Abstract
Background
Arterial baroreflex (BR) and cerebral autoregulation (CA) are two major regulatory mechanisms that maintain constant cerebral perfusion. Little is known about the interplay between these mechanisms, particularly when considering the effects of ageing or sex.
Purpose
We studied the relationship between dynamic CA and BR sensitivity (BRS) in healthy subjects by sex and in different age strata.
Methods
95 healthy adults (52% female), 20–80 years-old, were recruited. Arterial blood pressure (Finometer), 3-lead electrocardiogram and cerebral blood flow velocity in middle cerebral arteries (transcranial Doppler) were monitored. We assessed CA by transfer function analysis and BRS in frequency and time domain.
Results
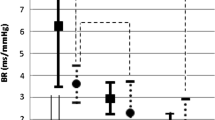
With increasing age, BRS diminished (ANCOVA R2 = 0.281, p < 0.001) but CA parameters did not change significantly (p > 0.05). Overall, there was an inverse relationship between the efficacy of BRS and CA low-frequency gain [multivariate linear regression β = 0.41 (0.31; 0.61), p < 0.001]. However, this association suffers changes with ageing: in older subjects BRS and CA were not correlated [β = 0.10 (− 0.41; 0.62), p = 0.369]. Instead, decreasing systolic blood pressure correlated with less efficient CA [lower CA low-frequency gain β = − 0.02 (− 0.03; − 0.02), p = 0.003]. Sex did not affect BRS and CA relationship.
Conclusions
Cerebral blood supply is governed by a tuned balance between BR and CA which is lost with age as BRS decreases dramatically. Low systolic blood pressure values might be harmful to older subjects as they might reduce the ability to keep cerebral blood flow tightly controlled.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABP:
-
Arterial blood pressure
- BR:
-
Baroreflex
- BRS:
-
Baroreflex sensitivity
- CA:
-
Cerebral autoregulation
- CBFV:
-
Cerebral blood flow velocity
- CrCP:
-
Critical closing pressure
- CVRi:
-
Cerebrovascular resistance index
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- HF:
-
High-frequency spectral band
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- HRV:
-
Heart rate variability
- LF:
-
Low-frequency spectral band
- MBP:
-
Mean ABP
- MCA:
-
Middle cerebral artery
- PP:
-
Pulse pressure
- RAP:
-
Ratio-area-product
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- SDNN:
-
Standard deviation of normal RR intervals
- TCD:
-
Transcranial Doppler
- TFA:
-
Transfer function analysis
- VLF:
-
Very-low frequency spectral band
- xBRS:
-
Time domain cross-correlation BRS
- α-index:
-
Frequency domain BRS gain
References
Azevedo E, Castro P (2016) Cerebral autoregulation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Baker SE, Limberg JK, Ranadive SM, Joyner MJ (2016) ‘Neurovascular control of blood pressure is influenced by aging, sex, and sex hormones’. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 311:R1271–R1275
Bakker SL, de Leeuw FE, de Groot JC, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, Breteler MM (1999) Cerebral vasomotor reactivity and cerebral white matter lesions in the elderly. Neurology 52:578–583
Bakker SL, de Leeuw FE, den Heijer T, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Breteler MM (2004) Cerebral haemodynamics in the elderly: the rotterdam study. Neuroepidemiology 23:178–184
Brown WR, Thore CR (2011) Review: cerebral microvascular pathology in aging and neurodegeneration. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37:56–74
Carey BJ, Eames PJ, Blake MJ, Panerai RB, Potter JF (2000) Dynamic cerebral autoregulation is unaffected by aging. Stroke 31:2895–2900
Carlstrom M, Wilcox CS, Arendshorst WJ (2015) Renal autoregulation in health and disease. Physiol Rev 95:405–511
Castro PM, Santos R, Freitas J, Panerai RB, Azevedo E (2014) Autonomic dysfunction affects dynamic cerebral autoregulation during Valsalva maneuver: comparison between healthy and autonomic dysfunction subjects. J Appl Physiol (1985) 117:205–213
Castro P, Azevedo E, Serrador J, Rocha I, Sorond F (2017a) Hemorrhagic transformation and cerebral edema in acute ischemic stroke: link to cerebral autoregulation. J Neurol Sci 372:256–261
Castro P, Freitas J, Santos R, Panerai R, Azevedo E (2017b) Indexes of cerebral autoregulation do not reflect impairment in syncope: insights from head-up tilt test of vasovagal and autonomic failure subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 117(9):1817–1831
