Abstract
Purpose
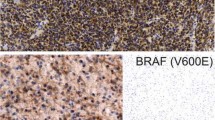
Pilocytic astrocytomas (PCAs) are characterized by two dominant molecular alterations of the BRAF gene, i.e., BRAFV600E mutation and KIAA1549-BRAF fusions which show a differential pattern of frequency across different age-groups.
Methods
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues of 358 (pediatric 276 and adult 82) consecutive PCAs were evaluated for BRAFV600E mutation by Sanger sequencing and KIAA1549:BRAF fusion transcripts (KIAA1549:BRAF 16-9, KIAA1549:BRAF 15-9, and KIAA1549:BRAF 16-11) by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, which were correlated with different clinicopathological features.
Results
BRAFV600E mutation was detected in 8.9% pediatric and 9.75% adult PCAs, whereas 41.1% and 25.7% of pediatric and adult cases showed KIAA1549-BRAF fusions respectively. BRAFV600E did not show any statistically significant correlation with any of the clinical parameters (age, location, and gender). KIAA1549:BRAF fusions showed a significant statistical association with the pediatric age group and cerebellar location. KIAA1549-BRAF 16-9 was the commonest variant and was predominantly associated with cerebellar location than non-cerebellar whereas fusion variant 15-9 negatively correlated with cerebellar locations.
Conclusions
The present study showed overall frequency of 53.5% and 37.3% BRAF alterations in pediatric and adult PCA cases respectively. BRAF fusion in PCA cases showed a different distribution pattern across age groups and locations; while no such differential pattern was observed for BRAFV600E.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Truitt G, Boscia A, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2018) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro-Oncology 20:iv1–iv86
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW, Kleihues P (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114:97–109
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Kleihues P, Ellison DW (2016) The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol 131:803–820
Bornhorst M, Frappaz D, Packer RJ (2016) Pilocytic astrocytomas. In: Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 329–344
Jones DTW, Kocialkowski S, Liu L, Pearson DM, Bäcklund LM, Ichimura K, Collins VP (2008) Tandem duplication producing a novel oncogenic BRAF fusion gene defines the majority of pilocytic astrocytomas. Cancer Res 68:8673–8677
Forshew T, Tatevossian RG, Lawson ARJ, Ma J, Neale G, Ogunkolade BW, Jones TA, Aarum J, Dalton J, Bailey S, Chaplin T, Carter RL, Gajjar A, Broniscer A, Young BD, Ellison DW, Sheer D (2009) Activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway: a signature genetic defect in posterior fossa pilocytic astrocytomas. J Pathol 218:172–181
Sievert AJ, Jackson EM, Gai X, Hakonarson H, Judkins AR, Resnick AC, Sutton LN, Storm PB, Shaikh TH, Biegel JA (2009) Duplication of 7q34 in pediatric low-grade astrocytomas detected by high-density single-nucleotide polymorphism-based genotype arrays results in a novel BRAF fusion gene. Brain Pathol 19:449–458
Jones DTW, Kocialkowski S, Liu L, Pearson DM, Ichimura K, Collins VP (2009) Oncogenic RAF1 rearrangement and a novel BRAF mutation as alternatives to KIAA1549:BRAF fusion in activating the MAPK pathway in pilocytic astrocytoma. Oncogene 28:2119–2123
Roth JJ, Santi M, Pollock AN, Harding BN, Rorke-Adams LB, Tooke LS, Biegel JA (2015) Chromosome band 7q34 deletions resulting in KIAA1549-BRAF and FAM131B-BRAF fusions in pediatric low-grade Gliomas. Brain Pathol 25:182–192
