Abstract
Introduction
Poor sleep quality and excessive daytime sleepiness are common in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF), and both are negatively correlated with health-related quality of life (HRQoL). The objective of our study was to evaluate subjective and objective sleep quality in adult CF patients and its effect on HRQoL.
Materials and methods
This was a descriptive, prospective, cross-sectional study of CF patients > 18 years of age. Patients underwent nocturnal polysomnography (PSG) and were administered the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index questionnaire (PSQI) and the Cystic Fibrosis Quality of Life Questionnaire (CFQR 14 + Spain).
Results
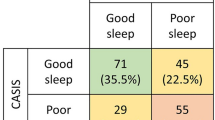
The study included 23 patients, 14 women (61%). The mean age of the participants was 32 + 18 years. The mean PSQI score was 5.57 + 3.55; 13 (56.5%) of the patients were poor sleepers, and 13% reported poor sleep quality; seven (30%) had sleep latency > 30 min, 10 (43.5%) had sleep efficiency < 85%. Nineteen underwent polysomnography. According to PSG measurements, sleep efficiency was less than 90% in 61% of the patients. Pathological values were found for the following parameters: intra-sleep wakefulness in 12 patients (63%); microarousal index in 12 patients (63%); and apnea–hypopnea index (AHI) in 2 patients. The desaturation time with SpO2 < 90% (T90) was > 30% in 3 patients. We observed a significant correlation between PSQI and all dimensions of CFQR 14.
Conclusions
Subjective and objective sleep efficiency decreases in adult CF patients. Sleep quality has an impact on HRQoL. The PSQI questionnaire was able to discriminate sleep quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen DH (1938) Cystic fibrosis in the pancreas and its relationship to celiac disease. Am J Dis Child 56:344–399
Kerem B, Rommens JM, Buchanan JA, Markiewicz D, Cax TK, Chakravarti A et al (1989) Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science 245:1073–1080
Verhaeghe C, Delbecque K, de Leval L, Oury C, Bours V (2007) Early inflammation in the airways of a cystic fibrosis foetus. J Cystic Fibros 6(4):304–308
Nir M, Lanng S, Johansen HK, Koch C (1996) Long term survival and nutritional data in patients with cystic fibrosis treated in Danish Centre. Thorax 51:1023–1027
Chetta A, Pisi G, Zanini A, Foresi A, Grzincich GL, Aiello M et al (2001) Six minute walking test in cystic fibrosis adults with mild to moderate lung disease: comparison to healthy subjects. Respir Med 95:986–991
Katz ES (2014) Cystic fibrosis and sleep. Clin Chest Med 35:495–504
Flume PA, Ciolino J, Gray S, Lester MK (2009) Patient-reported pain and impaired sleep quality in adult patients with cystic fibrosis. J Cystic Fibros 8:321–325
Jankelowitz L, Reid KJ, Wolfe L, Cullina J, Zee PC, Jain M (2005) Cystic fibrosis patients have poor sleep quality despite normal sleep latency and efficiency. Chest 127:1593–1599
Naqvi SK, Sotelo C, Murry L, Simakajornboon N (2008) Sleep architecture in children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis and the association with severity of lung disease. Sleep Breath 12(1):77–83
Dancey DR, Tullis ED, Heslegrave R, Thornley K, Hanly PJ (2002) Sleep quality and daytime function in adults with cystic fibrosis and severe lung disease. Eur Respir J 19:504–510
Fauroux B, Pepin JL, Boelle PY, Cracowski C, Murris-Espin M, Nove-Josserand R et al (2012) Sleep quality and nocturnal hypoxemia and hypercapnia in children and young adults with cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child 97:960–966
Sawicki GS, Sellers DE, Robinson WM (2008) Self-reported physical and psychological symptom burden in adults with cystic fibrosis. J Pain Symptom Manage 35:372–380
Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi Rcoates A, et al (2005) Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J 26:319–338
Report ERS Task Force (2012) Multiethnic reference values for spirometry for the age range of 3 to 95 years: global lung function 2012 equations. Eur Respir J 40:1324–1343
Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Enright P, Brusasco V, Crapo RO, Burgos F et al (2005) Interpretative strategies for lung function tests. Eur Respir J 26:948–968
American Thoracic Society (2003) ATS/ACCP statement on cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167:211–277
Oliveira G, Gaspar I, Cruz I, Dorado A, Pérez- Ruiz E et al (2010) Validation of the Spanish version of the revised cystic fibrosis quality of life questionnaire in adolescents and adults (CFQR 14 + Spain). Arch Bronconeumol 46:165–175
Henry B, Staab D, Prados C, Aussge P, de Ponth-Brune S, Grosskotf C et al (1998) How to measure quality of life in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients across countries and cultures: the Cystic Fibrosis Questionnaire (CFQ) abtrac. Pediatr Pulmonol 17(suppl):392–393
Quittner AL, Buu A, Messer MA, Modi AC, Watrous M (2005) Development and validation of the cystic Fibrosis Questionnaire in The United States: a health-related quality of life measure for cystic fibrosis. Chest 128:2347–2354
Rayuela A, Macías JA (1997) Propiedades clinimétricas de la versión castellana del cuestionario Pittsburg. Vigilia-Sueno 9:81–94
Lloberes P, Duran Cantolla J, Martínez–García MA, Marín JM, Ferrer A, Corral J et al (2011) Diagnóstico y tratamiento del síndrome de apneas-hipopneas del sueño. [Diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome.]. Arch Bronconeumol 47:143–156
Berry RB, Budhiraja R, Gottlieb DJ, Gozal D, Iber C, Kapur VK et al (2012) Rules for scoring respiratory events in sleep: update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the scoring of sleep associated events. Deliberations of the sleep apnea definitions task force of the American academy of sleep medicine. J Clin Sleep Med 8:597–619
Perin C, Fagondes SC, Casarotto FC et al (2012) Sleep findings and predictors of sleep desaturation in adult cystic fibrosis patients. Sleep Breath 16:1041–1048
Villa MP, Pagani J, Lucidi V, Palamides S, Ronchetti R (2001) Nocturnal oximetry in infants with cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child 84:50–54
Morrell MJ, Dempsey JA (2002) Impact of Sleep on ventilation. In: McNicholas WT, Phillipson EA (eds) Breathing disorders in sleep. WB Saunders, London, pp 3–17
Muller NL, Francias PW, Gurwitz D, Levison H, Bryan AL (1980) Mechanism of hemoglobin desaturation during rapid eye movement sleep in normal subjects and in patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 121:463–469
Spier S, Rivlin J, Hughes D, Levison H (1984) The effect of oxygen on sleep, blood gases and ventilation in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 129:712–718
Zinmam R, Cory M, Coates AL et al (1989) Nocturnal Home oxygen in the treatment of hypoxemic cystic fibrosis patients. J Pediatr 114:368–377
Stokes DC, McBride JT, Wall MA, Erba G, Strieder DJ (1980) Sleep Hypoxemia in young adults with cystic fibrosis. Am J Dis Child 134:741–743
Milross MA, Piper AJ, Norman M, Willson GN, Grunstein RR, Sullivan CE, Bye PT (2001) Predicting sleep-disordered breathing with cystic fibrosis. Chest 120:1239–1245
Ramos RT, Salles C, Gregorio PB, Barros AT, Santana A, Araujo Filho-JB, Acosta AX (2009) Evaluation of the upper airway in children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73:1780–1785
Coffey MJ, Fitzgerald MX, Mc Nicholas WT (1991) Comparison of oxygen desaturation during sleep and exercise in patients with cystic fibrosis. Chest 100:659–662
Bradley S, Salin P, Wilson J, Johns D, Walters EH, Naughton MT (1999) Hypoxemia and hypercapnia during exercise and sleep in patients with cystic fibrosis. Chest 116:647
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank SEPAR for providing a Publibeca grant that allowed us to obtain the assistance of Medical Science Consulting, who advised us in the writing of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Íscar-Urrutia, M., Madrid-Carbajal, C.J., Rubinos-Cuadrado, G. et al. Objective and Subjective Sleep Efficiency in Adult Patients with Cystic Fibrosis and Impact on Quality of Life. Lung 196, 761–767 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-018-0167-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-018-0167-x