalbaugh CA, Blackhurst DW, Hines WB (2007) Abdominal CT scanning in reproductive-age women with right lower quadrant abdominal pain: does its use reduce negative appendectomy rates and healthcare costs? Am Surg 73(6):580–584, discussion 584
Webb EM, Nguyen A, Wang ZJ, Stengel JW, Westphalen AC, Coakley FV (2011) The negative appendectomy rate: who benefits from preoperative CT? AJR Am J Roentgenol 197(4):861–866. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.5369
Kim K, Kim YH, Kim SY, Kim S, Lee YJ, Kim KP, Lee HS, Ahn S, Kim T, S-s H, Song KJ, Kang S-B, Kim D-W, Park SH, Lee KH (2012) Low-dose abdominal CT for evaluating suspected appendicitis. N Engl J Med 366(17):1596–1605. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1110734
Raja AS, Wright C, Sodickson AD, Zane RD, Schiff GD, Hanson R, Baeyens PF, Khorasani R (2010) Negative appendectomy rate in the era of CT: an 18-year perspective. Radiology 256(2):460–465. doi:10.1148/radiol.10091570
Drake FT, Florence MG, Johnson MG, Jurkovich GJ, Kwon S, Schmidt Z, Thirlby RC, Flum DR (2012) Progress in the diagnosis of appendicitis: a report from Washington State’s Surgical Care and Outcomes Assessment Program. Ann Surg 256(4):586–594. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e31826a9602
Abou-Nukta F, Bakhos C, Arroyo K, Koo Y, Martin J, Reinhold R, Ciardiello K (2006) Effects of delaying appendectomy for acute appendicitis for 12 to 24 hours. Arch Surg 141(5):504–506. doi:10.1001/archsurg.141.5.504, Chicago, Ill : 1960
Bickell NA, Aufses AH, Rojas M, Bodian C (2006) How time affects the risk of rupture in appendicitis. J Am Coll Surg 202(3):401–406. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.11.016
Stahlfeld K, Hower J, Homitsky S, Madden J (2007) Is acute appendicitis a surgical emergency? Am Surg 73(6):626–629, discussion 629–630
Andersson RE (2007) The natural history and traditional management of appendicitis revisited: spontaneous resolution and predominance of prehospital perforations imply that a correct diagnosis is more important than an early diagnosis. World J Surg 31(1):86–92. doi:10.1007/s00268-006-0056-y
Rao PM, Rhea JT, Novelline RA, Mostafavi AA, Lawrason JN, McCabe CJ (1997) Helical CT combined with contrast material administered only through the colon for imaging of suspected appendicitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 169(5):1275–1280
Rao PM, Rhea JT, Novelline RA, Mostafavi AA, McCabe CJ (1998) Effect of computed tomography of the appendix on treatment of patients and use of hospital resources. N Engl J Med 338(3):141–146. doi:10.1056/nejm199801153380301
Singh A, Danrad R, Hahn PF, Blake MA, Mueller PR, Novelline RA (2007) MR imaging of the acute abdomen and pelvis: acute appendicitis and beyond. Radiographics: a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc 27 (5):1419–1431. doi:10.1148/rg.275065021
Cobben L, Groot I, Kingma L, Coerkamp E, Puylaert J, Blickman J (2009) A simple MRI protocol in patients with clinically suspected appendicitis: results in 138 patients and effect on outcome of appendectomy. Eur Radiol 19(5):1175–1183. doi:10.1007/s00330-008-1270-9
Leeuwenburgh MMN, Wiarda BM, Jensch S, van Es HW, Stockmann HBAC, Gratama JWC, Cobben LPJ, Bossuyt PMM, Boermeester MA, Stoker J (2013) Accuracy and interobserver agreement between MR-non-expert radiologists and MR-experts in reading MRI for suspected appendicitis. Eur J Radiol. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.09.022
Chooi WK, Brown JA, Zetler P, Wiseman S, Cooperberg P (2007) Imaging of acute appendicitis and its impact on negative appendectomy and perforation rates: the St. Paul’s experience. Can Assoc Radiol J=Journal l'Association canadienne des radiologistes 58(4):220–224
Kim K, Lee CC, Song K-J, Kim W, Suh G, Singer AJ (2008) The impact of helical computed tomography on the negative appendectomy rate: a multi-center comparison. J Emerg Med 34(1):3–6. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2007.05.042
Piper HG, Rusnak C, Orrom W, Hayashi A, Cunningham J (2008) Current management of appendicitis at a community center—how can we improve? Am J Surg 195(5):585–588. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.12.033, discussion 588–589
Coursey CA, Nelson RC, Patel MB, Cochran C, Dodd LG, Delong DM, Beam CA, Vaslef S (2010) Making the diagnosis of acute appendicitis: do more preoperative CT scans mean fewer negative appendectomies? A 10-year study. Radiology 254(2):460–468. doi:10.1148/radiol.09082298
Eriksson S, Granström L (1995) Randomized controlled trial of appendicectomy versus antibiotic therapy for acute appendicitis. Br J Surg 82(2):166–169
Hansson J, Körner U, Khorram-Manesh A, Solberg A, Lundholm K (2009) Randomized clinical trial of antibiotic therapy versus appendicectomy as primary treatment of acute appendicitis in unselected patients. Br J Surg 96(5):473–481. doi:10.1002/bjs.6482
Vons C, Barry C, Maitre S, Pautrat K, Leconte M, Costaglioli B, Karoui M, Alves A, Dousset B, Valleur P, Falissard B, Franco D (2011) Amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid versus appendicectomy for treatment of acute uncomplicated appendicitis: an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 377(9777):1573–1579. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60410-8
Hansson J, Körner U, Ludwigs K, Johnsson E, Jönsson C, Lundholm K (2012) Antibiotics as first-line therapy for acute appendicitis: evidence for a change in clinical practice. World J Surg 36(9):2028–2036. doi:10.1007/s00268-012-1641-x
Paajanen H, Grönroos JM, Rautio T, Nordström P, Aarnio M, Rantanen T, Hurme S, Dean K, Jartti A, Mecklin J-P, Sand J, Salminen P (2013) A prospective randomized controlled multicenter trial comparing antibiotic therapy with appendectomy in the treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis (APPAC trial). BMC Surg 13:3. doi:10.1186/1471-2482-13-3
Antevil JL, Rivera L, Langenberg BJ, Hahm G, Favata MA, Brown CVR (2006) Computed tomography-based clinical diagnostic pathway for acute appendicitis: prospective validation. J Am Coll Surg 203(6):849–856. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2006.08.012
Toorenvliet BR, Wiersma F, Bakker RFR, Merkus JWS, Breslau PJ, Hamming JF (2010) Routine ultrasound and limited computed tomography for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. World J Surg 34(10):2278–2285. doi:10.1007/s00268-010-0694-y
John H, Neff U, Kelemen M (1993) Appendicitis diagnosis today: clinical and ultrasonic deductions. World J Surg 17(2):243–249
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Joy Velasco for her editorial help with the manuscript.
Conflicts of interests
There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liese, J., Halbinger, T.M., Ulrich, F. et al. Appendicitis—the balance between cost effectiveness and safety remains challenging. Langenbecks Arch Surg 399, 493–501 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-014-1179-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-014-1179-5