Abstract
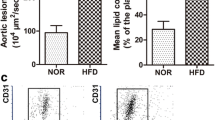
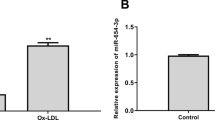
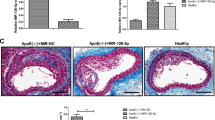
Several miRNAs have been demonstrated to be involved in endothelial dysfunction during atherosclerosis (AS). However, the detailed roles and underlying mechanisms of miR-34a in AS-associated endothelial cell apoptosis are far from being addressed. Apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE−/−) mice fed with high-fat diet (HFD) were used as in vivo model of AS. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-treated human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) were applied as in vitro model of AS. The effects of miR-34a on atherosclerotic lesions were evaluated by hematoxylin–eosin (HE) and Oil Red O staining. Pecam-1+ endothelial cells were isolated from the aortic arch with flow cytometry. qRT-PCR and western blot were employed to measure gene and protein expression. The effects of miR-34a on cell viability, cell cycle distribution, and apoptosis were assessed by Cell counting kit (CCK)-8 and flow cytometry analysis. The relationship between miR-34a and Bcl-2 was confirmed by online softwares, luciferase reporter assay, and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP). miR-34a was upregulated in HFD-induced ApoE−/− mice and ox-LDL-treated HAECs. Anti-miR-34a decreased atherosclerotic lesions and inhibited Pecam-1+ endothelial cells apoptosis in HFD-induced ApoE−/− mice. Moreover, anti-miR-34a significantly promoted cell viability, alleviated cell cycle arrest, and restrained apoptosis in ox-LDL-treated HAECs. Furthermore, Bcl-2 was identified as a target of miR-34a, and miR-34a inhibited Bcl-2 expression via binding to its 3′UTR. Rescue experiments demonstrated that Bcl-2 overexpression dramatically reversed miR-34a-mediated inhibition of cell growth and promotion of apoptosis in ox-LDL-exposed HAECs. Depletion of miR-34a facilitated endothelial cell growth and blocked apoptosis in AS by upregulating Bcl-2, offering a promising avenue for AS therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herrington W, Lacey B, Sherliker P, Armitage J, Lewington S (2016) Epidemiology of atherosclerosis and the potential to reduce the global burden of atherothrombotic disease. Circ Res 118:535–546
Wang B, Zhong Y, Huang D, Li J (2016) Macrophage autophagy regulated by miR-384-5p-mediated control of Beclin-1 plays a role in the development of atherosclerosis. Am J Transl Res 8:606–614
Chen C, Wang Y, Yang S, Li H, Zhao G, Wang F, Yang L, Wang DW (2015) MiR-320a contributes to atherogenesis by augmenting multiple risk factors and down-regulating SRF. J Cell Mol Med 19:970–985
Xu Q (2006) The impact of progenitor cells in atherosclerosis. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 3:94–101
Chavakis E, Dimmeler S (2002) Regulation of endothelial cell survival and apoptosis during angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:887–893
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Wojciechowska A, Braniewska A, Kozar-Kaminska K (2017) MicroRNA in cardiovascular biology and disease. Adv Clin Exp Med 26:865–874
Laffont B, Rayner KJ (2017) MicroRNAs in the pathobiology and therapy of atherosclerosis. Can J Cardiol 33:313–324
Li Y, Yang C, Zhang L, Yang P (2017) MicroRNA-210 induces endothelial cell apoptosis by directly targeting PDK1 in the setting of atherosclerosis. Cell Mol Biol Lett 22:3
Ye J, Guo R, Shi Y, Qi F, Guo C, Yang L (2016) miR-155 regulated inflammation response by the SOCS1-STAT3-PDCD4 axis in atherogenesis. Mediat Inflamm 2016:8060182
Samanta S, Balasubramanian S, Rajasingh S, Patel U, Dhanasekaran A, Dawn B, Rajasingh J (2016) MicroRNA: a new therapeutic strategy for cardiovascular diseases. Trends Cardiovasc Med 26:407–419
Tang F, Yang TL, Zhang Z, Li XG, Zhong QQ, Zhao TT, Gong L (2017) MicroRNA-21 suppresses ox-LDL-induced human aortic endothelial cells injuries in atherosclerosis through enhancement of autophagic flux: involvement in promotion of lysosomal function. Exp Cell Res 359:374–383
Jyy O, Bernardo BC, Singla S, Patterson NL, Lin R, Mcmullen JR (2017) Identification of miR-34 regulatory networks in settings of disease and anti-miR-therapy: implications for treating cardiac pathology and other diseases. RNA Biol 14:500–513
