Abstract
Purpose
To document the findings of corneal biopsies for progressive microbial keratitis in a large tertiary referral institution.
Methods
A retrospective medical records review of all patients who underwent at least one corneal biopsy for the diagnosis of microbial keratitis at Sydney Eye Hospital, Australia between January 1, 2010 and December 31, 2016 was performed.
Results
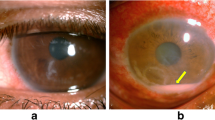
Thirty-eight patients (18 men and 20 women) underwent a corneal biopsy for progressive microbial keratitis unresponsive to broad-spectrum topical antimicrobials. Risk factors for microbial keratitis included contact lens wear in 8 (21%), recent intraocular surgery in 5 cases (13%), recent agricultural trauma in 3 cases (8%), exposure keratopathy due to Graves’ orbitopathy in 1 case (3%), and profound systemic immunosuppression due to chemotherapy for leukaemia in 1 case (3%). The remaining 20 patients had no identifiable risk factors. Fifteen patients (39%) had a positive biopsy result, which identified bacteria in 6 cases and Mycobacteria in 1 case, both by culture of the biopsy specimen. Three cases of fungus were identified on culture of biopsy specimen, two of which were also confirmed on histopathology and an additional case was identified from histopathology alone. A single case of Acanthamoeba was diagnosed by culture and histopathology, and an additional 3 cases were diagnosed on histopathology alone. A corneal biopsy yielded new organisms in 73% (11/15) cases where the culture results of biopsy specimens were positive.
Conclusion
Corneal biopsy is an important tool in the diagnosis of progressive keratitis, often identifying causal organisms not found on corneal scraping alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan BD, Dart JK (1995) Strategies for the management of microbial keratitis. Br J Ophthalmol 79(8):777–786
Asbell P, Stenson S (1982) Ulcerative keratitis. Survey of 30 years’ laboratory experience. Arch Ophthalmol 100(1):77–80
Jones DB (1979) Initial therapy of suspected microbial corneal ulcers. II. Specific antibiotic therapy based on corneal smears. Surv Ophthalmol 24(2):97, 105–97, 116
Jones DB (1981) Polymicrobial keratitis. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 79:153–617
Pachigolla G, Blomquist P, Cavanagh HD (2007) Microbial keratitis pathogens and antibiotic susceptibilities: a 5-year review of cases at an urban county hospital in North Texas. Eye Contact lens 33(1):45–49
Lichtinger A, Yeung SN, Kim P et al (2012) Shifting trends in bacterial keratitis in Toronto: an 11-year review. Ophthalmology 119(9):1785–1790
Gupta N, Tandon R (2008) Investigative modalities in infectious keratitis. Indian J Ophthalmol 56(3):209–213
Younger JR, Johnson RD, Holland GN et al (2012) Microbiologic and histopathologic assessment of corneal biopsies in the evaluation of microbial keratitis. Am J Ophthalmol 154(3):512–519 e512
Lee P, Green WR (1990) Corneal biopsy. Indications, techniques, and a report of a series of 87 cases. Ophthalmology 97(6):718–721
Alexandrakis G, Haimovici R, Miller D et al (2000) Corneal biopsy in the management of progressive microbial keratitis. Am J Ophthalmol 129(5):571–576
Kompa S, Langefeld S, Kirchhof B et al (1999) Corneal biopsy in keratitis performed with the microtrephine. Graefe’s Arch Cin Exp Ophthalmol 237(11):915–919
Hwang DG (1993) Lamellar flap corneal biopsy. Ophthalmic Surg 24(8):512–515
Kim JH, Yum JH, Lee D et al (2008) Novel technique of corneal biopsy by using a femtosecond laser in infectious ulcers. Cornea 27(3):363–365
Mikulska M, Furfaro E, Viscoli C (2015) Non-cultural methods for the diagnosis of invasive fungal disease. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 13(1):103–117
Acknowledgements
Dr. Nicole Carnt and Richard Rawson provided assistance to this project.
Funding
Dr. Robaei was supported by an NHMRC Early Careers fellowship (APP1073846). Professor Stephanie Watson was supported by an NHMRC Career Development Fellowship (APP1050524). The sponsor had no role in the design or conduct of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (place name of institute/committee) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robaei, D., Chan, UT., Khoo, P. et al. Corneal biopsy for diagnosis of recalcitrant microbial keratitis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 256, 1527–1533 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-018-3981-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-018-3981-1