Abstract
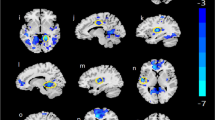
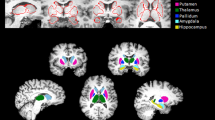
Although depression and anxiety disorders are common comorbid conditions in alcohol dependence, few structural brain imaging studies have compared alcohol-dependent subjects with and without such comorbidity. In the current study, brain scans of 35 alcohol-dependent with and 40 individuals without diagnosis of a comorbid ICD-10 depressive or anxiety disorder receiving detoxification inpatient treatment were evaluated. Thickness and volumes of automatically segmented neuroanatomical structures were measured in FreeSurfer. Furthermore, associations of brain structure with biological markers and clinical severity markers of alcohol dependence were assessed. Despite comparable addiction severity, the non-comorbid group had evidence of higher cytotoxic effects of alcohol use on hepatic and haematological markers, and showed significantly smaller volumes of total cerebral, and cerebellar grey matter. Similarly, they showed unexpected smaller hippocampal and nucleus accumbens volumes, and thinner frontal, temporal and occipital cortices. Smaller brain volumes correlated with increased markers of hepatic and haematological dysfunction, and with longer duration of alcohol dependence in the non-comorbid group. Evidence of higher biomarkers of alcohol use may be indicative of more severe alcohol dependence or higher vulnerability to ethanol toxicity in this group. Furthermore, psychopathology-related drug treatment, which occurred in 53% of the comorbid group over the recent years, or tissue inflammation may have a moderate effect on the grade of cerebral atrophy in alcohol-dependent patients. Longitudinal studies are needed to investigate this issue more fully.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laramée P, Kusel J, Leonard S, Aubin HJ, François C, Daeppen JB (2013) The economic burden of alcohol dependence in Europe. Alcohol Alcohol 48(3):259–269
Wang YP, Andrade LH (2013) Epidemiology of alcohol and drug use in the elderly. Curr Opin Psychiatry 26(4):343–348
Maimaris W, McCambridge J (2014) Age of first drinking and adult alcohol problems: systematic review of prospective cohort studies. J Epidemiol Community Health 68(3):268–274
Monte SM de la, Kril JJ (2014) Human alcohol-related neuropathology. Acta Neuropathol 127:71–90
Carlen PL, Wortzman G, Holgate RC, Wilkinson DA, Rankin JG (1978) Reversible cerebral atrophy in recently abstinent chronic alcoholics measured by computed tomography scans. Science 200:1076–1078
Cala LA (1987) Is CT scan a valid indicator of brain atrophy in alcoholism? Acta Med Scand 221(S717):27–32
Schroth G, Naegele T, Klose U, Mann K, Petersen D (1988) Reversible brain shrinkage in abstinent alcoholics, measured by MRI. Neuroradiology 30:121–126
Maes M, Vandoolaeghe E, Degroote J, Altamura C, Roels C, Hermans P (2000) Linear CT-scan measurements in alcohol-dependent patients with and without delirium tremens. Alcohol 20(2):117–123
Mann K, Ackermann B, Croissant B, Mundle G, Nakovics H, Diehl A (2005) Neuroimaging of gender differences in alcohol dependence: Are woman more vulnerable? Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29(5):896–901
Bleich S, Sperling W, Degner D, Graesel E, Bleich K, Wilhelm J et al (2003) Lack of association between hippocampal volume reduction and first-onset alcohol withdrawal seizure. A volumetric MRI study. Alcohol Alcohol 38(1):40–44
Chanraud S, Martelli C, Delain F, Kostogianni N, Douaud G, Aubin HJ et al (2007) Brain Morphometry and cognitive performance in detoxified alcohol-dependents with preserved psychosocial functioning. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(2):429–438
Kril JJ, Halliday GM, Svoboda MD, Cartwright H (1997) The cerebral cortex is damaged in chronic alcoholics. Neuroscience 79(4):983–998
Makris N, Oscar-Berman M, Kim S, Hodge SM, Kennedy DN, Caviness VS et al (2008) Decreased volume of the brain reward system in alcoholism. Biol Psychiatry 64(3):192–202
Bühler M, Mann K (2011) Alcohol and the human brain: a systematic review of different neuroimaging methods. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35(10):1771–1793
Fortier CB, Leritz EC, Salat DH, Venne JR, Maksimovskiy AL, Williams V et al (2011) Reduced cortical thickness in abstinent alcoholics and association with alcoholic behavior. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35(12):2193–2201
Momenan R, Steckler LE, Saad ZS, van Rafelghem S, Kerich MJ, Hommer DW (2012) Effects of alcohol dependence on cortical thickness as determined by magnetic resonance imaging. Psychiat Res Neuroimaging 204(2–3):101–111
Xiao P, Dai Z, Zhong J, Zhu Y, Shi H, Pan P (2015) Regional grey matter deficits in alcohol dependence: a meta-analysis of voxel based morphometry studies. Drug Alcohol Depend 153:22–28
