Abstract
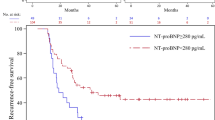
The aim of the present study was to assess whether elevated B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels, as an objective marker of heart failure, is a predictor of subsequent thromboembolic events in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) during oral anticoagulant therapy. This was a post hoc analysis of a single-center, prospective, observational study. Consecutive patients with AF (261 patients, 74 ± 9 years old, 153 paroxysmal AF) treated with warfarin were included for the analysis. BNP level at baseline examination was measured to assess the relationship of this parameter with subsequent thromboembolic events. BNP levels at the time of entry were 161 ± 188 (5–1,500, median 105) pg/ml. During an average follow-up time of 762 ± 220 (median 742) days, nine (1.8%/year) thromboembolic events occurred. Receiver operating characteristic curve showed that an optimal cut-off value for BNP to predict thromboembolic events was 218 pg/ml. There were six thromboembolic events observed among patients with a baseline BNP levels ≥200 pg/ml (n = 73) as compared to three such events in those with baseline BNP levels <200 pg/ml (n = 188). Kaplan–Meier curves for BNP level showed that elevated BNP level (≥200 pg/ml) was significantly associated with thromboembolic events (p < 0.01). Cox-proportional hazard analysis also revealed that a high BNP level (≥200 pg/ml) was a significant predictor of subsequent thromboembolic events (hazard ratio 5.32, p = 0.018). Elevated BNP levels (≥200 pg/ml) could be a useful marker of subsequent thromboembolic events in patients with AF during oral anticoagulant therapy. However, the number of patients and events in this study was small and drawing a definite conclusion was not possible with this small sample size. Therefore, further larger-scale, multicenter studies are needed to confirm these findings.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hart RG, Pearce LA, Aguilar MI (2007) Meta-analysis: antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Ann Intern Med 146:857–867
Go AS, Hylek EM, Chang Y, Phillips KA, Henault LE, Capra AM, Jensvold NG, Selby JV, Singer DE (2003) Anticoagulation therapy for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: how well do randomized trials translate into clinical practice? JAMA 290:2685–2692
Loh E, Sutton MS, Wun CC, Rouleau JL, Flaker GC, Gottlieb SS, Lamas GA, Moyé LA, Goldhaber SZ, Pfeffer MA (1997) Ventricular dysfunction and the risk of stroke after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 336:251–257
Lip GYH, Gibbs CR (1999) Does heart failure confer a hypercoagulable state? Virchow’s triad revisited. J Am Coll Cardiol 33:1424–1426
Maisel AS, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, McCord J, Hollander JE, Duc P, Omland T, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, Wu AH, Clopton P, Steg PG, Westheim A, Knudsen CW, Perez A, Kazanegra R, Herrmann HC, McCullough PA, Breathing Not Properly Multinational Study Investigators (2002) Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N Engl J Med 347:161–167
Silvet H, Young-Xu Y, Walleigh D, Ravid S (2003) Brain natriuretic peptide is elevated in outpatients with atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol 92:1124–1127
Kim BJ, Hwang SJ, Sung KC, Kim BS, Kang JH, Lee MH, Park JR (2007) Assessment of factors affecting plasma BNP levels in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation and preserved left ventricular systolic function. Int J Cardiol 118:145–150
Knudsen CW, Omland T, Clopton P, Westheim A, Wu AH, Duc P, McCord J, Nowak RM, Hollander JE, Storrow AB, Abraham WT, McCullough PA, Maisel A (2005) Impact of atrial fibrillation on the diagnostic performance of B-type natriuretic peptide concentration in dyspneic patients: an analysis from the breathing not properly multinational study. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:838–844
Shimizu H, Murakami Y, Inoue S, Ohta Y, Nakamura K, Katoh H, Sakne T, Takahashi N, Ohata S, Sugamori T, Ishibashi Y, Shimada T (2002) High plasma brain natriuretic polypeptide level as a marker of risk for thromboembolism in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Stroke 33:1005–1010
Shibazaki K, Kimura K, Okada Y, Iguchi Y, Terasawa Y, Aoki J (2009) Heart failure may be associated with the onset of ischemic stroke with atrial fibrillation: a brain natriuretic peptide study. J Neurol Sci 281:55–57
Sadanaga T, Sadanaga M, Ogawa S (2010) Evidence that D-dimer levels predict subsequent thromboembolic and cardiovascular events in patients with atrial fibrillation during oral anticoagulant therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:2225–2231
Ogawa S, Aizawa F, Atarashi H, Inoue H, Okumura K, Kamakura S, Kumagai K, Koretsune Y, Sugi K, Mitamura H, Yasaka M, Yamashita T (2008) Guidelines for pharmacotherapy of atrial fibrillation (JCS 2008) (in Japanese). Circ J 72(Suppl):1581–1638
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y, Tomita K, Nitta K, Yamagata K, Tomino Y, Yokoyama H, Hishida A (2009) Collaborators developing the Japanese equation for estimated GFR. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis 53:982–992
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D, for the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group (1999) A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Ann Intern Med 130:461–470
Doust J, Lehman R, Glasziou P (2006) The role of BNP testing in heart failure. Am Fam Physician 74:1893–1898
Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Investigators (1996) Adjusted-dose warfarin versus low-intensity, fixed-dose warfarin plus aspirin for high-risk patients with atrial fibrillation: stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation III randomised clinical trial. Lancet 348:633–638
Gage BF, Waterman AD, Shannon W, Boechler M, Rich MW, Radford MJ (2001) Validation of clinical classification schemes for predicting stroke: results from the National Registry of Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA 285:2864–2870
Stroke Risk in Atrial Fibrillation Working Group (2008) Comparison of 12 risk stratification schemes to predict stroke in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Stroke 39:1901–1910
Yamaguchi T, for Japanese Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation-Embolism Secondary Prevention Cooperative Study Group (2000) Optimal intensity of warfarin therapy for secondary prevention of stroke in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial. Stroke 31:817–821
Wu AH, Smith A, Wieczorek S, Mather JF, Duncan B, White CM, McGill C, Katten D, Heller G (2003) Biological variation for N-terminal pro- and B-type natriuretic peptides and implications for therapeutic monitoring of patients with congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol 92:628–631
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadanaga, T., Kohsaka, S., Mitamura, H. et al. Elevated B-type natriuretic peptide level as a marker of subsequent thromboembolic events in patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart Vessels 26, 530–535 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-010-0084-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-010-0084-2