Cin H, Meyer C, Herr R, Janzarik WG, Lambert S, Jones DTW, Jacob K, Benner A, Witt H, Remke M, Bender S, Falkenstein F, van Anh TN, Olbrich H, von Deimling A, Pekrun A, Kulozik AE, Gnekow A, Scheurlen W, Witt O, Omran H, Jabado N, Collins VP, Brummer T, Marschalek R, Lichter P, Korshunov A, Pfister SM (2011) Oncogenic FAM131B-BRAF fusion resulting from 7q34 deletion comprises an alternative mechanism of MAPK pathway activation in pilocytic astrocytoma. Acta Neuropathol 121:763–774
Helgager J, Lidov HG, Mahadevan NR, Kieran MW, Ligon KL, Alexandrescu S (2017) A novel GIT2-BRAF fusion in pilocytic astrocytoma. Diagn Pathol 12:82
Hsiao SJ, Karajannis MA, Diolaiti D, Mansukhani MM, Bender JG, Kung AL, Garvin JH Jr (2017) A novel, potentially targetable TMEM106B-BRAF fusion in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud 3:a001396
Pathak P, Kumar A, Jha P, Purkait S, Faruq M, Suri A, Suri V, Sharma MC, Sarkar C (2017) Genetic alterations related to BRAF-FGFR genes and dysregulated MAPK/ERK/mTOR signaling in adult pilocytic astrocytoma. Brain Pathol 27:580–589
Wan PTC, Garnett MJ, Roe SM, Lee S, Niculescu-Duvaz D, Good VM, Project CG, Jones CM, Marshall CJ, Springer CJ, Barford D, Marais R (2004) Mechanism of activation of the RAF-ERK signaling pathway by oncogenic mutations of B-RAF. Cell 116:855–867
The St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital–Washington University Pediatric Cancer Genome Project (2013) Whole-genome sequencing identifies genetic alterations in pediatric low-grade gliomas. Nat Genet 45:602–612
Hasselblatt M, Riesmeier B, Lechtape B, Brentrup A, Stummer W, Albert FK, Sepehrnia A, Ebel H, Gerß J, Paulus W (2011) BRAF-KIAA1549 fusion transcripts are less frequent in pilocytic astrocytomas diagnosed in adults. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37:803–806
Schindler G, Capper D, Meyer J, Janzarik W, Omran H, Herold-Mende C, Schmieder K, Wesseling P, Mawrin C, Hasselblatt M, Louis DN, Korshunov A, Pfister S, Hartmann C, Paulus W, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A (2011) Analysis of BRAF V600E mutation in 1,320 nervous system tumors reveals high mutation frequencies in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, ganglioglioma and extra-cerebellar pilocytic astrocytoma. Acta Neuropathol 121:397–405
Horbinski C (2013) To BRAF or not to BRAF: is that even a question anymore? J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 72:2–7
Behling F, Barrantes-Freer A, Skardelly M, Nieser M, Christians A, Stockhammer F, Rohde V, Tatagiba M, Hartmann C, Stadelmann C, Schittenhelm J (2016) Frequency of BRAF V600E mutations in 969 central nervous system neoplasms. Diagn Pathol 11:55
Matallanas D, Birtwistle M, Romano D, Zebisch A, Rauch J, von Kriegsheim A, Kolch W (2011) Raf family kinases: old dogs have learned new tricks. Genes Cancer 2:232–260
Pakneshan S, Salajegheh A, Smith RA, Lam AK-Y (2013) Clinicopathological relevance of BRAF mutations in human cancer. Pathology 45:346–356
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S, Teague J, Woffendin H, Garnett MJ, Bottomley W, Davis N, Dicks E, Ewing R, Floyd Y, Gray K, Hall S, Hawes R, Hughes J, Kosmidou V, Menzies A, Mould C, Parker A, Stevens C, Watt S, Hooper S, Wilson R, Jayatilake H, Gusterson BA, Cooper C, Shipley J, Hargrave D, Pritchard-Jones K, Maitland N, Chenevix-Trench G, Riggins GJ, Bigner DD, Palmieri G, Cossu A, Flanagan A, Nicholson A, Ho JWC, Leung SY, Yuen ST, Weber BL, Seigler HF, Darrow TL, Paterson H, Marais R, Marshall CJ, Wooster R, Stratton MR, Futreal PA (2002) Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 417:949–954
Faulkner C, Ellis HP, Shaw A, Penman C, Palmer A, Wragg C, Greenslade M, Haynes HR, Williams H, Lowis S, White P, Williams M, Capper D, Kurian KM (2015) BRAF fusion analysis in pilocytic astrocytomas: KIAA1549-BRAF 15-9 fusions are more frequent in the midline than within the cerebellum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 74:867–872
