Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate ophthalmological and molecular findings in eight patients with a clinical diagnosis of neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). New pathological mutations are described and variability in the ophthalmic phenotype and NF2 allelic heterogeneity are discussed.
Methods
Eye examination was performed in eight NF2 patients, and it included the measurement of the visual acuity, biomicroscopy, dilated fundus examination, color fundus photography, infrared photography, and spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT). Molecular analysis was performed with whole-exome sequencing using DNA derived from peripheral blood mononuclear cells from each individual.
Results
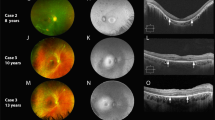
Ophthalmological features were present in all patients, ranging from subtle retinal alterations identified only using SD-OCT to severe ocular damage present at birth. Six mutations were observed: two patients with stop codon mutation as shown on table 1 and result section, three patients with frameshift mutation as shown on table 1 and result section. Three novel mutations were found among them.
Conclusions
It is a descriptive study of a rare disease, with poor previous literature. Clinical and genetic data are shown, reviving the need to further studies to clarify the genotype-phenotype correlations in NF2.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
NIH conference statement (1990) Neurofibromatosis 1 (von Recklinghausen disease) and neurofibromatosis 2 (bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis). Ann Intern Med 113:39–52
Seizinger BR, Rouleau GA, Ozelius LJ et al (1987) Genetic linkage of von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis to the nerve growth factor receptor gene. Cell 49:589–594
Roleau G, Seizinger BR, Ozelius LG et al (1987) Genetic linkage analysis of bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis to a DNA marker on chromosome 22. Nature 329:246–248
Cooper J, Giancotti FG (2014) Molecular insights into NF2/Merlin tumor suppressor function. FEBS Lett 16:2743–2752
Rodrigues LO, Batista PB, Goloni-Bertollo EM et al (2014) Neurofibromatosis part 1 – diagnosis and differential diagnosis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 72:241–250
Basser ME, Kuramoto L, Woods R et al (2005) The location of constitutional neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) splice site mutations is associated with the severity of NF2. J Med Genet 42:540–546
Evans DG, Howard E, Giblin C et al (2010) Birth incidence and prevalence of tumor-prone syndromes: estimates from a UK family genetic register service. Am J Med Genet 152A:327–332
Antinheimo J, Sankila R, Carpén O, Pukkala E, Sainio M, Jääskeläinen J (2000) Population-based analysis of sporadic and type 2 neurofibromatosis-associated meningiomas and schwannomas. Neurology 54:71–76
Evans DGR (2009) Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2): a clinical and molecular review. Orphanet J Rare Dis 4:16
Feucht M, Kluwe L, Mautner VF, Richard G (2008) Correlation of nonsense and frameshift mutations with severity of retinal abnormalities in neurofibromatosis 2. Arch Ophthalmol 126:1376–1380
Parry DM, MacCollin MM, Kaiser-Kupfer MI et al (1996) Germ-line mutations in the neurofibromatosis 2 gene: correlations with disease severity and retinal abnormalities. Am J Hum Genet 59:529–539
Moon KH, Kim HT, Lee D, Rao MB, Levine EM, Lim DS, Kim JW (2018) Differential expression of NF2 in neuroepithelial compartments is necessary for mammalian eye development. Dev Cell 44:13–28
Kaye LD, Rothner AD, Beauchamp GR, Meyers SM, Estes ML (1992) Ocular findings associated with neurofibromatosis type II. Ophthalmology 99:1424–1429
Bosch MM, Boltshauser E, Harpes P, Landau K (2006) Ophthalmologic findings and a long-term course in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2. Am J Ophthalmol 141:1068–1077
Feucht M, Griffiths B, Niemüller I, Haase W, Richard G, Mautner VF (2008) Neurofibromatosis 2 leads to higher incidence of strabismological and neuro-ophthalmological disorders. Acta Ophthalmol 86:882–886
Waisberg V, Rodrigues LO, Nehemy MB, Frassom M, De Miranda DM (2016) Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography findings in neurofibromatosis type 2. Inves Ophthalmol Vis Sci 57:OCT262–OCT267
Schwede T (2003) SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3381–3385
Ahronowitz I, Xin W, Kiely R, Sims K, Maccollin M, Nunes FP (2007) Mutational spectrum of the NF2 gene: a meta-analysis of 12 years of research and diagnostic laboratory findings. Hum Mutat 28:1–12
Kluwe L, Mautner V, Heinrich B et al (2003) Molecular study of frequency of mosaicism in neurofibromatosis 2 patients with bilateral vestibular schwannomas. J Med Genet 40:109–114
Kluwe L, Mautner VF (1998) Mosaicism in sporadic neurofibromatosis 2 patients. Hum Mol Genet 7:2051–2055
Chan C, Koch CA, Kaiser-Kupfer MI et al (2002) Loss of heterozygosity for the NF gene in retinal and optic nerve lesions of patients with neurofibromatosis 2. J Pathol 198:14–20
Viola F, Villani E, Natacci F et al (2012) Choroidal abnormalities detected by near-infrared reflectance imaging as a new diagnostic criterion for neurofibromatosis 1. Ophthalmology 119:369–375
Moramarco A, Giustini S, Nofroni I, Mallone F, Miraglia E, Lacovino C, Calvieri S, Lambiase A (2018) Near-infrared imaging: an in vivo, non-invasive diagnostic tool in neurofibromatosis type 1. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 256:307–311
Landau K, Yasargil GM (1993) Ocular fundus in neurofibromatosis type 2. Br J Ophthalmol 77:646–649
Meyers SM, Gutman FA, Kaye LD, Rothner AD (1995) Retinal changes associated with neurofibromatosis 2. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 93:245–257
Sisk RA, Berrocal AM, Schefler AC, Dubovy SR, Bauer MS (2010) Epirretinal membranes indicate a severe phenotype of neurofibromatosis type 2. Retina 30:51–58
McLaughlin ME, Pepin SM, MacCollin MM, Choopong P, Lessell S (2007) Ocular pathologic findings of neurofibromatosis type 2. Arch Ophthalmol 125:389–394
Acknowledgments
This research was partially supported by Federal University of Minas Gerais, Brazil.
Funding
This study was partially funded by FAPEMIG (Grupos Emergentes).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
All procedures performed in the study involving human participants were in accordance with ethical standards of the institutional committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waisberg, V., Rodrigues, L.O.C., Nehemy, M.B. et al. Ocular alterations, molecular findings, and three novel pathological mutations in a series of NF2 patients. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 257, 1453–1458 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-019-04348-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-019-04348-5