Abstract
Purpose
To date, there have been many studies on postoperative complications and oncologic outcomes, but the findings remain controversial. The purpose of the study was to determine the prognostic value of serum inflammatory markers as pretreatment in curatively resected colorectal cancer. The effects of serum inflammatory marker levels on postoperative morbidity were also examined.
Methods
Prospectively collected data from 1590 patients with primary sporadic colorectal adenocarcinoma who underwent curative resection between September 2012 and December 2013 at our institution were retrospectively analyzed. White blood cell count (× 103/mcl), neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and Glasgow prognostic score (GPS) were evaluated. GPS was determined as follows: GPS of 2, elevated CRP level (> 1.0 mg/dl) and hypoalbuminemia (< 3.5 g/dl); GPS of 1, elevated CRP or hypoalbuminemia; and GPS of 0, neither elevated CRP nor hypoalbuminemia.
Results
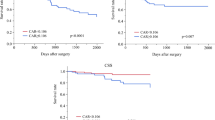
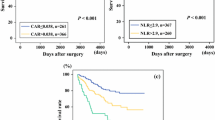
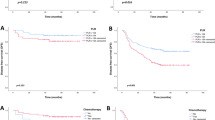
The median follow-up period for the 1590 patients was 59 months. The overall postoperative morbidity rate was 24.8%. In multivariate analysis, female sex (P = 0.006), rectal cancer other than colon cancer (P < 0.001), CEA level > 5 ng/ml (P < 0.001), ESR > 27 mm/h (P = 0.014), and a GPS of 1 or 2 (P < 0.001) were independent risk predictors for morbidity. A GPS of 1 or 2 (P < 0.001) and postoperative morbidity (P < 0.001) significantly affected both overall survival and disease-free survival in multivariate analyses.
Conclusions
A GPS of 1 or 2 is a significant risk factor for postoperative morbidity and a prognostic factor for long-term survival.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M (2010) Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 140(6):883–899
Quail DF, Joyce JA (2013) Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med 19(11):1423–1437
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F (2008) Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454(7203):436–444
McMillan DC, Crozier JEM, Canna K, Angerson WJ, McArdle CS (2007) Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic score (GPS) in patients undergoing resection for colon and rectal cancer. Int J Color Dis 22(8):881–886
Petrelli F, Barni S, Coinu A, Bertocchi P, Borgonovo K, Cabiddu M, Ghilardi M, Zaniboni A (2015) The Modified Glasgow Prognostic Score and survival in colorectal cancer: a pooled analysis of the literature. Rev Recent Clin Trials 10(2):135–141
Shibutani M, Maeda K, Nagahara H, Noda E, Ohtani H, Nishiguchi Y, Hirakawa K (2013) A high preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with poor survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 33(8):3291–3294
Suzuki Y, Okabayashi K, Hasegawa H, Tsuruta M, Shigeta K, Kondo T, Kitagawa Y (2018) Comparison of preoperative inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients with colorectal cancer. Ann Surg 267(3):527–531
Granger DN, Kubes P (1994) The microcirculation and inflammation: modulation of leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion. J Leukoc Biol 55(5):662–675
Huh JW, Lee WY, Park YA, Cho YB, Kim HC, Yun SH, Chun HK (2019) Oncological outcome of surgical site infection after colorectal cancer surgery. Int J Color Dis 34(2):277–283
Huh JW, Kim CH, Lim SW, Kim HR, Kim YJ (2013) Early recurrence in patients undergoing curative surgery for colorectal cancer: is it a predictor for poor overall survival? Int J Color Dis 28(8):1143–1149
Mauricio SF et al (2013) Relationship between nutritional status and the Glasgow Prognostic Score in patients with colorectal cancer. Nutrition 29(4):625–629
Cohen ME, Bilimoria KY, Ko CY, Hall BL (2009) Development of an American College of Surgeons National Surgery Quality Improvement Program: morbidity and mortality risk calculator for colorectal surgery. J Am Coll Surg 208(6):1009–1016