Yang X, Tian F, Zhang H, Zeng J, Chen T, Wang S, Jia Z, Gong Q (2016) Cortical and subcortical gray matter shrinkage in alcohol-use disorders: a voxel-based meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 66:92–103
Fein G, Di Sclafani V, Cardenas VA, Goldmann H, Tolou-Shams M, Meyerhoff DJ (2002) Cortical gray matter loss in treatment-naive alcohol dependent individuals. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26(4):558–564
Fein G (2013) Lifetime and current mood and anxiety disorders in short-term and long-term abstinent alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 37(11):1930–1938
Fein G (2015) Psychiatric comorbidity in alcohol dependence. Neuropsychol Rev 25(4):456–475
Regier DA, Farmer ME, Rae DS, Locke BZ, Keith SJ, Judd LL et al (1990) Comorbidity of mental disorders with alcohol and other drug abuse—results from the epidemiologic catchment area (ECA) study. JAMA 264(19):2511–2518
Schneider U, Altmann A, Baumann M, Bernzen J, Bertz B, Bimber U et al (2001) Comorbid anxiety and affective disorder in alcohol dependent patients seeking treatment: the first multicentre study in Germany. Alcohol Alcohol 36(3):219–223
Grant BF, Stinson FS, Dawson DA, Chou SP, Dufour MC, Compton W et al (2004) Prevalence and co-occurrence of substance use disorders and independent mood and anxiety disorders: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry 61:807–816
Kushner MG, Sher KJ, Erickson DJ (1999) Prospective analysis of the relation between DSM-III anxiety disorders and alcohol use disorders. Am J Psychiatry 156(5):723–732
Sinha R, Robinson J, O´Malley S (1998) Stress response dampening: effects of gender and family history of alcoholism and anxiety disorders. Psychopharmacology 137:311–320
Schuckit MA (2006) Comorbidity between substance use disorders and psychiatric conditions. Addiction 101(Suppl. 1):76–88
Campbell S, Marriott M, Nahmias C, MacQueen GM (2004) Lower hippocampal volume in patients suffering from depression: meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry 161(4):598–607
Koolschijn PCMP., van Haren NEM, Lensvelt-Mulders GJLM., Hulshoff Pol HE, Kahn RS (2009) Brain volume abnormalities in major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging studies. Hum Brain Mapp 30:3719–3735
Schmaal L, Veltman DJ, van Erp TG, Saemann PG, Frodl Jahanshad N (2016) Subcortical brain alterations in major depressive disorder: findings from the ENIGMA major depressive disorder working group. Mol Psychiatry 21(6):806–812
Campbell S, MacQueen G (2006) An update on region brain volume differences associated with mood disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry 19:25–33
Grieve SM, Korgaonkar MS, Koslow SH, Gordon E, Williams LM (2013) Widespread reductions in grey matter volume in depression. Neuroimage Clin 3:332–339
Brühl AB, Delsignore A, Komossa K, Weidt S (2014) Neuroimaging in social anxiety disorder—a meta-analytic review resulting in a new neurofunctional model. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 47:260–280
Del Casale A, Serata D, Rapinesi C, Kotzalidis GD, Angeletti G, Tatarelli R et al (2013) Structural neuroimaging in patients with panic disorder: findings and limitations of recent studies. Psychiatr Danub 25(2):108–114
Radua J, Mataix-Cols D (2009) Voxel-wise meta-analysis of grey matter changes in obsessive–compulsive disorder. Br J Psychiatry 195:393–402
Rotge JY, Langbour N, Guehl D, Bioulac B, Jaafari N, Allard M et al (2010) Gray matter alterations in obsessive–compulsive disorder: an anatomic likelihood estimation meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:686–691
Goldstein RZ, Volkow ND (2002) Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex. Am J Psychiatry 159(10):1642–1652
Gilpin NW, Herman MA, Roberto M (2015) The central amygdala as an integrative hub for anxiety and alcohol use disorders. Biol Psychiatry 77(10):859–869
Miguel-Hidalgo JJ, Wei J, Andrew M, Overholser JC, Jurjus G, Stockmeier CA, Rajkowska G (2002) Glia pathology in the prefrontal cortex in alcohol dependence with and without depressive symptoms. Biol Psychiatry 52(12):1121–1133
Sameti M, Smith S, Patenaude B, Fein G (2011) Subcortical volumes in long-term abstinent alcoholics: associations with psychiatric comorbidity. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35(3):1067–1080
Fein G, Shimotsu R, Chu R, Barakos J (2009) Parietal gray matter volume loss is related to spatial processing deficits in long-term abstinent alcoholic men. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:1806–1814
Bleich S, Bandelow B, Javaheripour K, Müller A, Degner D, Wilhelm J et al (2003) Hyperhomocysteinemia as a new risk factor for brain shrinkage in patients with alcoholism. Neurosci Lett 335(3):179–182
