Abstract
Background
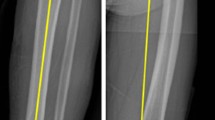
Restoration of correct coronal alignment is one of the main goals of total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Traditionally, TKA has been considered successful when a neutral mechanical hip–knee–ankle (HKA) axis within 3° is achieved. Recent studies have reported no differences or improved clinical outcomes following a slight under-correction of the HKA axis for a varus knee. However, the influence of under-correction of a valgus knee has not been reported. This study investigated the influence of post-operative HKA alignment in TKA patients with valgus deformity on clinical outcomes.
Methods
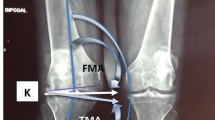
Ninety-three knees (93 patients) with pre-operative valgus alignment were evaluated with a mean follow-up period of 60 months. All patients were classified into three groups based on post-operative HKA alignment: neutral (0 ± 3°), mild valgus (3°–6°), and severe valgus (> 6°). These groups were compared using the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities osteoarthritis (WOMAC) index, the Knee Society (KS) knee score, KS function score, α-angle, β-angle, patella tilt angle, and the congruence angle.
Results
Sixty-nine knees were included in the neutral group, seventeen knees in the mild valgus group, and seven knees in the severe valgus group. In all cases, post-operative clinical and functional scores significantly improved compared to pre-operative scores. There were no differences between the three groups in post-operative clinical and functional scores. More post-operative patellar tilt angle outliers (> 10°) and congruence angle outliers (> 16°) were apparent in the severe valgus group (patellar tilt angle, 13 vs. 17 vs. 57.1%, p = 0.022; congruence angle, 32 vs. 47 vs. 71%, p = 0.035).
Conclusions
Slight under-correction following TKA for a valgus knee resulted in similar clinical outcomes. A residual valgus angle of more than 6° can induce patellar maltracking.
Level of evidence
III, Retrospective comparative study.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB (1994) Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement. Its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:153–156
Longstaff LM, Sloan K, Stamp N, Scaddan M, Beaver R (2009) Good alignment after total knee arthroplasty leads to faster rehabilitation and better function. J Arthroplast 24(4):570–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2008.03.002
Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE (2009) Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplast 24(6 Suppl):39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2009.04.034
Morgan SS, Bonshahi A, Pradhan N, Gregory A, Gambhir A, Porter ML (2008) The influence of postoperative coronal alignment on revision surgery in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 32(5):639–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-007-0391-0
Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Stoney JD (2009) Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 24(4):560–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2008.02.018
Slevin O, Hirschmann A, Schiapparelli FF, Amsler F, Huegli RW, Hirschmann MT (2017) Neutral alignment leads to higher knee society scores after total knee arthroplasty in preoperatively non-varus patients: a prospective clinical study using 3D-CT. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4744-y
Rames RD, Mathison M, Meyer Z, Barrack RL, Nam D (2017) No impact of under-correction and joint line obliquity on clinical outcomes of total knee arthroplasty for the varus knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4507-9
Vanlommel L, Vanlommel J, Claes S, Bellemans J (2013) Slight undercorrection following total knee arthroplasty results in superior clinical outcomes in varus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(10):2325–2330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2481-4
Howell SM, Papadopoulos S, Kuznik KT, Hull ML (2013) Accurate alignment and high function after kinematically aligned TKA performed with generic instruments. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(10):2271–2280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2621-x
Howell SM, Howell SJ, Kuznik KT, Cohen J, Hull ML (2013) Does a kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty restore function without failure regardless of alignment category? Clin Orthop Relat Res 471(3):1000–1007. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2613-z
Matziolis G, Adam J, Perka C (2010) Varus malalignment has no influence on clinical outcome in midterm follow-up after total knee replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130(12):1487–1491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-010-1064-9
Ranawat AS, Ranawat CS, Elkus M, Rasquinha VJ, Rossi R, Babhulkar S (2005) Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. J Bone Jt Surg Am 87(Suppl 1 Pt 2):271–284. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.E.00308
Rossi R, Rosso F, Cottino U, Dettoni F, Bonasia DE, Bruzzone M (2014) Total knee arthroplasty in the valgus knee. Int Orthop 38(2):273–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-013-2227-4
Bruzzone M, Ranawat A, Castoldi F, Dettoni F, Rossi P, Rossi R (2010) The risk of direct peroneal nerve injury using the Ranawat “inside-out” lateral release technique in valgus total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 25(1):161–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2008.08.016
Mizuno Y, Kumagai M, Mattessich SM, Elias JJ, Ramrattan N, Cosgarea AJ, Chao EY (2001) Q-angle influences tibiofemoral and patellofemoral kinematics. J Orthop Res 19(5):834–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0736-0266(01)00008-0
