Abstract
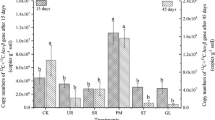
The anaerobic oxidation of ammonium (anammox) process plays a critical role in the loss of nitrogen (N) in paddy soils, yet the response of anammox to different fertilization is not well documented. In this study, three different fertilized (control, CK; soil treated with inorganic fertilizers, NPK; soil treated with inorganic fertilizer and involving the incorporation of straw, NPKS) paddy soils were selected to investigate the activity, functional gene abundance, diversity, and composition of anammox bacterial community using isotope-tracing technique, quantitative PCR assays, and Illumina sequencing. The anammox rate in the NPKS treatment was 2.4 nmol N g−1 soil h−1, significantly higher than that in CK and NPK treatments (1.7 and 1.8 nmol N g−1 soil h−1, respectively). Potential anammox contributed 6.2–7.8% to total N loss with the remainder being due to denitrification. Significant differences in the number of hydrazine synthase β-subunit (hzsB) gene were observed in three treatments with the highest value being observed in the NPK treatment. The anammox rate of per functional gene in the NPKS treatment (11.4 fmol day−1) was higher than that in CK and NPK treatments (8.3 and 7.0 fmol day−1, respectively). Three genera of anammox bacteria were identified: Candidatus Brocadia, Candidatus Anammoxoglobus, and Candidatus Scalindua, with Candidatus Brocadia being the dominant. Anammox bacteria diversity was significantly lower in the NPK than in CK and NPKS treatments as shown by Shannon, Simpson, Chao 1, and ACE indices (p < 0.05). The results showed that activity, abundance, and composition of anammox bacterial community depended on the type of fertilization.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano T, Yoshinaga I, Okada K, Yamagishi T, Ueda S, Obuchi A, Sako Y, Suwa Y (2007) Detection of anammox activity and diversity of anammox bacteria-related 16S rRNA genes in coastal marine sediment in Japan. Microbes Environ 22:232–242. https://doi.org/10.1264/Jsme2.22.232
Bai R, Xi D, He JZ, Hu HW, Fang YT, Zhang LM (2015) Activity, abundance and community structure of anammox bacteria along depth profiles in three different paddy soils. Soil Biol Biochem 91:212–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.08.040
Bastian FB, Chibucos MC, Gaudet P, Giglio M, Holliday GL, Huang H, Lewis SE, Niknejad A, Orchard S, Poux S, Skunca N, Robinson-Rechavi M (2015) The Confidence Information Ontology: a step towards a standard for asserting confidence in annotations. Database (Oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bav043
Bronick CJ, Lal R (2005) Soil structure and management: a review. Geoderma 124:3–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.03.005
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Tumbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Chen HH, Liu ST, Yang FL, Xue Y, Wang T (2009) The development of simultaneous partial nitrification, ANAMMOX and denitrification (SNAD) process in a single reactor for nitrogen removal. Bioresource Technol 100:1548–1554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.09.003
Dale OR, Tobias CR, Song BK (2009) Biogeographical distribution of diverse anaerobic ammonium oxidizing (anammox) bacteria in Cape Fear River Estuary. Environ Microbiol 11:1194–1207. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01850.x
Gu C, Zhou HF, Zhang QH, Zhao YH, Di HJ, Liang YC (2017) Effects of various fertilization regimes on abundance and activity of anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria in rice-wheat cropping systems in China. Sci Total Environ 599:1064–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.240
Harhangi HR, Le Roy M, van Alen T, Hu BL, Groen J, Kartal B, Tringe SG, Quan ZX, Jetten MSM, Op den Camp HJM (2012) Hydrazine synthase, a unique phylomarker with which to study the presence and biodiversity of anammox bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:752–758. https://doi.org/10.1128/Aem.07113-11
Hui C, Guo XX, Sun PF, Lin H, Zhang QC, Liang YC, Zhao YH (2017) Depth-specific distribution and diversity of nitrite-dependent anaerobic ammonium and methane-oxidizing bacteria in upland-cropping soil under different fertilizer treatments. Appl Soil Ecol 113:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.02.005
