Abstract
Purpose
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) has become the method of choice in the treatment of hydrocephalus. Age and etiology could determine success rates (SR) of ETV. The purpose of this study is to assess these factors in pediatric population.
Methods
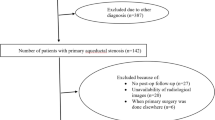
Retrospective study on 51 children with obstructive hydrocephalus that underwent ETV was performed. The patients were divided into three groups per their age at the time of the treatment: < 6, 6–24, and > 24 months of age. All ETV procedures were performed by the same neurosurgeon.
Results
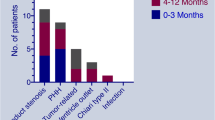
Overall SR of ETV was 80% (40/51) for all etiologies and ages. In patients < 6 months of age SR was 56.2% (9/16), while 6–24 months of age was 88.9% (16/18) and > 24 months was 94.1% (16/17) (p = 0.012). The highest SR was obtained on aqueductal stenosis. SR of posthemorrhagic, postinfectious, and spina bifida related hydrocephalus was 60% (3/5), 50% (1/2), and 14.3% (1/7), respectively. While SR rate at the first ETV attempt was 85.3%, it was 76.9% in patients with V-P shunt performed previously (p = 0.000).
Conclusions
Factors indicating a potential failure of ETV were young age and etiology such as spina bifida, other than isolated aqueductal stenosis. ETV is the method of choice even in patients with former shunting. Fast healing, distensible skulls, and lower pressure gradient in younger children, all can play a role in ETV failure. Based on our experience, ETV could be the first method of choice for hydrocephalus even in children younger than 6 months of age.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldauf J, Oertel J, Gaab MR, Schroeder HWS (2007) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children younger than 2 years of age. Childs Nerv Syst 23:623–626
Balthasar AJ, Kort H, Cornips EM, Beuls EA, Weber JW, Vles JS (2007) Analysis of the success and failure of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in infants less than 1 year of age. Childs Nerv Syst 23:151–155
Bargalló N, Olondo L, Garcia AI, Capurro S, Caral L, Rumia J (2005) Functional analysis of third ventriculostomy patency by quantification of CSF stroke volume by using cine phase-contrast imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 26:2514–2521
Beems T, Grotenhuis JA (2002) Is the success of endoscopic third ventriculostomy age-dependent? An analysis of the results of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children. Childs Nerv Syst 18:605–608
Bognar L, Markia B (2005) Retrospective analysis of 400 neuroendoscopic interventions: the Hungarian experience. Neurosurg Focus 19:E10
Brichtova E, Chlachula M, Hrbac T, Lipina R (2013) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in previously shunted children, Minim Invasive Surg 584567, 4 pages
Brockmeyer D, Abtin K, Carey L, Walker ML (1998) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: an outcome analysis. Pediatr Neurosurg 28(5):236–240
Buxton A, Macarthur D, Mallucci C, Punt J, Vloeberghs M (1998) Neuroendoscopy in the premature population. Childs Nerv Syst 14:649–652
Buxton N, Macarthur D, Mallucci C, Punt J, Vioeberghs M (1998) Neuroendoscopic third ventriculostomy in patients less than 1 year old. Pediatr Neurosurg 29:73–76
Chi JH, Fullerton HJ, Gupta N (2005) Time trends and demographics of deaths from congenital hydrocephalus in the United States: National Center for Health Statistics data, 1979 to 1998. J Neurosurg 103:113–118
Cinalli G, Sainte-Rose C, Chumas P, Zerah M, Brunelle F, Lot G, Pierre-Kahn A, Renier D (1999) Failure of third ventriculostomy in the treatment of aqueductal stenosis in children. J Neurosurg 90:448–454
Constantini S, Sgouros S, Kulkarni A (2013) Neuroendoscopy in the youngest age group. World Neurosurg 79(2 Suppl):S23
Durnford AJ, Kirkham FJ, Mathad N, Sparrow OC (2011) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the treatment of childhood hydrocephalus: validation of a success score that predicts long-term outcome. J Neurosurg Pediatr 8:489–493
Etus V, Ceylan S (2005) Success of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children less than 2 years of age. Neurosurg Rev 28:284–288
Fritsch MJ, Kienke S, Ankermann T, Padoin M, Mehdorn HM (2005) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in infants. J Neurosurg 103:50–53
Fukuhara T, Vorster SJ, Luciano MG (2000) Risk factors for failure of endoscopic third ventriculostomy for obstructive hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 46(5):1100–1109 discussion 1109-11
Furlanetti LL, Santos MV, Santos de Oliveira R (2012) The success of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children: analysis of prognostic factors. Pediatr Neurosurg 48:352–359
Gallo P, Szathmari A, Biasi SD, Carmine M (2010) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in obstructive infantile hydrocephalus: remarks about the so-called ‘unsuccessful cases’. Pediatr Neurosurg 46:435–441
Gangemi M, Donati P, Maiuri F, Longatti P, Godano U, Mascari C (1999) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy for hydrocephalus. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 42:128–132
Gorayeb RP, Cavalheiro S, Zymberg ST (2004) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children younger than 1 year of age. J Neurosurg 100:427–429
Hader WJ, Walker RL, Myles ST, Hamilton M (2008) Complications of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in previously shunted patients. Neurosurgery 63(suppl 1):168–174
Hopf NJ, Grunert P, Fries G, Resch KD, Perneczky A (1999) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: outcome analysis of 100 consecutive procedures. Neurosurgery 44:795–806
