Abstract
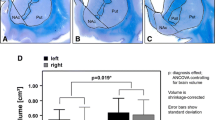
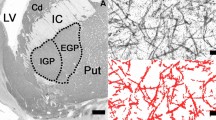
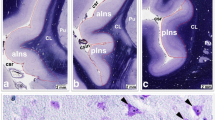
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the globus pallidus internus was recently proposed as a potential new treatment target for opioid addiction. DBS requires computer-assisted-3D planning to implant the stimulation electrode precisely. As volumes of brain regions may differ in addiction compared to healthy controls, our aim was to investigate possible volume differences in addicts compared to healthy controls. Volumes of the globus pallidus externus (PE) and internus (PI) in heroin addicts (n = 14) and healthy controls (n = 12) were assessed using morphometry of serial whole-brain sections. Total brain volume was larger in the heroin group (mean 1479 ± 62 cm3 vs. mean 1352 ± 103 cm3), as the heroin group was more than 10 years younger (p = 0.001). Despite larger mean whole brain volume, the mean relative volume of the PE and PI was smaller in addicted subjects compared to healthy controls (PE 0.658 ± 0.183 × 10−3 vs. 0.901 ± 0.284 × 10−3; ANOVA F(1, 24) = 6.945, p = 0.014, η2 = 0.224; PI 0.253 ± 0.095 × 10−3 vs. 0.345 ± 0.107 × 10−3; ANOVA F(1, 24) = 5.374, p = 0.029, η2 = 0.183). These findings were not significantly confounded by age, duration of autolysis, and fixation time. Our results provide further evidence for structural and not only functional deficits of the globus pallidus in addiction. In the context of previous studies, our findings support the idea of shared pathophysiological processes between comorbid depression and impulsivity in opioid addiction.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Degenhardt L, Charlson F, Mathers B, Hall WD, Flaxman AD, Johns N, Vos T (2014) The global epidemiology and burden of opioid dependence: results from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Addiction.109:1320–1333. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.12551
Unick GJ, Ciccarone D (2017) US regional and demographic differences in prescription opioid and heroin-related overdose hospitalizations. Int J Drug Policy 46:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2017.06.003
Kuhn J, Lenartz D, Huff W, Lee S, Koulousakis A, Klosterkoetter J, Sturm V (2007) Remission of alcohol dependency following deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens: valuable therapeutic implications? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:1152–1153. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2006.113092
Müller U, Sturm V, Voges J, Heinze H-J, Galazky I, Büntjen L, Heldmann M, Frodl T, Steiner J, Bogerts B (2016) Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation for alcohol addiction—safety and clinical long-term results of a pilot trial. Pharmacopsychiatry 49:170–173. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-104507
Kuhn J, Möller M, Treppmann JF, Bartsch C, Lenartz D, Gruendler TOJ, Maarouf M, Brosig A, Barnikol UB, Klosterkötter J, Sturm V (2014) Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens and its usefulness in severe opioid addiction. Mol Psychiatry 19:145–146. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.196
Muller UJ, Truebner K, Schiltz K, Kuhn J, Mawrin C, Dobrowolny H, Bernstein H-G, Bogerts B, Steiner J (2015) Postmortem volumetric analysis of the nucleus accumbens in male heroin addicts: implications for deep brain stimulation. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 265:647–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-015-0617-x
Muller UJ, Schiltz K, Mawrin C, Dobrowolny H, Frodl T, Bernstein H-G, Bogerts B, Truebner K, Steiner J (2017) Total hypothalamic volume is reduced in postmortem brains of male heroin addicts. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 268:243–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-017-0809-7
Jaeger D, Kita H (2011) Review functional connectivity and integrative properties of globus pallidus neurons. Neuroscience 198:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.050
Goldberg JA, Bergman H (2011) Review computational physiology of the neural networks of the primate globus pallidus: function and dysfunction. Neuroscience 198:171–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.08.068
Moussawi K, Kalivas PW, Lee JW (2016) Abstinence from drug dependence after bilateral globus pallidus hypoxic-ischemic injury. BPS 80:e79–e80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.04.005
Isometsä ET (2001) Psychological autopsy studies—a review. Eur Psychiatry 16:379–385