Jetten MSM, Wagner M, Fuerst J, van Loosdrecht M, Kuenen G, Strous M (2001) Microbiology and application of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (‘anammox’) process. Curr Opin Biotechnol 12:283–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-1669(00)00211-1
Jetten MSM, Op den Camp HJM, Kuenen JG, Strous M (2010) Description of the order Brocadiales. In: Krieg NR, Staley JT, Hedlund BP, Paster BJ, Ward N, Ludwig W, Whitman WB (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 506–603
Juretschko S, Timmermann G, Schmid M, Schleifer KH, Pommerening-Roser A, Koops HP, Wagner M (1998) Combined molecular and conventional analyses of nitrifying bacterium diversity in activated sludge: Nitrosococcus mobilis and Nitrospira-like bacteria as dominant populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3042–3051
Kartal B, Maalcke WJ, de Almeida NM, Cirpus I, Gloerich J, Geerts W, Op Den Camp HJ, Harhangi HR, Janssen-Megens EM, Francoijs KJ (2011) Molecular mechanism of anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Nature 479:127–130. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10453
Khramenkov SV, Kozlov MN, Kevbrina MV, Dorofeev AG, Kazakova EA, Grachev VA, Kuznetsov BB, Polyakov DY, Nikolaev YA (2013) A novel bacterium carrying out anaerobic ammonium oxidation in a reactor for biological treatment of the filtrate of wastewater fermented sludge. Microbiology 82:628–636. https://doi.org/10.1134/S002626171305007X
Kögel-Knabner I, Amelung W, Cao Z, Fiedler S, Frenzel P, Jahn R, Kalbitz K, Kölbl A, Schloter M (2010) Biogeochemistry of paddy soils. Geoderma 157:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.03.009
Koop-Jakobsen K, Giblin AE (2009) Anammox in tidal marsh sediments: the role of salinity, nitrogen loading, and marsh vegetation. Estuar Coast 32:238–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-008-9131-y
Long A, Heitman J, Tobias C, Philips R, Song B (2013) Co-occurring anammox, denitrification, and codenitrification in agricultural soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1128/Aem.02520-12
Magoc T, Salzberg SL (2011) FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr507
Mulder A, van de Graaf AA, Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (1995) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation discovered in a denitrifying fluidized bed reactor. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 16:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.1995.tb00281.x
Munkholm LJ, Schjonning P, Debosz K, Jensen HE, Christensen BT (2002) Aggregate strength and mechanical behaviour of a sandy loam soil under long-term fertilization treatments. Eur J Soil Sci 53:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2389.2002.00424.x
Nakamura A, Tun CC, Asakawa S, Kimura M (2003) Microbial community responsible for the decomposition of rice straw in a paddy field: estimation by phospholipid fatty acid analysis. Biol Fertil Soils 38:288–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-003-0658-6
Neef A, Amann R, Schlesner H, Schleifer KH (1998) Monitoring a widespread bacterial group: in situ detection of planctomycetes with 16S rRNA-targeted probes. Microbiology 144:3257–3266. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-144-12-3257
Nie SA, Li H, Yang XR, Zhang ZJ, Weng BS, Huang FY, Zhu GB, Zhu YG (2015) Nitrogen loss by anaerobic oxidation of ammonium in rice rhizosphere. ISME J 9:2059–2067. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.25
Nie SA, Lei XM, Zhao LX, Brookes PC, Wang F, Chen CR, Yang WH, Xing SH (2018) Fungal communities and functions response to long-term fertilization in paddy soils. Appl Soil Ecol 130:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2018.06.008
Pan FF, Yu WT, Ma Q, Zhou H, Jiang CM, Xu YG, Ren JF (2017) Influence of 15N-labeled ammonium sulfate and straw on nitrogen retention and supply in different fertility soils. Biol Fertil Soils 53:303–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-017-1177-1
Risgaard-Petersen N, Meyer RL, Schmid M, Jetten MSM, Enrich-Prast A, Rysgaard S, Revsbech NP (2004) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation in an estuarine sediment. Aquat Microb Ecol 36:293–304. https://doi.org/10.3354/Ame036293
Rysgaard S, Thastum P, Dalsgaard T, Christensen PB, Sloth NP (1999) Effects of salinity on NH4 + adsorption capacity, nitrification, and denitrification in Danish estuarine sediments. Estuaries 22:21–30. https://doi.org/10.2307/1352923