Tian Y, Rich BE, Vena N, Craig JM, MacConaill LE, Rajaram V, Goldman S, Taha H, Mahmoud M, Ozek M, Sav A, Longtine JA, Lindeman NI, Garraway LA, Ligon AH, Stiles CD, Santagata S, Chan JA, Kieran MW, Ligon KL (2011) Detection of KIAA1549-BRAF fusion transcripts in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded pediatric low-grade gliomas. J Mol Diagn 13:669–677
Kondo A, Shimizu Y, Adachi S et al (2018) A comprehensive method for detecting fusion genes in paediatric brain tumours. Cancer Genomics - Proteomics 15:343–348
Appay R, Fina F, Macagno N, Padovani L, Colin C, Barets D, Ordioni J, Scavarda D, Giangaspero F, Badiali M, Korshunov A, M. Pfister S, T.W. Jones D, Figarella-Branger D (2018) Duplications of KIAA1549 and BRAF screening by droplet digital PCR from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded DNA is an accurate alternative for KIAA1549-BRAF fusion detection in pilocytic astrocytomas. Mod Pathol 31:1490–1501
Ryall S, Arnoldo A, Krishnatry R, Mistry M, Khor K, Sheth J, Ling C, Leung S, Zapotocky M, Guerreiro Stucklin A, Lassaletta A, Shago M, Tabori U, Hawkins CE (2017) Multiplex detection of pediatric low-grade glioma signature fusion transcripts and duplications using the NanoString nCounter system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 76:562–570
Ida CM, Vrana JA, Rodriguez FJ, Jentoft ME, Caron AA, Jenkins SM, Giannini C (2013) Immunohistochemistry is highly sensitive and specific for detection of BRAF V600E mutation in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. Acta Neuropathol Commun 1:20
Theeler BJ, Ellezam B, Sadighi ZS, Mehta V, Tran MD, Adesina AM, Bruner JM, Puduvalli VK (2014) Adult pilocytic astrocytomas: clinical features and molecular analysis. Neuro-Oncology 16:841–847
Qaddoumi I, Orisme W, Wen J, Santiago T, Gupta K, Dalton JD, Tang B, Haupfear K, Punchihewa C, Easton J, Mulder H, Boggs K, Shao Y, Rusch M, Becksfort J, Gupta P, Wang S, Lee RP, Brat D, Peter Collins V, Dahiya S, George D, Konomos W, Kurian KM, McFadden K, Serafini LN, Nickols H, Perry A, Shurtleff S, Gajjar A, Boop FA, Klimo PD, Mardis ER, Wilson RK, Baker SJ, Zhang J, Wu G, Downing JR, Tatevossian RG, Ellison DW (2016) Genetic alterations in uncommon low-grade neuroepithelial tumors: BRAF, FGFR1, and MYB mutations occur at high frequency and align with morphology. Acta Neuropathol 131:833–845
Deng MY, Sill M, Chiang J, Schittenhelm J, Ebinger M, Schuhmann MU, Monoranu CM, Milde T, Wittmann A, Hartmann C, Sommer C, Paulus W, Gärtner J, Brück W, Rüdiger T, Leipold A, Jaunmuktane Z, Brandner S, Giangaspero F, Nozza P, Mora J, Morales la Madrid A, Cruz Martinez O, Hansford JR, Pietsch T, Tietze A, Hernáiz-Driever P, Stoler I, Capper D, Korshunov A, Ellison DW, von Deimling A, Pfister SM, Sahm F, Jones DTW (2018) Molecularly defined diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor (DLGNT) comprises two subgroups with distinct clinical and genetic features. Acta Neuropathol 136:239–253
Chiang JCH, Harreld JH, Orr BA, Sharma S, Ismail A, Segura AD, Ellison DW (2017) Low-grade spinal glioneuronal tumors with BRAF gene fusion and 1p deletion but without leptomeningeal dissemination. Acta Neuropathol 134:159–162
Kumar A, Pathak P, Purkait S, Faruq M, Jha P, Mallick S, Suri V, Sharma MC, Suri A, Sarkar C (2015) Oncogenic KIAA1549-BRAF fusion with activation of the MAPK/ERK pathway in pediatric oligodendrogliomas. Cancer Genet 208:91–95
Taha H, Yehia M, Mahmoud M, el-Beltagy M, Ghabriel M, el-Naggar S (2015) Incidence of KIAA1549-BRAF fusion gene in Egyptian pediatric low grade glioma. Clin Transl Med 4:10
Gierke M, Sperveslage J, Schwab D, Beschorner R, Ebinger M, Schuhmann MU, Schittenhelm J (2016) Analysis of IDH1-R132 mutation, BRAF V600 mutation and KIAA1549–BRAF fusion transcript status in central nervous system tumors supports pediatric tumor classification. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142:89–100
