Abstract
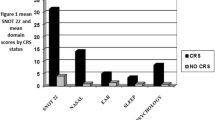
Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) may arise due to odontogenic etiologies. However, it is unknown whether odontogenic CRS has a differential impact on patients’ quality of life (QOL) compared to standard, inflammatory (but non-odontogenic) CRS. The objective of this study was to determine whether there is a difference in the impact of sinonasal symptomatology on general health-related QOL in odontogenic CRS compared to non-odontogenic CRS. This was a retrospective review of 21 odontogenic CRS patients who visited our tertiary care center. The severity of sinonasal symptomatology and CRS-specific QOL detriment was measured using the 22-item Sinonasal Outcomes Test (SNOT-22) and general health-related QOL was measured using the health utility index from the 5-item EuroQol survey (EQ-5D HUV). Compared to non-odontogenic CRS, odontogenic CRS was not associated with a difference in SNOT-22 score [linear regression coefficient (β) = − 1.57, 95% CI − 12.47 to 9.32, p = 0.777] but was significantly associated with decreased EQ-5D HUV (β = − 0.10, 95% CI − 0.17 to − 0.03, p = 0.008). We also found that the magnitude of association (β) between SNOT-22 and EQ5D-HUV was greater for odontogenic CRS patients compared to non-odontogenic CRS patients (p = 0.045). Our findings suggest sinonasal symptoms may have a greater impact on general QOL in odontogenic CRS compared to non-odontogenic CRS. The reason for this remains unknown, but deserves further study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zirk M, Dreiseidler T, Pohl M et al (2017) Odontogenic sinusitis maxillaris: a retrospective study of 121 cases with surgical intervention. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 45(4):520–525
Hoehle LP, Phillips KM, Bergmark RW et al (2016) Symptoms of chronic rhinosinusitis differentially impact general health-related quality of life. Rhinology 54(4):316–322
Phillips KM, Hoehle LP, Bergmark RW et al (2017) Acute exacerbations mediate quality of life impairment in chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 5(2):422–426
Phillips KM, Hoehle LP, Caradonna DS et al (2016) Association of severity of chronic rhinosinusitis with degree of comorbid asthma control. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 117(6):651–654
Sedaghat AR, Gray ST, Wilke CO et al (2012) Risk factors for development of chronic rhinosinusitis in patients with allergic rhinitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 2(5):370–375
Sedaghat AR, Phipatanakul W, Cunningham MJ (2013) Atopy and the development of chronic rhinosinusitis in children with allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 1(6):689–691
Carey RM, Adappa ND, Palmer JN et al (2016) Taste receptors: regulators of sinonasal innate immunity. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol 1(4):88–95
Stevens WW, Peters AT (2015) Immunodeficiency in chronic sinusitis: recognition and treatment. Am J Rhinol Allergy 29(2):115–118
Bose S, Grammer LC, Peters AT (2016) Infectious chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 4(4):584–589
London NR, Lane AP (2016) Innate immunity and chronic rhinosinusitis: what we have learned from animal models. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol 1(3):49–56
Mehra P, Jeong D (2008) Maxillary sinusitis of odontogenic origin. Curr Infect Dis Rep 10(3):205–210
Brook I (2006) Sinusitis of odontogenic origin. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135(3):349–355
Lopez-Carriches C, Lopez-Carriches I, Bryan RB (2016) Odontogenic sinusitis caused by an inflammation of a dentigerous cyst and subsequent finding of a fibrous dysplasia. A case report. Open Dent J 10:647–655
McCarty JL, David RM, Lensing SY et al (2017) Root cause analysis: an examination of odontogenic origins of acute maxillary sinusitis in both immunocompetent & immunocompromised patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr 41(3):484–488
Ferguson M (2014) Rhinosinusitis in oral medicine and dentistry. Aust Dent J 59(3):289–295
Rosenfeld RM, Piccirillo JF, Chandrasekhar SS et al (2015) Clinical practice guideline (update): adult sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 152(2 Suppl):S39
Orlandi RR, Kingdom TT, Hwang PH et al (2016) International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 6(Suppl 1):S209
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J et al (2012) European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. Rhinol Suppl 23:298
Workman AD, Granquist EJ, Adappa ND (2018) Odontogenic sinusitis: developments in diagnosis, microbiology, and treatment. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 26(1):27–33
Hopkins C, Gillett S, Slack R et al (2009) Psychometric validity of the 22-item Sinonasal Outcome Test. Clin Otolaryngol 34(5):447–454
EuroQol Group. EuroQol–a new facility for the measurement of health-related quality of life. Health Policy 1990;16(3):199–208
R Development Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2011
Patel NA, Ferguson BJ (2012) Odontogenic sinusitis: an ancient but under-appreciated cause of maxillary sinusitis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 20(1):24–28
Simuntis R, Kubilius R, Vaitkus S (2014) Odontogenic maxillary sinusitis: a review. Stomatologija 16(2):39–43
Mehra P, Murad H (2004) Maxillary sinus disease of odontogenic origin. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 37(2):347–364
Bewick J, Morris S, Hopkins C et al (2018) Health utility reporting in chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Clin Otolaryngol 43(1):90–95
Guilemany JM, Angrill J, Alobid I et al (2009) United airways: the impact of chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps in bronchiectasic patient’s quality of life. Allergy 64(10):1524–1529
Remenschneider AK, D’Amico L, Gray ST et al (2015) The EQ-5D: a new tool for studying clinical outcomes in chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 125(1):7–15
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the contribution of the patients who participated in this study.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaudin, R.A., Hoehle, L.P., Smeets, R. et al. Impact of odontogenic chronic rhinosinusitis on general health-related quality of life. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275, 1477–1482 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-4977-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-4977-5