Sato Y, Ohta H, Yamagishi T, Guo Y, Nishizawa T, Rahman MH, Kuroda H, Kato T, Saito M, Yoshinaga I, Inubushi K, Suwa Y (2012) Detection of anammox activity and 16S rRNA genes in ravine paddy field soil. Microbes Environ 27:316–319. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.ME11330
Schmid M, Twachtmann U, Klein M, Strous M, Juretschko S, Jetten M, Metzger JW, Schleifer KH, Wagner M (2000) Molecular evidence for genus level diversity of bacteria capable of catalyzing anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Syst Appl Microbiol 23:93–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0723-2020(00)80050-8
Schmid M, Walsh K, Webb R, Rijpstra WIC, van de Pas-Schoonen K, Verbruggen MJ, Hill T, Moffett B, Fuerst J, Schouten S, Damste JSS, Harris J, Shaw P, Jetten M, Strous M (2003) Candidatus “Scalindua brodae”, sp. nov., Candidatus “Scalindua wagneri”, sp. nov., two new species of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 26:529–538. https://doi.org/10.1078/072320203770865837
Schmid MC, Maas B, Dapena A, de Pas-Schoonen KV, de Vossenberg JV, Kartal B, van Niftrik L, Schmidt I, Cirpus I, Kuenen JG, Wagner M, Damste JSS, Kuypers M, Revsbech NP, Mendez R, Jetten MSM, Strous M (2005) Biomarkers for in situ detection of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1677–1684. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.4.1677-1684.2005
Scholer A, Jacquiod S, Vestergaard G, Schulz S, Schloter M (2017) Analysis of soil microbial communities based on amplicon sequencing of marker genes. Biol Fertil Soils 53:485–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-017-1205-1
Shan J, Yang PP, Shang XX, Rahman MM, Yan XY (2018) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation and denitrification in a paddy soil as affected by temperature, pH, organic carbon, and substrates. Biol Fertil Soils 54:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-018-1263-z
Shen JP, Zhang LM, Guo JF, Ray JL, He JZ (2010) Impact of long-term fertilization practices on the abundance and composition of soil bacterial communities in Northeast China. Appl Soil Ecol 46:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2010.06.015
Shen LD, Liu S, Lou LP, Liu WP, Xu XY, Zheng P, Hu BL (2013) Broad distribution of diverse anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria in Chinese agricultural soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:6167–6172. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00884-13
Shen LD, Liu S, Huang Q, Lian X, He ZF, Geng S, Jin RC, He YF, Lou LP, Xu XY, Zheng P, Hu BL (2014) Evidence for the co-occurrence of nitrite-dependent anaerobic ammonium and methane oxidation processes in a flooded paddy field. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:7611–7619. https://doi.org/10.1128/Aem.02379-14
Shen LD, Wu HS, Gao ZQ, Xu XH, Chen TX, Liu S, Cheng HX (2015) Occurrence and importance of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria in vegetable soils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:5709–5718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6454-z
Shen LD, Zheng PH, Ma SJ (2016) Nitrogen loss through anaerobic ammonium oxidation in agricultural drainage ditches. Biol Fertil Soils 52:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-015-1058-4
Shen LD, Wu HS, Liu X, Li J (2017) Vertical distribution and activity of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria in a vegetable field. Geoderma 288:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.11.007
Strous M, Van Gerven E, Zheng P, Kuenen JG, Jetten MSM (1997) Ammonium removal from concentrated waste streams with the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) process in different reactor configurations. Water Res 31:1955–1962. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00055-9
Strous M, Pelletier E, Mangenot S, Rattei T, Lehner A, Taylor MW, Horn M, Daims H, Bartol-Mavel D, Wincker P, Barbe V, Fonknechten N, Vallenet D, Segurens B, Schenowitz-Truong C, Medigue C, Collingro A, Snel B, Dutilh BE, Op den Camp HJM, van der Drift C, Cirpus I, van de Pas-Schoonen KT, Harhangi HR, van Niftrik L, Schmid M, Keltjens J, van de Vossenberg J, Kartal B, Meier H, Frishman D, Huynen MA, Mewes HW, Weissenbach J, Jetten MSM, Wagner M, Le Paslier D (2006) Deciphering the evolution and metabolism of an anammox bacterium from a community genome. Nature 440:790–794. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04647