Jones RF, Kwok BC, Stening WA, Vonau M (1994) The current status of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the management of non-communicating hydrocephalus. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 37(1):28–36
Jones RF, Kwok BC, Stening WA, Vonau M (1994) Neuroendoscopic third ventriculostomy. A practical alternative to extracranial shunts in non-communicating hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir Suppl 61:79–83
Jones RF, Kwok BC, Stening WA, Vonau M (1996) Third ventriculostomy for hydrocephalus associated with spinal dysraphism: indications and contraindications. Eur J Pediatr Surg 6:5–6
Kadrian D, vanGelder J, Florida D, Jones R, Vonau M, Teo C, Stening W, Kwok B (2008) Long-term reliability of endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Neurosurgery 62(Suppl 2):614–621
Kim SK, Wang KC, Cho BK (2000) Surgical outcome of pediatric hydrocephalus treated by endoscopic III ventriculostomy: prognostic factors and interpretation of postoperative neuroimaging. Childs Nerv Syst 16:161–169
Koch D, Wagner W (2004) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in infants of less 1 year of age: which factors influence the outcome? Childs Nerv Syst 20:405–411
Koch-Wiewrodt D, Wagner W (2006) Success and failure of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in young infants: are there different age distributions? Childs Nerv Syst 22:1537–1541
Kulkarni AV, Drake JM, Kestle JR, Mallucci CL, Sgouros S, Constantini S, Canadian Pediatric Neurosurgery Study Group (2010) Predicting who will benefit from endoscopic third ventriculostomy compared with shunt insertion in childhood hydrocephalus using the ETV Success Score. J Neurosurg Pediatr 6:310–315
Kulkarni AV, Drake JM, Mallucci CL, Sgouros S, Roth J, Constantini S, Canadian Pediatric Neurosurgery Study Group (2009) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the treatment of childhood hydrocephalus. J Pediatr 155:254–259
Lipina R, Reguli S, Dolezilová V, Kuncíková M, Podesvová H (2008) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy for obstructive hydrocephalus in children younger than 6 months of age: is it a firstchoice method? Childs Nerv Syst 24:1021–1027
Mohanty A, Vasudev MK, Sampath S, Radesh S, Kolluri VRS (2002) Failed endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children: management options. Pediatr Neurosurg 37:304–309 001; 35: 131–135
Naftel RP, Reed GT, Kulkarni AV, Wellons JC (2011) Evaluating the Children’s Hospital Alabama endoscopic third ventriculostomy experience using the endoscopic third ventriculostomy success score. J Neurosurg Pediatr 8:494–501
O’Brien DF, Seghedoni A, Collins DR, Hayhurst C, Mallucci CL (2006) Is there an indication for ETV in young infants in aetiologies other than isolated aqueduct stenosis? Childs Nerv Syst 22:1565–1572
Oertel JMK, Gaab M, Schroeder HW (2009) Endoscopic options in children: experience with 134 procedures. J Neurosurg Pediatr 3:81–89
Ogiwara H, Dipatri AJ Jr, Alden TD, Bowman RM, Tomita T (2010) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy for obstructive hydrocephalus in children younger than 6 months of age. Childs Nerv Syst 26:343–347
Oi S, Di Rocco C (2006) Proposal of ‘evolution theory in cerebrospinal fluid dynamics’ and minor pathway hydrocephalus in developing immature brain. Childs Nerv Syst 22:662–669
Pereira JL, Ayres-Basto R, Seixas M, Vaz MLR (2002) Neuroendoscopia no tratamento da hidrocefalia obstrutiva. Acta Méd Port 15:355–364
Peretta P, Ragazzi P, Galarza M, Genitori L, Giordano F, Mussa F, Cinalli G (2006) Complications and pitfalls of neuroendoscopic surgery in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 105:187–193
Pollay M (2010) The function and structure of the cerebrospinal fluid system. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res 7:9
Rekate HL (2004) Selecting patients for endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Neurosurg Clin N Am 15:39–49
Sacko O, Boetto S, Lauwers-Cances V, Dupuy M, Roux FE (2010) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy: outcome analysis in 368 procedures. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5:68–74
Siomin V, Cinalli G, Grotenhuis A, Golash A, Oi S, Kothbauer K, Weiner H, Roth J, Beni-Adani L, Pierre-Kahn A, Takahashi Y, Mallucci C, Abbott R, Wisoff J, Constantini S (2002) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy in patients with cerebrospinal fluid infection and/or hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 97(3):519–524
Siomin V, Weiner H, Wisoff J, Cinalli G, Pierre-Kahn A, Saint-Rose C, Abbott R, Elran H, Beni-Adani L, Ouaknine G, Constantini S (2001) Repeat endoscopic third ventriculostomy: is it worth trying? Childs Nerv Syst 17:551–555
Teo C, Jones R (1996) Management of hydrocephalus by endoscopic third ventriculostomy in patients with myelomeningocele. Pediatr Neurosurg 25(2):57–63 discussion 6
Wagner W, Koch D (2005) Mechanisms of failure after endoscopic third ventriculostomy in young infants. J Neurosurg 103:43–49
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that author has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Duzce University Clinical Researches Ethics Committee has approved this respective study (date: 2017, number 117). This study has been accepted as an e-poster presentation for ESPN biennial congress, 6–9 May 2018, in Bonn, Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duru, S., Peiro, J.L., Oria, M. et al. Successful endoscopic third ventriculostomy in children depends on age and etiology of hydrocephalus: outcome analysis in 51 pediatric patients. Childs Nerv Syst 34, 1521–1528 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3811-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3811-0