Castro P, Serrador J, Rocha I, Sorond F, Elsa, Azevedo (2017c) Efficacy of cerebral autoregulation in early ischemic stroke predicts smaller infarcts and better outcomes. Front Neurol 8:113
Claassen JA, Meel-van den Abeelen AS, Simpson DM, Panerai RB, Network international Cerebral Autoregulation Research (2016) Transfer function analysis of dynamic cerebral autoregulation: a white paper from the international cerebral autoregulation research network. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36:665–680
Deegan BM, Serrador JM, Nakagawa K, Jones E, Sorond FA, Olaighin G (2011) ‘The effect of blood pressure calibrations and transcranial Doppler signal loss on transfer function estimates of cerebral autoregulation’. Med Eng Phys 33:553–562
Faraci FM, Brian JE Jr (1994) Nitric oxide and the cerebral circulation. Stroke 25:692–703
Freitas J, Santos R, Azevedo E, Carvalho M, Boomsma F, Meiracker A, Falcao A, de Freitas, Abreu-Lima C (2007) Hemodynamic, autonomic and neurohormonal behaviour of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy and neurally mediated syncope patients during supine and orthostatic stress. Int J Cardiol 116:242–248
Gribbin B, Pickering TG, Sleight P, Peto R (1971) Effect of age and high blood pressure on baroreflex sensitivity in man. Circ Res 29:424–431
Groschel K, Terborg C, Schnaudigel S, Ringer T, Riecker A, Witte OW, Kastrup A (2007) Effects of physiological aging and cerebrovascular risk factors on the hemodynamic response to brain activation: a functional transcranial Doppler study. Eur J Neurol 14:125–131
Hart EC, Charkoudian N, Wallin BG, Curry TB, Eisenach JH, Joyner MJ (2009) Sex differences in sympathetic neural-hemodynamic balance: implications for human blood pressure regulation. Hypertension 53:571–576
Iadecola C (2004) Neurovascular regulation in the normal brain and in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:347–360
Kastrup A, Thomas C, Hartmann C, Schabet M (1997) Sex dependency of cerebrovascular CO2 reactivity in normal subjects. Stroke 28:2353–2356
Krejza J, Mariak Z, Walecki J, Szydlik P, Lewko J, Ustymowicz A (1999) Transcranial color Doppler sonography of basal cerebral arteries in 182 healthy subjects: age and sex variability and normal reference values for blood flow parameters. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172:213–218
La Rovere MT, Pinna GD, Raczak G (2008) Baroreflex sensitivity: measurement and clinical implications. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 13:191–207
Lantelme P, Khettab F, Custaud MA, Rial MO, Joanny C, Gharib C, Milon H (2002) Spontaneous baroreflex sensitivity: toward an ideal index of cardiovascular risk in hypertension?. J Hypertens 20:935–944
Loutzenhiser R, Griffin K, Williamson G, Bidani A (2006) Renal autoregulation: new perspectives regarding the protective and regulatory roles of the underlying mechanisms. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290:R1153–R1167
Lucini D, Pagani M, Mela GS, Malliani A (1994) Sympathetic restraint of baroreflex control of heart period in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Clin Sci (Lond) 86:547–556
Ma H, Guo ZN, Liu J, Xing Y, Zhao R, Yang Y (2016) Temporal course of dynamic cerebral autoregulation in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 47:674–681
Madureira J, Castro P, Azevedo E (2017) Demographic and systemic hemodynamic influences in mechanisms of cerebrovascular regulation in healthy adults. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 26:500–508
Mancia G, Laurent S, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Burnier M, Caulfield MJ, Cifkova R, Clement D, Coca A, Dominiczak A, Erdine S, Fagard R, Farsang C, Grassi G, Haller H, Heagerty A, Kjeldsen SE, Kiowski W, Mallion JM, Manolis A, Narkiewicz K, Nilsson P, Olsen MH, Rahn KH, Redon J, Rodicio J, Ruilope L, Schmieder RE, Struijker-Boudier HA, Van Zwieten PA, Viigimaa M, Zanchetti A (2009) Reappraisal of European guidelines on hypertension management: a European Society of Hypertension Task Force document. Blood Press 18:308–347
Meel-van den Abeelen AS, van Beek AH, Slump CH, Panerai RB, Claassen JA (2014) Transfer function analysis for the assessment of cerebral autoregulation using spontaneous oscillations in blood pressure and cerebral blood flow. Med Eng Phys 36:563–575
