Abstract
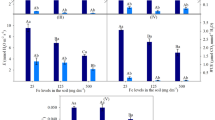
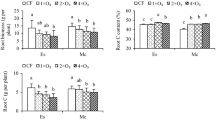
Tropospheric O3 (ozone) stress can negatively affect forest productivity and crop yields. Yet, relatively little attention has been paid to the effects of O3 stress on belowground system. Here, a pot experiment was conducted in open top chambers to monitor the response of physico-chemical properties, main microbial groups, and potential enzyme activities of a soil cropped to soybean (Glycine max; a highly sensitive species to O3) and exposed to background O3 concentration (45 ± 5 ppb, control) and O3 stress (80 ± 10 ppb, O3+ and 110 ± 10 ppb, O3++) with sampling at branching, flowering, and podding stages. The growth of soybean was significantly inhibited by O3 stress, which showed significant effects on soil microbial biomass C and pH during the whole growth of soybean at the highest concentration. The O3++ stress significantly decreased soil pH at flowering stage, and increased soil pH at podding stage; the O3+ stress and growth stage × O3+ stress showed significant influences on the potential activities of acid phosphomonoesterase, invertase, and amylase. The O3 stress significantly reduced the abundances of total PLFAs (phospholipid fatty acid), bacterial PLFAs, and AMF (arbuscular mycorrhizal) PLFAs at branching and podding stages. Our results suggest that the main soil microbial groups might be indirectly affected by the O3 stress through the alteration of soil physico-chemical properties with changes in the potential enzyme activities of soil.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Andersen CP (2003) Source-sink balance and carbon allocation below ground in plants exposed to ozone. New Phytol 157:213–228
Andersen CP, Rygiewicz PT (1995) Allocation of carbon in mycorrhizal Pinus ponderosa seedlings exposed to ozone. New Phytol 131:471–480
Baldrian P (2009) Microbial enzyme-catalyzed processes in soils and their analysis. Plant Soil Environ 55:370–378
Baldrian P, Větrovský T (2012) Scaling down the analysis of environmental processes: monitoring enzyme activity in natural substrates on a millimeter resolution scale. Appl Environ Microb 78:3473–3475
Bao X, Li Q, Hua J, Zhao T, Liang W (2014) Interactive effects of elevated ozone and UV-B radiation on soil nematode diversity. Ecotoxicology 23:11–20
Bossio DA, Scow KM (1998) Impacts of carbon and flooding on soil microbial communities: phospholipid fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization patterns. Microb Ecol 35:265–278
Bossio DA, Fleck JA, Scow KM, Fujii R (2006) Alteration of soil microbial communities and water quality in restored wetlands. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1223–1233
Burkey KO, Carter TE Jr (2009) Foliar resistance to ozone injury in the genetic base of U.S. and Canadian soybean and prediction of resistance in descendent cultivars using coefficient of parentage. Field Crop Res 111:207–217
Burns RG, De Forest JL, Marxsen J, Sinsabaugh RL, Stromberger ME, Wallenstein MD, Weintraub MN, Zoppini A (2013) Soil enzymes in a changing environment: current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol Biochem 58:216–234
Caldwell BA (2005) Enzyme activities as a component of soil biodiversity: a review. Pedobiologia 49:637–644
Carter MR, Gregorich EG (2007) Soil sampling and methods of analysis, 2nd ed. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton
Cesco S, Tonon G, Tomasi N, Pinton R, Terzano R, Neumann G, Weisskopf L, Renella G, Landi L, Nannipieri P (2012) Plant-borne flavonoids released into the rhizosphere: impact on soil bio-activities related to plant nutrition: a review. Biol Fertil Soils 48:123–149
Chang EH, Chiu CY (2015) Changes in soil microbial community structure and activity in a cedar plantation invaded by moso bamboo. Appl Soil Ecol 91:1–7
Chen Z, Wang XK, Feng ZZ, Xiao Q, Duan X (2009) Impact of elevated O3 on soil microbial community function under wheat crop. Water Air Soil Pollut 198:189–198
Chen Z, Wang X, Yao F, Zheng F, Feng Z (2010) Elevated ozone changed soil microbial community in a rice paddy. Soil Sci Soc Am J 74:829–837