Thamdrup B, Dalsgaard T (2002) Production of N2 through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to nitrate reduction in marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1312–1318. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.68.3.1312-1318.2002
Van de Graaf AA, de Bruijn P, Robertson LA, Jetten MSM, Kuenen JG (1996) Autotrophic growth of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms in a fluidized bed reactor. Microbiology 142:2187–2196. https://doi.org/10.1099/13500872-142-8-2187
Vestergaard G, Schulz S, Scholer A, Schloter M (2017) Making big data smart-how to use metagenomics to understand soil quality. Biol Fertil Soils 53:479–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-017-1191-3
Wang J, Gu JD (2013) Dominance of Candidatus Scalindua species in anammox community revealed in soils with different duration of rice paddy cultivation in Northeast China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:1785–1798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4036-x
Wang YF, Gu JD (2014) Effects of allylthiourea, salinity, and pH on ammonia/ammonium-oxidizing prokaryotes in mangrove sediment incubated in laboratory microcosms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:3257–3274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5399-3
Wang SY, Zhu GB, Peng YZ, Jetten MSM, Yin CQ (2012a) Anammox bacterial abundance, activity, and contribution in riparian sediments of the Pearl River estuary. Environ Sci Technol 46:8834–8842. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3017446
Wang Y, Zhu GB, Harhangi HR, Zhu B, Jetten MSM, Yin C, Op den Camp HJM (2012b) Co-occurrence and distribution of nitrite-dependent anaerobic ammonium and methane-oxidizing bacteria in a paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 336:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02654.x
Yamamoto T, Takaki K, Koyama T, Furukawa K (2008) Long-term stability of partial nitrification of swine wastewater digester liquor and its subsequent treatment by anammox. Bioresour Technol 99:6419–6425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.11.052
Yang XR, Li H, Nie SA, Su JQ, Weng BS, Zhu GB, Yao HY, Gilbert JA, Zhu YG (2015) Potential contribution of anammox to nitrogen loss from paddy soils in Southern China. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:938–947. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02664-14
Yuan HZ, Ge TD, Zhou P, Liu SL, Roberts P, Zhu HH, Zou ZY, Tong CL, Wu JS (2013) Soil microbial biomass and bacterial and fungal community structures responses to long-term fertilization in paddy soils. J Soils Sediments 13:877–886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0664-8
Zhu Z (2008) Research on soil nitrogen in China. Acta Pedol Sin 45:778–783. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2008.05.003
Zhu GB, Wang SY, Wang Y, Wang CX, Risgaard-Petersen N, Jetten MSM, Yin CQ (2011) Anaerobic ammonia oxidation in a fertilized paddy soil. ISME J 5:1905–1912. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.63
Zhu GB, Wang SY, Zhou LL, Wang Y, Zhao SY, Xia C, Wang WD, Zhou R, Wang CX, Jetten MSM, Hefting MM, Yin CQ, Qu JH (2015a) Ubiquitous anaerobic ammonium oxidation in inland waters of China: an overlooked nitrous oxide mitigation process. Sci Rep 5:17306. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17306
Zhu GB, Xia C, Wang SY, Zhou LL, Liu L, Zhao SY (2015b) Occurrence, activity and contribution of anammox in some freshwater extreme environments. Environ Microbiol Rep 7:961–969. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12341
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (4170010194) and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, China (2017J0101612).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1848 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, S., Lei, X., Zhao, L. et al. Response of activity, abundance, and composition of anammox bacterial community to different fertilization in a paddy soil. Biol Fertil Soils 54, 977–984 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-018-1320-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-018-1320-7