Tomioka K, Murakami M, Fujimori A, Watanabe M, Koizumi T, Goto S, Otsuka K, Aoki T (2017) Risk factors for transumbilical wound complications in laparoscopic gastric and colorectal surgery. In Vivo 31(5):943–948
Vather R, O'Grady G, Bissett IP, Dinning PG (2014) Postoperative ileus: mechanisms and future directions for research. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 41(5):358–370
Gessler B, Eriksson O, Angenete E (2017) Diagnosis, treatment, and consequences of anastomotic leakage in colorectal surgery. Int J Color Dis 32(4):549–556
Oh BY, Park YA, Huh JW, Yun SH, Kim HC, Chun HK, Kim SH, Ha SY, Lee WY, Cho YB (2018) Prognostic impact of tumor-budding grade in stages 1-3 colon cancer: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Surg Oncol 25(1):204–211
Balkwill F, Mantovani A (2001) Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet 357(9255):539–545
Miki C, Konishi N, Ojima E, Hatada T, Inoue Y, Kusunoki M (2004) C-reactive protein as a prognostic variable that reflects uncontrolled up-regulation of the IL-1-IL-6 network system in colorectal carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 49(6):970–976
Ishizuka M, Nagata H, Takagi K, Iwasaki Y, Kubota K (2013) Inflammation-based prognostic system predicts survival after surgery for stage IV colorectal cancer. Am J Surg 205(1):22–28
Forrest LM, McMillan DC, McArdle CS, Angerson WJ, Dunlop DJ (2004) Comparison of an inflammation-based prognostic score (GPS) with performance status (ECOG) in patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy for inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 90(9):1704–1706
Scott HR, McMillan DC, Forrest LM, Brown DJF, McArdle CS, Milroy R (2002) The systemic inflammatory response, weight loss, performance status and survival in patients with inoperable non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 87(3):264–267
Shibutani M, Maeda K, Nagahara H, Ohtani H, Sugano K, Ikeya T, Kimura K, Amano R, Kubo N, Tanaka H, Muguruma K, Ohira M, Hirakawa K (2014) Elevated preoperative serum C-reactive protein levels are associated with poor survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 61(136):2236–2240
Maccio A et al (2005) Hemoglobin levels correlate with interleukin-6 levels in patients with advanced untreated epithelial ovarian cancer: role of inflammation in cancer-related anemia. Blood 106(1):362–367
Mantovani G, Macciò A, Madeddu C, Mura L, Gramignano G, Lusso MR, Mulas C, Mudu MC, Murgia V, Camboni P, Massa E, Ferreli L, Contu P, Rinaldi A, Sanjust E, Atzei D, Elsener B (2002) Quantitative evaluation of oxidative stress, chronic inflammatory indices and leptin in cancer patients: correlation with stage and performance status. Int J Cancer 98(1):84–91
Mantovani G, Macciò A, Madeddu C, Mura L, Massa E, Mudu M, Mulas C, Lusso M, Gramignano G, Piras M (2001) Serum values of proinflammatory cytokines are inversely correlated with serum leptin levels in patients with advanced stage cancer at different sites. J Mol Med (Berl) 79(7):406–414
Tuomisto AE, Makinen MJ, Vayrynen JP (2019) Systemic inflammation in colorectal cancer: underlying factors, effects, and prognostic significance. World J Gastroenterol 25(31):4383–4404
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study proposal, design, analysis, data collection, and writing of manuscript are attributed to Sung Chul Lee and Jung Wook Huh. All authors drafted the work, and Woo Yong Lee, Seong Hyeon Yun, Hee Cheol Kim, Yong Beom Cho, Yoon Ah Park, and Jung Kyong Shin revised it critically for content. All authors approve the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Samsung Medical Center (No. 2019-04-126).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 41 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.C., Huh, J.W., Lee, W.Y. et al. Prognostic value of serum inflammatory markers in colorectal cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis 35, 1211–1219 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-020-03591-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-020-03591-1