Chen S, Zhang Y, Chen H, Hu Z (2012) Effects of elevated O3 on soil respiration in a winter wheat–soybean rotation cropland. Soil Res 50:500–506
Chen FL, Zheng H, Zhang K, Ouyang ZY, Li HL, Wu B, Shi Q (2013) Soil microbial community structure and function responses to successive planting of Eucalyptus. J Environ Sci 25:2102–2111
Cheng L, Booker FL, Burkey KO, Tu C, Shew HD, Rufty TW, Fiscus EL, Deforest JL, Hu S (2011) Soil microbial responses to elevated CO2 and O3 in a nitrogen-aggrading agroecosystem. PLoS One 6:e21377
Cheng Y, Wang J, Mary B, Zhang JB, Cai ZC, Chang SX (2013) Soil pH has contrasting effects on gross and net nitrogen mineralizations in adjacent forest and grassland soils in central Alberta. Soil Biol Biochem 57:848–857
Cole MA (1977) Lead inhibition of enzyme synthesis in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 3:262–268
Cooley DR, Manning WJ (1987) The impact of ozone on assimilate partitioning in plants: a review. Environ Pollut 47:95–113
Dermody O, Long SP, DeLucia EH (2006) How does elevated CO2 or ozone affect the leaf–area index of soybean when applied independently? New Phytol 169:145–155
Feng Z, Kobayashi K (2009) Assessing the impacts of current and future concentrations of surface ozone on crop yield with meta-analysis. Atmos Environ 43:1510–1519
Feng ZZ, Hu EZ, Wang XK, Jiang LJ, Liu XJ (2015) Ground-level O3 pollution and its impacts on food crops in China: a review. Environ Pollut 199:42–48
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:626–631
Fiscus EL, Booker FL, Burkey KO (2005) Crop responses to ozone: uptake, modes of action, carbon assimilation and partitioning. Plant Cell Environ 28:997–1011
Frostegård A, Bååth E (1996) The use of phospholipid fatty acid analysis to estimate bacterial and fungal biomass in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 22:59–65
He F, Wang H, Chen Q, Yang B, Gao Y, Wang L (2015) Short-term response of soil enzyme activity and soil respiration to repeated carbon nanotubes exposure. Soil Sediment Contam 24:250–261
Hofmockel KS, Zak DR, Moran KK, Jastrow JD (2011) Changes in forest soil organic matter pools after a decade of elevated CO2 and O3. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1518–1527
Hu E, Yuan Z, Zhang H, Zhang W, Wang X, Jones SB, Wang N (2018) Impact of elevated tropospheric ozone on soil C, N and microbial dynamics of winter wheat. Agric Ecosyst Environ 253:166–176
Islam KR, Mulchi CL, Ali AA (2000) Interactions of tropospheric CO2 and O3 enrichments and moisture variations on microbial biomass and respiration in soil. Glob Chang Biol 6:255–265
Johnson JL, Temple KL (1964) Some variables affecting the measurement of “catalase activity” in soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 28:207–209
Kanerva T, Palojärvi A, Rämö K, Manninen S (2008) Changes in soil microbial community structure under elevated tropospheric O3 and CO2. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2502–2510
Karnosky DF, Skelly JM, Percy KE, Chappelka AH (2007) Perspectives regarding 50 years of research on effects of tropospheric ozone air pollution on US forests. Environ Pollut 147:489–506
Kim DO, Jeong SW, Lee CY (2003) Antioxidant capacity of phenolic phytochemicals from various cultivars of plums. Food Chem 81:321–326
Kourtev PS, Ehrenfeld JG, Haggblom AM (2002) Exotic plant species alter the microbial community structure and function in the soil. Ecology 83:3152–3166
Kumari S, Agrawal M, Tiwari S (2013) Impact of elevated CO2 and elevated O3 on Beta vulgaris L: pigments, metabolites, antioxidants, growth and yield. Environ Pollut 174:279–288
Larson JL, Zak DR, Sinsabaugh RL (2002) Extracellular enzyme activity beneath temperate trees growing under elevated carbon dioxide and ozone. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:1848–1856
Lepš J, Šmilauer P (2003) Multivariate analysis of ecological data using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press
Li X, Deng Y, Li Q, Lu C, Wang J, Zhang H, Zhu J, Zhou J, He Z (2013) Shifts of functional gene representation in wheat rhizosphere microbial communities under elevated ozone. ISME J 7:660–671