Antonelli M, Badiali M, Moi L, Buttarelli FR, Baldi C, Massimino M, Sanson M, Giangaspero F (2015) KIAA1549:BRAF fusion gene in pediatric brain tumors of various histogenesis: KIAA1549:BRAF fusion gene in pediatric brain tumors. Pediatr Blood Cancer 62:724–727
Myung JK, Cho H, Park C-K et al (2012) Analysis of the BRAF(V600E) mutation in central nervous system tumors. Transl Oncol 5:430–436
Dahiya S, Yu J, Kaul A, Leonard JR, Gutmann DH (2012) Novel BRAF alteration in a sporadic pilocytic astrocytoma. Case Rep Med 2012:1–4
Horbinski C, Nikiforova MN, Hagenkord JM, Hamilton RL, Pollack IF (2012) Interplay among BRAF, p16, p53, and MIB1 in pediatric low-grade gliomas. Neuro-oncology 14:777–789
Khater F, Langlois S, Cassart P et al (2018) Recurrent somatic BRAF insertion (p.V504_R506dup): a tumor marker and a potential therapeutic target in pilocytic astrocytoma. Oncogene 38:2994–3002
Lassaletta A, Zapotocky M, Mistry M, Ramaswamy V, Honnorat M, Krishnatry R, Guerreiro Stucklin A, Zhukova N, Arnoldo A, Ryall S, Ling C, McKeown T, Loukides J, Cruz O, de Torres C, Ho CY, Packer RJ, Tatevossian R, Qaddoumi I, Harreld JH, Dalton JD, Mulcahy-Levy J, Foreman N, Karajannis MA, Wang S, Snuderl M, Nageswara Rao A, Giannini C, Kieran M, Ligon KL, Garre ML, Nozza P, Mascelli S, Raso A, Mueller S, Nicolaides T, Silva K, Perbet R, Vasiljevic A, Faure Conter C, Frappaz D, Leary S, Crane C, Chan A, Ng HK, Shi ZF, Mao Y, Finch E, Eisenstat D, Wilson B, Carret AS, Hauser P, Sumerauer D, Krskova L, Larouche V, Fleming A, Zelcer S, Jabado N, Rutka JT, Dirks P, Taylor MD, Chen S, Bartels U, Huang A, Ellison DW, Bouffet E, Hawkins C, Tabori U (2017) Therapeutic and prognostic implications of BRAF V600E in pediatric low-grade gliomas. J Clin Oncol 35:2934–2941
Brandner S, von Deimling A (2015) Diagnostic, prognostic and predictive relevance of molecular markers in gliomas: molecular markers in gliomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 41:694–720
Banerjee A, Jakacki RI, Onar-Thomas A, Wu S, Nicolaides T, Young Poussaint T, Fangusaro J, Phillips J, Perry A, Turner D, Prados M, Packer RJ, Qaddoumi I, Gururangan S, Pollack IF, Goldman S, Doyle LA, Stewart CF, Boyett JM, Kun LE, Fouladi M (2017) A phase I trial of the MEK inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244) in pediatric patients with recurrent or refractory low-grade glioma: a pediatric brain tumor consortium (PBTC) study. Neuro-Oncology 19:1135–1144
Upadhyaya SA, Robinson GW, Harreld JH, Klimo PD, Hoehn ME, Orr BA, Qaddoumi IA (2018) Marked functional recovery and imaging response of refractory optic pathway glioma to BRAFV600E inhibitor therapy: a report of two cases. Childs Nerv Syst 34:605–610
Ross JS, Wang K, Chmielecki J, Gay L, Johnson A, Chudnovsky J, Yelensky R, Lipson D, Ali SM, Elvin JA, Vergilio JA, Roels S, Miller VA, Nakamura BN, Gray A, Wong MK, Stephens PJ (2016) The distribution of BRAF gene fusions in solid tumors and response to targeted therapy: BRAF fusions in solid tumors. Int J Cancer 138:881–890
Miller C, Guillaume D, Dusenbery K, Clark HB, Moertel C (2017) Report of effective trametinib therapy in 2 children with progressive hypothalamic optic pathway pilocytic astrocytoma: documentation of volumetric response. J Neurosurg Pediatr 19:319–324
Drobysheva A, Klesse LJ, Bowers DC, Rajaram V, Rakheja D, Timmons CF, Wang J, Koral K, Gargan L, Ramos E, Park JY (2017) Targeted MAPK pathway inhibitors in patients with disseminated pilocytic astrocytomas. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 15:978–982
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Mrs. Prachi Gogte, Mr.Vinayak Kadam, Mr. Sandeep Dhanavade, and Mrs.Dipika Dhanavade for their technical assistance.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Terry Fox Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interests in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix. Detailed methodology of nucleic acid extraction, PCR with subsequent sequencing for BRAFV600E and RT-PCR for BRAF fusions
