Abstract
Purpose
To observe the characteristics of highly myopic macular holes (HMMHs) with macular retinoschisis (MRS) by optical coherence tomography (OCT) and explore the possible relationship between HMMHs and different types of MRS.
Methods
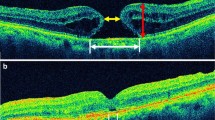
We consecutively reviewed the clinical data and OCT images of the patients with HMMHs from June 2015 to February 2021. Then we picked eyes with MRS from these HMMHs for analysis. The minimum linear diameter (MLD), basal diameter (BD), and height (H) of HMMHs were measured. HMMHs were grouped according to the extent or layer involvement of the concomitant MRS and the characteristics were compared among groups. The impact of MRS on the MLD of macular hole was analyzed with multivariable linear regression.
Results
We included 127 patients with MRS from 168 HMMHs (75.5%) for analysis.
According to the different classification systems, the most frequent type of MRS in HMMHs was S3 (foveal but not entire macular area MRS) (62.2%) and both inner- and outer- (I/O-MRS) involved types. In our study, HMMHs with more extensive MRS had larger MLD, larger BD, larger H, and poorer best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA). Meanwhile, HMMHs with outer layer-involved MRS (outer MRS and I/O-MRS) had larger BD than HMMH with only inner layer-involved MRS. (All P < 0.05) Multivariable linear regression further illustrated only the extent of MRS was significantly associated with the MLD of HMMH, while there was no significant correlation between the involved retinal layers and the MLD of HMMH.
Conclusion
HMMH with MRS presented as a predominant type in HMMHs. The MRS was always with a relatively large extent and involved both inner and outer layers. MLD of HMMH was mainly affected by the extent of MRS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong YL, Saw SM (2016) Epidemiology of pathologic myopia in Asia and worldwide. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila) 5:394–402. https://doi.org/10.1097/APO.0000000000000234
Ohno-Matsui K, Lai TY, Lai CC, Cheung CM (2016) Updates of pathologic myopia. Prog Retin Eye Res 52:156–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.12.001
Ruiz-Medrano J, Montero JA, Flores-Moreno I, Arias L, Garcia-Layana A, Ruiz-Moreno JM (2019) Myopic maculopathy: current status and proposal for a new classification and grading system (ATN). Prog Retin Eye Res 69:80–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2018.10.005
Cheng C, Teo K, Tan CS, Lee SY, Loh BK, Wong E, Wong D, Wong TY, Cheung CM (2016) Myopic retinoschisis in Asians: structural features and determinants of visual acuity and prognostic factors for progression. Retina 36:717–726. https://doi.org/10.1097/iae.0000000000000757
Lin CW, Ho TC, Yang CM (2015) The development and evolution of full thickness macular hole in highly myopic eyes. Eye (Lond) 29:388–396. https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2014.312
Shimada N, Tanaka Y, Tokoro T, Ohno-Matsui K (2013) Natural course of myopic traction maculopathy and factors associated with progression or resolution. Am J Ophthalmol 156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2013.06.031
Jo Y, Ikuno Y, Nishida K (2012) Retinoschisis: a predictive factor in vitrectomy for macular holes without retinal detachment in highly myopic eyes. Br J Ophthalmol 96:197–200. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2011.203232
Alkabes M, Pichi F, Nucci P, Massaro D, Dutra Medeiros M, Corcostegui B, Mateo C (2014) Anatomical and visual outcomes in high myopic macular hole (HM-MH) without retinal detachment: a review. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 252:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-013-2555-5
Panozzo GMA (2004) Optical coherence tomography findings in myopic traction maculopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 122:1455–1460. https://doi.org/10.1001/archopht.122.10.1455
Sun CB, Liu Z, Xue AQ, Yao K (2010) Natural evolution from macular retinoschisis to full-thickness macular hole in highly myopic eyes. Eye (Lond) 24:1787–1791. https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2010.123
Shimada N, Ohno-Matsui K, Yoshida T, Sugamoto Y, Tokoro T, Mochizuki M (2008) Progression from macular retinoschisis to retinal detachment in highly myopic eyes is associated with outer lamellar hole formation. Br J Ophthalmol 92:762–764. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2007.131359
Gaucher D, Haouchine B, Tadayoni R, Massin P, Erginay A, Benhamou N, Gaudric A (2007) Long-term follow-up of high myopic foveoschisis: natural course and surgical outcome. Am J Ophthalmol 143:455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2006.10.053