Crews FT, Nixon K (2009) Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and regeneration in alcoholism. Alcohol Alcohol 44:115–127
Sutherland GT, Sheedy D, Sheahan PJ, Kaplan W, Kril JJ (2014) Comorbidities, confounders and the white matter transcriptome in chronic alcoholism. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38(4):994–1001
Chen C-H, Walker J, Momenan R, Rawlings R, Heilig M, Hommer DW (2012) Relationship between liver function and brain shrinkage in patients with alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 36(4):625–632
de Bruin EA, Lemmens PH, Hulshoff Pol HE, Verbaten MN, Kenemans JL (2012) Relationship between carbohydrate-deficient transferrin, gamma-glutamyltransferase, and mean corpuscular volume levels and alcohol-related brain volume decreases in male drinkers. Hum Psychopharmacol 27(6):559–565
WHO (World Health Organization) (1993) International classification of psychiatric disorders ICD-10. Chapter V (F), clinical diagnostic guidelines, 2nd edn; WHO, Bern
Fischl B, Dale AM (2000) Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11050–11055
Fischl B, Salat DH, Busa E, Albert M, Dieterich M, Haselgrove C et al (2002) Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron 33:341–355
Desikan RS, Segonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D et al (2006) An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 31:968–980
Benjamini Y, Krieger A, Yekutieli D (2006) Adaptive linear step-up procedures that control the false discovery rate. Biometrika 93:491–507
Wang Q, Jie W, Liu JH, Yang JM, Gao TM (2017) An astroglial basis of major depressive disorder? An overview. Glia. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23143
Rothermundt M, Arolt V, Peters M, Gutbrodt H, Fenker J, Kersting A, Kirchner H (2001) Inflammatory markers in major depression and melancholia. J Affect Disord 63(1–3):93–102
Wedekind D, Neumann K, Falkai P, Malchow B, Engel KR, Jamrozinski K et al (2011) S100ß and homocysteine in the acute alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 261(2):133–138
Davenport J (1996) Macrocytic anemia. Am Fam Physician 53(1):155–162
Di Benedetto B, Rupprecht R (2013) Targeting glia cells: novel perspectives for the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases. Curr Neuropharmacol 11(2):171–185
Sanacora G, Banasr M (2013) From pathophysiology to novel antidepressant drugs: glial contributions to the pathology and treatment of mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 73(12):1172–1179
Young LT (2002) Neuroprotective effects of antidepressant and mood stabilizing drugs. J Psychiat Neurosci 27(1):8–9
Durazzo TC1, Mon A, Gazdzinski S, Meyerhoff DJ (2013) Chronic cigarette smoking in alcohol dependence: associations with cortical thickness and N-acetylaspartate levels in the extended brain reward system. Addict Biol 18(2):379–391
Franklin TR, Wetherill RR, Jagannathan K, Johnson B, Mumma J, Hager N et al (2014) The effects of chronic cigarette smoking on gray matter volume: influence of sex. Zang Y-F. ed. PLoS One 9(8):e104102
Midanik L (1982) Over-reports of recent alcohol consumption in a clinical population: a validity study. Drug Alcohol Depend 9:101–110
Del Boca FK, Noll JA (2000) Truth or consequences: the validity of self-report data in health services research on addictions. Addiction 95(Suppl 3):S347-S360
Babor TF, Steinberg K, Anton R, Del Boca F (2000) Talk is cheap: measuring drinking outcomes in clinical trials. J Stud Alcohol 61(1):55–63
Acknowledgements
This collaboration and research project was supported by the EUSARNAD program of the “European Commission 7th Framework Program” (Marie Curie International Research Staff Exchange Scheme Program).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
D. J. Stein has received research grants and/or consultancy honoraria from Abbott, ABMRF, Astrazeneca, Biocodex, Eli-Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Johnson & Johnson, Lundbeck, National Responsible Gambling Foundation, Novartis, Orion, Pfizer, Pharmacia, Roche, Servier, Solvay, Sumitomo, Sun, Takeda, Tikvah, and Wyeth. U. Havemann-Reinecke has received research grants and/or consultancy honoraria from CNMPB (Centre of nanomicroscopy and molecular biology of the Brain of the DFG, German research Federation), Astra Zeneca, Lundbeck, Lilly, Janssen. The other authors declare no conflict of interest with respect to subjects of the paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uhlmann, A., Bandelow, B., Stein, D.J. et al. Grey matter structural differences in alcohol-dependent individuals with and without comorbid depression/anxiety—an MRI study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 269, 285–294 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-018-0870-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-018-0870-x