Appendix. Detailed methodology of nucleic acid extraction, PCR with subsequent sequencing for BRAFV600E and RT-PCR for BRAF fusions
DNA and RNA extraction
Selected FFPE blocks were subjected to genomic DNA and total RNA extraction from four sections each of 10 μm thickness. Sections were deparaffinized with limonene (Sigma Aldrich, USA) followed by overnight digestion. DNA was extracted using QIAamp DNA mini kit (Qiagen) as per manufacturer’s instructions. Extracted DNA was checked for quality (260:280 ratio) and quantity by Nanodrop (Thermo Scientific, USA). The integrity of the DNA was assessed by PCR for beta-actin (ACTB-208 bp) housekeeping gene (Table 1) and the positive samples were then subjected to PCR for BRAF Exon 15. Total RNA extraction was performed using RecoverAll total nucleic acid isolation kit (Ambion, Thermo Scientific, USA). RNA was quantitated using Nanodrop (Thermo Scientific, USA) and complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized from 100 ng RNA using RevertAid™ H Minus First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Scientific, USA). The quality of cDNA was determined using ACTB housekeeping gene PCR and cDNA amplifiable for ACTB gene were subjected to RT-PCR for KIAA1549-BRAF fusion.
BRAF polymerase chain reaction and sequencing
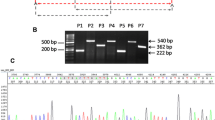
Amplification was carried out in a total volume of 20 μl reaction containing 10 μl of 2× master mix (Thermo Scientific, USA), 1 μl each of 10 pmol forward and reverse primer (Table 1), and 100 ng of template DNA. PCR conditions were initial denaturation at 94 °C for 3 min, 35 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 54 °C for 45 s, 72 °C for 45 s, and a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. PCR products were electrophoresed on 1.5% agarose gel and purified with EXOSAP-IT (USB, Affymetrix). Direct DNA sequencing was performed on the purified PCR products using BigDye v3.1 cycle sequencing kit (Thermo Scientific, USA) followed by purification with BigDye × terminator kit. The purified products were sequenced on ABI3500 Genetic Analyzer (Thermo Scientific, USA) and sequences analyzed using Chromas Lite software and compared with the reference sequence for BRAFV600E mutation and other adjoining mutations.
KIAA1549-BRAF fusions: reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction
RT-PCR was performed for 3 different fusion transcripts; KIAA1549-BRAF 16-9 (124 bp), KIAA1549-BRAF 15-9 (159 bp) and KIAA1549-BRAF 16-11 (182 bp). PCR reaction contained 2 μl of template cDNA, 5 μl of 2X PCR master mix (Thermo Scientific, USA), and 0.5 μl of forward and reverse primers specific for each fusion transcript (Table 1) in a total volume of 10 μl. PCR program was as follows; 94 °C for 3 min followed by 40 cycles of 94 °C for 45 s, 57–61 °C for 45 s, and 72 °C for 45 s, and completed with an extension step at 72 °C for 10 min. Annealing temperature for KIAA1549-BRAF 16-9 (124 bp), KIAA1549-BRAF 15-9 (159 bp) andKIAA1549-BRAF 16-11 (182 bp) fusion transcripts were 57 °C, 59 °C, and 61 °C respectively. PCR products were separated on 10% polyacrylamide gel, stained with ethidium bromide, and visualized under UV illumination (Alpha Imager, Bioscreen, USA).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurani, H., Gurav, M., Shetty, O. et al. Pilocytic astrocytomas: BRAFV600E and BRAF fusion expression patterns in pediatric and adult age groups. Childs Nerv Syst 35, 1525–1536 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-019-04282-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-019-04282-1