Ceklic L, Munk MR, Wolf-Schnurrbusch U, Gekkieva M, Wolf S (2017) Visual acuity outcomes of ranibizumab treatment in pathologic myopic eyes with macular retinoschisis and choroidal neovascularization. Retina 37:687–693. https://doi.org/10.1097/iae.0000000000001236
Li J, Liu B, Li Y, Zhao X, Chen S, Huang X, Lian P, Li T, Jin C, Liang X, Lu L (2021) Clinical characteristics of eyes with different grades of myopic traction maculopathy: based on the new classification system. Retina 41:1496–1501. https://doi.org/10.1097/IAE.0000000000003043
Yu Y, Liang X, Wang Z, Wang J, Liu W (2018) Clinical and morphological comparisons of idiopathic macular holes between stage 3 and stage 4. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 256:2327–2333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-018-4158-7
Hogan MJ, Alvarado JA, Weddell JE (1971) Histology of the Human Eye. In: The macular region. W.B.Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 491–497
Wu PC, Chen YJ, Chen YH, Chen CH, Shin SJ, Tsai CL, Kuo HK (2009) Factors associated with foveoschisis and foveal detachment without macular hole in high myopia. Eye (Lond) 23:356–361. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6703038
Baumann C, Almarzooqi A, Blobner K, Zapp D, Kirchmair K, Schwer LS, Lohmann CP, Kaye SB (2021) Repeatability and reproducibility of macular hole size measurements using optical coherence tomography. J Clin Med 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10132899
Takahashi H, Tanaka N, Shinohara K, Uramoto K, Yokoi T, Yoshida T, Ohno-Matsui K (2021) Importance of paravascular vitreal adhesions for development of myopic macular retinoschisis detected by ultra-widefield OCT. Ophthalmology 128:256–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2020.06.063
Takahashi H, Tanaka N, Shinohara K, Yokoi T, Yoshida T, Uramoto K, Ohno-Matsui K (2019) Ultra-widefield optical coherence tomographic imaging of posterior vitreous in eyes with high myopia. Am J Ophthalmol 206:102–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2019.03.011
Hsieh YT, Yang CM (2019) Retinal detachment due to paravascular abnormalities-associated breaks in highly myopic eyes. Eye (Lond) 33:572–579. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-018-0255-4
Schneider EW, Jaffe GJ (2020) Baseline characteristics of vitreomacular traction progressing to full-thickness macular or lamellar holes in the phase III trials of enzymatic vitreolysis. Retina 40:1579–1584. https://doi.org/10.1097/IAE.0000000000002634
Ohno-Matsui K, Jonas JB (2018) Posterior staphyloma in pathologic myopia. Prog Retin Eye Res 70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2018.12.001
Zheng F, Wong C-W, Sabanayagam C, Cheung Y-B, Matsumura S, Chua J, Man REK, Ohno-Matsui K, Wong T-Y, Cheng C-Y, Tai ES, Lamoureux ELED, Schmetterer L, Kuo A, Hoang QV, Saw S-M (2020) Prevalence, risk factors and impact of posterior staphyloma diagnosed from wide-field optical coherence tomography in Singapore adults with high myopia. Acta Ophthalmol 99:e144–e153. https://doi.org/10.1111/aos.14527
VanderBeek BL, Johnson MW (2012) The diversity of traction mechanisms in myopic traction maculopathy. Am J Ophthalmol 153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2011.06.016
Fujimoto M, Hangai M, Suda K, Yoshimura N (2010) Features associated with foveal retinal detachment in myopic macular retinoschisis. Am J Ophthalmol 150:863–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2010.06.023
Shih YF, Fitzgerald ME, Norton TT, Gamlin PD, Hodos W, Reiner A (1993) Reduction in choroidal blood flow occurs in chicks wearing goggles that induce eye growth toward myopia. Curr Eye Res 12:219–227. https://doi.org/10.3109/02713689308999467
Akyol N, Kükner AS, Ozdemir T, Esmerligil S (1996) Choroidal and retinal blood flow changes in degenerative myopia. Can J Ophthalmol 31:113–119
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were adhered to the Helsinki Declaration and its lateral amendments. Approval was granted by the ethical review committee of Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Consent for publication
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and photographs.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Yang, X., Wang, Z. et al. Observation of macular hole associated with retinoschisis in patients with high myopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 261, 57–65 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-022-05766-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-022-05766-8