Han H, Qu G, Han C, Wang Y, Sun T, Li F, Wang J, Luo S (2015) MiR-34a, miR-21 and miR-23a as potential biomarkers for coronary artery disease: a pilot microarray study and confirmation in a 32 patient cohort. Exp Mol Med 47:e138
Raitoharju E, Lyytikäinen LP, Levula M, Oksala N, Mennander A, Tarkka M, Klopp N, Illig T, Kähönen M, Karhunen PJ (2011) miR-21, miR-210, miR-34a, and miR-146a/b are up-regulated in human atherosclerotic plaques in the Tampere Vascular Study. Atherosclerosis 219:211–217
Fish JE, Cybulsky MI (2015) ApoE attenuates atherosclerosis via miR-146a. Circ Res 117:3–6
Burris RL, Xie CH, Thampi P, Wu X, Melnyk SB, Nagarajan S (2010) Dietary rice protein isolate attenuates atherosclerosis in apoE-deficient mice by upregulating antioxidant enzymes. Atherosclerosis 212:107–115
Gimbrone MA Jr, Garcia-Cardena G (2016) Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Circ Res 118:620–636
Xie W, Li L, Zhang M, Cheng HP, Gong D, Lv YC, Yao F, He PP, Ouyang XP, Lan G, Liu D, Zhao ZW, Tan YL, Zheng XL, Yin WD, Tang CK (2016) MicroRNA-27 prevents atherosclerosis by suppressing lipoprotein lipase-induced lipid accumulation and inflammatory response in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. PLoS One 11:e0157085
Jensen HA, Mehta JL (2016) Endothelial cell dysfunction as a novel therapeutic target in atherosclerosis. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 14:1021–1033
Feinberg MW, Moore KJ (2016) MicroRNA regulation of atherosclerosis. Circ Res 118:703–720
Gao Y, Peng J, Ren Z, He NY, Li Q, Zhao XS, Wang MM, Wen HY, Tang ZH, Jiang ZS (2016) Functional regulatory roles of microRNAs in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta 460:164–171
Farooqi AA, Tabassum S, Ahmad A (2017) MicroRNA-34a: a versatile regulator of myriads of targets in different cancers. Int J Mol Sci 18:E2089
Slabáková E, Culig Z, Remšík J, Sou Ccaronek K (2017) Alternative mechanisms of miR-34a regulation in cancer. Cell Death Dis 8:e3100
Boon RA, Iekushi K, Lechner S, Seeger T, Fischer A, Heydt S, Kaluza D, Treguer K, Carmona G, Bonauer A, Horrevoets AJ, Didier N, Girmatsion Z, Biliczki P, Ehrlich JR, Katus HA, Muller OJ, Potente M, Zeiher AM, Hermeking H, Dimmeler S (2013) MicroRNA-34a regulates cardiac ageing and function. Nature 495:107–110
Ito T, Yagi S, Yamakuchi M (2010) MicroRNA-34a regulation of endothelial senescence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 398:735–740
Zhao T, Li J, Chen AF (2010) MicroRNA-34a induces endothelial progenitor cell senescence and impedes its angiogenesis via suppressing silent information regulator 1. Am J Phys Endocrinol Metabol 299:E110
Bernardo BC, Gao XM, Tham YK, Kiriazis H, Winbanks CE, Ooi JY, Boey EJ, Obad S, Kauppinen S, Gregorevic P, Du XJ, Lin RC, McMullen JR (2014) Silencing of miR-34a attenuates cardiac dysfunction in a setting of moderate, but not severe, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. PLoS One 9:e90337
Yang Y, Cheng HW, Qiu Y, Dupee D, Noonan M, Lin YD, Fisch S, Unno K, Sereti KI, Liao R (2015) MicroRNA-34a plays a key role in cardiac repair and regeneration following myocardial infarction. Circ Res 117:450–459
Hockenbery D, Nunez G, Milliman C, Schreiber RD, Korsmeyer SJ (1990) Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature 348:334–336
Thorp E, Li Y, Bao L, Yao PM, Kuriakose G, Rong J, Fisher EA, Tabas I (2009) Brief report: increased apoptosis in advanced atherosclerotic lesions of ApoE−/− mice lacking macrophage Bcl-2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:169–172
Zhang T, Tian F, Wang J, Jing J, Zhou SS, Chen YD (2015) Atherosclerosis-associated endothelial cell apoptosis by miR-429-mediated downregulation of Bcl-2. Cell Physiol Biochem 37:1421–1430
Liu G, Li Y, Gao XG (2016) microRNA-181a is upregulated in human atherosclerosis plaques and involves in the oxidative stress-induced endothelial cell dysfunction through direct targeting Bcl-2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20:3092–3100
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Henan Provincial Department of Education research project (No. 162102310550).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, G., Sun, G., Liu, H. et al. Downregulation of miR-34a promotes endothelial cell growth and suppresses apoptosis in atherosclerosis by regulating Bcl-2. Heart Vessels 33, 1185–1194 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-018-1169-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-018-1169-6