Bernstein HG, Stanarius A, Baumann B, Henning H, Krell D, Danos P, Falkai P, Bogerts B (1998) Nitric oxide synthase-containing neurons in the human hypothalamus: reduced number of immunoreactive cells in the paraventricular nucleus of depressive patients and schizophrenics. Neuroscience 83:867–875
Bielau H, Trübner K, Krell D, Agelink MW, Bernstein HG, Stauch R, Mawrin C, Danos P, Gerhard L, Bogerts B, Baumann B (2005) Volume deficits of subcortical nuclei in mood disorders. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 255:401–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-005-0581-y
Baumann B, Danos P, Krell D, Diekmann S, Leschinger A, Stauch R, Wurthmann C, Bernstein HG, Bogerts B (1999) Reduced volume of limbic system-affiliated basal ganglia in mood disorders: preliminary data from a postmortem study. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 11:71–78
Bernstein HG, Baumann B, Danos P, Diekmann S, Bogerts B, Gundelfinger ED, Braunewell KH (1999) Regional and cellular distribution of neural visinin-like protein immunoreactivities (VILIP-1 and VILIP-3) in human brain. J Neurocytol 28:655–662
Gundersen HJ, Jensen EB (1987) The efficiency of systematic sampling in stereology and its prediction. J Microsc 147:229–263
Pollo C, Kaelin-Lang A, Oertel MF, Stieglitz L, Taub E, Fuhr P, Lozano AM, Raabe A, Schupbach M (2014) Directional deep brain stimulation: an intraoperative double-blind pilot study. Brain. 137:2015–2026.https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awu102
Andersen SN, Skullerud K (1999) Hypoxic/ischaemic brain damage, especially pallidal lesions, in heroin addicts. Forensic Sci Int 102:51–59
Bernstein H-G, Trübner K, Krebs P, Dobrowolny H, Bielau H, Steiner J, Bogerts B (2014) Increased densities of nitric oxide synthase expressing neurons in the temporal cortex and the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of polytoxicomanic heroin overdose victims: possible implications for heroin neurotoxicity. Acta Histochem 116:182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2013.07.006
Cadet JL, Bisagno V, Milroy CM (2013) Neuropathology of substance use disorders. Acta Neuropathol 127:91–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-013-1221-7
Pearson J, Baden MB, Richter RW (1976) Neuronal depletion in the globus pallidus of heroin addicts. Drug Alcohol Depend 1:349–356
Tolomeo S, Matthews K, Steele D, Baldacchino A (2018) Compulsivity in opioid dependence. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 81:333–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.09.007
Zippel-Schultz B, Specka M, Cimander K, Eschenhagen T, Golz J, Maryschok M, Nowak M, Poehlke T, Stover H, Helms TM, Scherbaum N (2016) Outcomes of patients in long-term opioid maintenance treatment. Subst Use Misuse 51:1493–1503. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826084.2016.1188946
Gos T, Krell D, Bielau H, Steiner J, Trübner K, Brisch R, Bernstein H-G, Jankowski Z, Bogerts B (2009) Demonstration of disturbed activity of external globus pallidus projecting neurons in depressed patients by the AgNOR staining method. J Affect Disord 119:149–155.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2009.03.010
Ruitenberg MFL, Wu T, Averbeck BB, Chou KL, Koppelmans V, Seidler RD (2018) Impulsivity in Parkinson’s disease is associated with alterations in affective and sensorimotor striatal networks. Front Neurol 9:105–112. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00279
Saga Y, Hoshi E, Tremblay L (2017) Roles of multiple globus pallidus territories of monkeys and humans in motivation, cognition and action: an anatomical, physiological and pathophysiological review. Front Neuroanat 11:10612–10659. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2017.00030
Acknowledgements
Renate Stauch, Sieglinde Funke and Gabriela Meyer-Lotz provided excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Sampling and preservation of the human brain material were done in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, German Law and approval by the local institutional review board.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, U.J., Mawrin, C., Frodl, T. et al. Reduced volumes of the external and internal globus pallidus in male heroin addicts: a postmortem study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 269, 317–324 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-018-0939-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-018-0939-6