Nasr N, Czosnyka M, Pavy-Le Traon A, Custaud MA, Liu X, Varsos GV, Larrue V (2014) Baroreflex and cerebral autoregulation are inversely correlated. Circ J 78:2460–2467
Nation DA, Edmonds EC, Bangen KJ, Delano-Wood L, Scanlon BK, Han SD, Edland SD, Salmon DP, Galasko DR, Bondi MW, Investigators Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2015) Pulse pressure in relation to tau-mediated neurodegeneration, cerebral amyloidosis, and progression to dementia in very old adults. JAMA Neurol 72:546–553
Ogoh S, Brothers RM, Eubank WL, Raven PB (2008) Autonomic neural control of the cerebral vasculature: acute hypotension. Stroke 39:1979–1987
Otite F, Mink S, Tan CO, Puri A, Zamani AA, Mehregan A, Chou S, Orzell S, Purkayastha S, Du R, Sorond FA (2014) Impaired cerebral autoregulation is associated with vasospasm and delayed cerebral ischemia in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 45:677–682
Panerai RB (2003) The critical closing pressure of the cerebral circulation. Med Eng Phys 25:621–632
Panerai RB, Deverson ST, Mahony P, Hayes P, Evans DH (1999) Effects of CO2 on dynamic cerebral autoregulation measurement. Physiol Meas 20:265–275
Panerai RB, Moody M, Eames PJ, Potter JF (2005) Cerebral blood flow velocity during mental activation: interpretation with different models of the passive pressure-velocity relationship. J Appl Physiol 99:2352–2362
Pierce GL, Harris SA, Seals DR, Casey DP, Barlow PB, Stauss HM (2016) Estimated aortic stiffness is independently associated with cardiac baroreflex sensitivity in humans: role of ageing and habitual endurance exercise. J Hum Hypertens 30:513–520
Purkayastha S, Fadar O, Mehregan A, Salat DH, Moscufo N, Meier DS, Guttmann CR, Fisher ND, Lipsitz LA, Sorond FA (2014) Impaired cerebrovascular hemodynamics are associated with cerebral white matter damage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34:228–234
Salinet AS, Robinson TG, Panerai RB (2013) Active, passive, and motor imagery paradigms: component analysis to assess neurovascular coupling. J Appl Physiol (1985) 114:1406–1412
Sykora M, Diedler J, Turcani P, Hacke W, Steiner T (2009) Baroreflex: a new therapeutic target in human stroke?. Stroke 40:e678–e682
Tzeng YC, Lucas SJ, Atkinson G, Willie CK, Ainslie PN (2010) Fundamental relationships between arterial baroreflex sensitivity and dynamic cerebral autoregulation in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 108:1162–1168
Tzeng YC, Ainslie PN, Cooke WH, Peebles KC, Willie CK, MacRae BA, Smirl JD, Horsman HM, Rickards CA (2012) ‘Assessment of cerebral autoregulation: the quandary of quantification’. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 303:H658–H671
Westerhof BE, Gisolf J, Stok WJ, Wesseling KH, Karemaker JM (2004) Time-domain cross-correlation baroreflex sensitivity: performance on the EUROBAVAR data set. J Hypertens 22:1371–1380
Willie CK, Tzeng YC, Fisher JA, Ainslie PN (2014) Integrative regulation of human brain blood flow. J Physiol 592:841–859
Xing CY, Tarumi T, Meijers RL, Turner M, Repshas J, Xiong L, Ding K, Vongpatanasin W, Yuan LJ, Zhang R (2017) Arterial pressure, heart rate, and cerebral hemodynamics across the adult life span. Hypertension 69:712–720
Yam AT, Lang EW, Lagopoulos J, Yip K, Griffith J, Mudaliar Y, Dorsch NW (2005) Cerebral autoregulation and ageing. J Clin Neurosci 12:643–646
Zanchetti A, Grassi G, Mancia G (2009) When should antihypertensive drug treatment be initiated and to what levels should systolic blood pressure be lowered? A critical reappraisal. J Hypertens 27:923–934
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ST, JM, EA and PC conceived and designed research. JM and PC conducted experiments. ST and PC analysed data. ST and PC wrote the manuscript, EA conveyed critical analysis of the results All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by Massimo Pagani.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teixeira, S.C., Madureira, J.B., Azevedo, E.I. et al. Ageing affects the balance between central and peripheral mechanisms of cerebrovascular regulation with increasing influence of systolic blood pressure levels. Eur J Appl Physiol 119, 519–529 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-4036-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-4036-3