Abstract
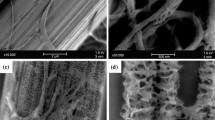
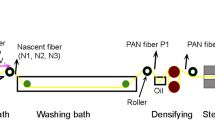
Ultrathin sectioning and solvent etching were used to assess microstructural changes in polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fibrils following a dry-jet wet spinning process. Morphologic assessment revealed the coexistence of fibrils and lamellae within the PAN fibers, with a frill-like structure found on the fibrils. The size of the lamella-like layers was consistent with a crystal size of 13.2 nm as characterized by X-ray diffraction and microfibrils were composed of alternate dark lamella-like crystal layers and surrounded by bright amorphous chains. Further, fibril arrangement followed a weave-like pattern. During the post-spinning process, break-rearrangement of chain-folded lamellae had an important role in fibril structure evolution. The high stream stretching and heat treatment induced the breaking of lamellae and the formation of new lamellae through the molecular chains rotating and slipping, resulting in a decrease in voids and the coalescence of microfibrils. Consequently, the fibrils were arranged in a more orderly manner and interlinked more tightly, a process conducive for the preparation of high quality PAN fibers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fischer L, Ruland W (1980) The influence of graphitization on the mechanical properties of carbon fibers. Colloid Polym Sci 258(8):917–922. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01584920
Chen R, Bin Y, Nakano Y, Kurata N, Matsuo M (2010) Effect of chemical crosslinking on mechanical and electrical properties of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene-carbon fiber blends prepared by gelation/crystallization from solutions. Colloid Polym Sci 288(3):307–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-009-2173-2
Xie Y, Lu L, Hou Z, Tang Y, Miao L, Liu X (2016) Fracture behavior of PAN-based carbon fiber tow in a chopping process on an elastic support. Fiber Polym 17(8):1262–1268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-6306-1
Gulgunje PV, Newcomb BA, Gupta K, Han GC, Tsotsis TK, Kumar S (2015) Low-density and high-modulus carbon fibers from polyacrylonitrile with honeycomb structure. Carbon 95(2):710–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.08.097
Akhlaghi O, Menceloglu YZ, Akbulut O (2016) Rheological behavior of poly(acrylonitrile) concentrated solutions: effect of Sb2O3 nanoparticles on shear and extensional flow. Colloid Polym Sci 294(9):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3907-6
Liu X, Zhu C, Dong H, Wang B, Liu R, Zhao N, Li S, Xu J (2015) Effect of microgel content on the shear and extensional rheology of polyacrylonitrile solution. Colloid Polym Sci 293(2):587–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3419-1
Tan L, Pan J, Wan A (2012) Shear and extensional rheology of polyacrylonitrile solution: effect of ultrahigh molecular weight polyacrylonitrile. Colloid Polym Sci 290(4):289–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-011-2546-1
Ouyang Q, Chen Y, Wang X, Ma H, Li D, Yang J (2015) Supramolecular structure of highly oriented wet-spun polyacrylonitrile fibers used in the preparation of high-performance carbon fibers. J Polym Res 22(12):229–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-015-0865-5
Chand S (2000) Review carbon fibers for composites. J Mater Sci 35(6):1303–1313. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004780301489
Chen JC, Harrison IR (2002) Modification of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) carbon fiber precursor via post-spinning plasticization and stretching in dimethyl formamide (DMF). Carbon 40(1):25–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(01)00050-1
Craig JP, Knudsen JP, Holland VF (1962) Characterization of acrylic fiber structure. Text Res J 32(6):435–448. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051756203200601
Tucker P, George W (2010) Microfibers within fibers: a review. Polym Eng Sci 12(5):364–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.760120509
Warner SB, Uhlmann DR, Jr LHP (1979) Oxidative stabilization of acrylic fibres. J Mater Sci 14(8):1893–1900. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00551029
Wang Q, Wang C, Yu M, Ma J (2010) Microstructure of fibrils separated from polyacrylonitrile fibers by ultrasonic etching. Sci China Technol Sci 53(6):1489–1494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-3142-1
Wang Q, Wang C, Bai Y, Yu M, Wang Y, Zhu B, Jing M, Ma J, Hu X, Zhao Y (2010) Fibrils separated from polyacrylonitrile fiber by ultrasonic etching in dimethylsulphoxide solution. J Appl Polym Sci Part B, Polym Phys 48:617–619. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.21929
Kunzmann C, Schmidt-Bilkenroth G, Moosburger-Will J, Horn S (2018) Microscopic investigation of polyacrylonitrile fiber fibrils separated by ultrasonic etching. J Mater Sci 53(6):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1858-z
Lednicky F, Pientka Z, Hromadkova J (2003) Ultrathin sectioning of polymeric materials for low-voltage transmission electron microscopy: relief on ultrathin sections. J Macromol Sci Part B, Phys 42(5):1039–1047. https://doi.org/10.1081/MB-120023556
Yu T, Zhu C, Gong J, Yang S, Ma J, Xu J (2014) Lamellae break induced formation of shish-kebab during hot stretching of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene precursor fibers investigated by in situ small angle X-ray scattering. Polymer 55(16):4299–4306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2014.06.056
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation, China (Grant Nos. 51773110 and 51573087), A Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program, China (Grant No. J14LA05), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (Grant No. ZR2016EMM16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Q., Jing, M., Wang, C. et al. Fibril microstructural changes of polyacrylonitrile fibers during the post-spinning process. Colloid Polym Sci 296, 1307–1311 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-018-4350-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-018-4350-7