Abstract
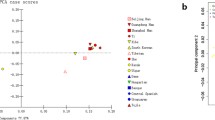
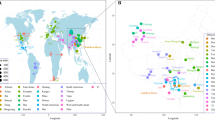
The Qiagen Investigator® DIPplex Kit multiplexes 30 autosomal INDELs plus amelogenin for forensic use. The aim of this study was to estimate the diversity of 30 INDEL loci in a sample of 530 Tibetan individuals from Qinghai Province, China, and to evaluate the usefulness of these loci for forensic genetics. The observed heterozygosity ranged from 14.3 to 53.4%, and combined power of discrimination, matching probability, and cumulative probability of exclusion were 0.99999999999172, 8.27999 × 10−12, and 0.9897, respectively, in the Qinghai Tibetan group. The results of pairwise genetic distance, principal component analysis, a multi-dimensional scaling plot, and a neighbour-joining tree between the Qinghai Tibetan and 49 reference populations revealed significant genetic differences between continental populations and a close genetic relationship between the Qinghai Tibetan and East Asian populations. This study indicates that the Investigator® DIPplex Kit can serve as an effective supplementary tool for forensic genetic tasks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
26 February 2020
Concerns have been raised about the ethics approval and informed consent procedures related to the research reported in this paper. The paper includes the following author declarations: “Written informed consent was obtained from all the participants”. Editorial action will be taken as appropriate once an investigation of the concerns is complete and all parties have been given an opportunity to respond in full.
References
Pereira R, Phillips C, Alves C, Amorim A, Carracedo A, Gusmão L (2009) A new multiplex for human identification using insertion/deletion polymorphisms. Electrophoresis 30(21):3682–3690
Bashir M, Hassan NHB (2016) Analysis of 30 Biallelic INDEL markers using the Investigator DIPplex® Kit. In: Goodwin W (ed) Forensic DNA typing protocols. Springer New York, New York, NY, pp 135–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3597-0_11
Lu D, Lou H, Yuan K, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhang C, Lu Y, Yang X, Deng L, Zhou Y, Feng Q, Hu Y, Ding Q, Yang Y, Li S, Jin L, Guan Y, Su B, Kang L, Xu S (2016) Ancestral origins and genetic history of Tibetan Highlanders. Am J Hum Genet 99(3):580–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.07.002
Guo Y, Shen C, Meng H, Dong Q, Kong T, Yang C, Wang H, Jin R, Zhu B (2016) Population differentiations and phylogenetic analysis of Tibet and Qinghai Tibetan groups based on 30 InDel loci. DNA Cell Biol 35(12):787–794. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2016.3395
Excoffier L, Lischer HEL (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10(3):564–567
Shi YY, He L (2005) SHEsis, a powerful software platform for analyses of linkage disequilibrium, haplotype construction, and genetic association at polymorphism loci. Cell Res 15(2):97–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cr.7290272
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Meng HT, Zhang YD, Shen CM, Yuan GL, Yang CH, Jin R, Yan JW, Wang HD, Liu WJ, Jing H (2015) Genetic polymorphism analyses of 30 InDels in Chinese Xibe ethnic group and its population genetic differentiations with other groups. Sci Rep 5:8260
Shen C, Zhu B, Yao T, Li Z, Zhang Y, Yan J, Wang B, Bie X, Tai F (2016) A 30-InDel assay for genetic variation and population structure analysis of Chinese Tujia group. Sci Rep 6:36842
Gao Z, Chen X, Zhao Y, Zhao X, Zhang S, Yang Y, Wang Y, Zhang J (2018) Forensic genetic informativeness of an SNP panel consisting of 19 multi-allelic SNPs. Forensic Sci Int Genet 34:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2018.01.006
Acknowledgments
We thank all sample donors for their contributions to this work and all those who helped with sample collection.
Funding
This work received financial support from the Department of Science & Technology of Sichuan Province (2017JY0233).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jian, H., Wang, L., Wang, H. et al. Population genetic analysis of 30 insertion–deletion (INDEL) loci in a Qinghai Tibetan group using the Investigator DIPplex Kit. Int J Legal Med 133, 1039–1041 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-018-1954-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-018-1954-x