Boettner F, Renner L, Arana Narbarte D, Egidy C, Faschingbauer M (2016) Total knee arthroplasty for valgus osteoarthritis: the results of a standardized soft-tissue release technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24(8):2525–2531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4054-9
Zhou K, Zhou Z, Shi X, Shen B, Kang P, Yang J, Pei F (2018) Effect of individual distal femoral valgus resection in total knee arthroplasty for patients with valgus knee: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg 52:309–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.02.048
Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt LW (1988) Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol 15(12):1833–1840
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN (1989) Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res (248):13–14
Malghem J, Maldague B (1989) Patellofemoral joint: 30 degrees axial radiograph with lateral rotation of the leg. Radiology 170(2):566–567. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.170.2.2911687
Cooke TD, Sled EA, Scudamore RA (2007) Frontal plane knee alignment: a call for standardized measurement. J Rheumatol 34(9):1796–1801
Kilincoglu V, Unay K, Akan K, Esenkaya I, Poyanli O (2011) Component alignment in simultaneous bilateral or unilateral total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 35(1):43–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-010-0993-9
Bae DK, Baek JH, Yoon KT, Son HS, Song SJ (2016) Comparison of patellofemoral outcomes after TKA using two prostheses with different patellofemoral design features. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4264-1
Merchant AC, Mercer RL, Jacobsen RH, Cool CR (1974) Roentgenographic analysis of patellofemoral congruence. J Bone Jt Surg Am 56(7):1391–1396
Moon YW, Seo JG, Yang JH, Shon MS (2008) Analysis of the patellofemoral congruence angle according to the rotational alignment of the femoral component in navigation-guided TKA. Orthopedics 31(10 Suppl 1):62–67
Lee WC, Kwan YH, Chong HC, Yeo SJ (2017) The minimal clinically important difference for knee society clinical rating system after total knee arthroplasty for primary osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25(11):3354–3359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4208-9
Karachalios T, Sarangi PP, Newman JH (1994) Severe varus and valgus deformities treated by total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Br 76(6):938–942
Huang TW, Lee CY, Lin SJ, Lee MS, Hsu RW, Shen WJ (2015) The influence of alignment on midterm outcome after total knee arthroplasty in patients with marked coronal femoral bowing. J Arthroplast 30(9):1531–1536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2015.03.027
Waterson HB, Clement ND, Eyres KS, Mandalia VI, Toms AD (2016) The early outcome of kinematic versus mechanical alignment in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomised control trial. Bone Jt J 98-B(10):1360–1368. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.98B10.36862
Yoon JR, Han SB, Jee MK, Shin YS (2017) Comparison of kinematic and mechanical alignment techniques in primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 96(39):e8157. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000008157
Keshmiri A, Dotzauer F, Baier C, Maderbacher G, Grifka J, Sendtner E (2017) Stability of capsule closure and postoperative anterior knee pain after medial parapatellar approach in TKA. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137(7):1019–1024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2706-y
Cerciello S, Robin J, Lustig S, Maccauro G, Heyse TJ, Neyret P (2016) The role of patelloplasty in total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 136(11):1607–1613. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-016-2577-7
Popovic N, Lemaire R (2003) Anterior knee pain with a posterior-stabilized mobile-bearing knee prosthesis: the effect of femoral component design. J Arthroplast 18(4):396–400
Ittenbach RF, Huang G, Barber Foss KD, Hewett TE, Myer GD (2016) Reliability and validity of the anterior knee pain scale: applications for use as an epidemiologic screener. PloS One 11(7):e0159204. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159204
Feller JA, Bartlett RJ, Lang DM (1996) Patellar resurfacing versus retention in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Jt Surg Br 78(2):226–228
Malo M, Vince KG (2003) The unstable patella after total knee arthroplasty: etiology, prevention, and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 11(5):364–371
Slevin O, Schmid FA, Schiapparelli FF, Rasch H, Amsler F, Hirschmann MT (2017) Coronal femoral TKA position significantly influences in vivo patellar loading in unresurfaced patellae after primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4627-2
Ritter MA, Davis KE, Meding JB, Pierson JL, Berend ME, Malinzak RA (2011) The effect of alignment and BMI on failure of total knee replacement. J Bone Jt Surg Am 93(17):1588–1596. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.J.00772
Funding
There is no funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. The protocol used to evaluate radiographic findings and intraoperative navigation data was approved by our institution’s investigational review board (SMC2017-06-008).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, SS., Lee, H., Lee, DH. et al. Slight under-correction following total knee arthroplasty for a valgus knee results in similar clinical outcomes. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 138, 1011–1019 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-018-2957-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-018-2957-2