Li Q, Yang Y, Bao X, Liu F, Liang W, Zhu J, Bezemer T, van der Putten W (2015) Legacy effects of elevated ozone on soil biota and plant growth. Soil Biol Biochem 91:50–57
Liu FL, Andersen MN, Jensen CR (2003) Loss of pod set caused by drought stress is associated with water status and ABA content of reproductive structures in soybean. Funct Plant Biol 30:271–280
Liu H, Liu S, Xue B, Lv Z, Meng Z, Yang X, Xue T, Yu Q, He K (2018) Ground-level ozone pollution and its health impacts in China. Atmos Environ 173:223–230
Lu C, Fang R, Li Q, Wang Y, Zhu J, Ma J, Chen X, Shi Y (2015) Elevated O3 and wheat cultivars influence the relative contribution of plant and microbe-derived carbohydrates to soil organic matter. Appl Soil Ecol 86:131–136
Madan R, Pankhurst C, Hawke B, Smith S (2002) Use of fatty acids for identification of AM fungi and estimation of the biomass of AM spores in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 34:125–128
Manninen S, Aaltonen H, Kanerva T, Rämö K, Palojärvi A (2010) Plant and soil microbial biomasses in Agrostis capillaris and Lathyrus pratensis monocultures exposed to elevated O3 and CO2 for three growing seasons. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1967–1975
Mao B, Yin H, Wang Y, Zhao TH, Tian RR, Wang W, Ye JS (2017a) Combined effects of O3 and UV radiation on secondary metabolites and endogenous hormones of soybean leaves. PLoS One 12:e0183147
Mao B, Wang Y, Zhao TH, Tian RR, Wang W, Ye JS (2017b) Combined effects of elevated O3 concentrations and enhanced uv-b radiation of the biometric and biochemical properties of soybean roots. Front Plant Sci 8:1568
Matyssek R, Sandermann H, Wieser G, Booker F, Cieslik S, Musselman R, Ernst D (2008) The challenge of making ozone risk assessment for forest trees more mechanistic. Environ Pollut 156:567–582
McCrady JK, Andersen CP (2000) The effect of ozone on below-ground carbon allocation in wheat. Environ Pollut 107:465–472
Meehl GA, Stocker TF, Collins WD, Friedlingstein P, Gaye AT, Gregory JM, Kitoh A, Knutti R, Murphy JM, Noda A, Raper SCB, Watterson IG, Weaver AJ, Zhao ZC (2007) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA
Mills G, Buse A, Gimeno B, Bermejo V, Holland M, Emberson L, Pleijel H (2006) A synthesis of AOT40-based response functions and critical levels of ozone for agricultural and horticultural crops. Atmos Environ 41:2630–2643
Moore-Kucera J, Dick RP (2008) PLFA profiling of microbial community structure and season shifts in soils of a Douglas-fir chronosequence. Microb Ecol 55:500–511
Morgan PB, Mies TA, Bollero GA, Nelson RL, Long SP (2006) Season-long elevation of ozone concentration to projected 2050 levels under fully open-air conditions substantially decreases the growth and production of soybean. New Phytol 170:333–343
Nannipieri P, Giagnoni L, Landi L, Renella G (2011) Role of phosphatase enzymes in soil. Phosphorus in action. Springer, Berlin, pp 215–243
Nannipieri P, Trasar-Cepeda C, Dick RP (2018) Soil enzyme activity: a brief history and biochemistry as a basis for appropriate interpretations and meta-analysis. Biol Fertil Soils 54:11–19
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1982) Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of American, Madison
Olsson PA, Bååth E, Jakobsen I, Söderström B (1995) The use of phospholipid and neutral lipid fatty acids to estimate biomass of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in soil. Mycol Res 99:623–629
Pietri JCA, Brookes PC (2009) Substrate inputs and pH as factors controlling microbial biomass, activity and community structure in an arable soil. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1396–1405
Pritsch K, Ernst D, Fleischmann F, Gayler S, Grams TEE, Göttlein A, Heller W, Koch N, Lang H, Matyssek R, Munch JC, Olbrich M, Scherb H, Stich S, Winkler JB, Schloter M (2008) Plant and soil system responses to ozone after 3 years in a lysimeter study with juvenile beech (Fagus sylvatica, L.). Water Air Soil Pollut 8:139–154
Reddy GB, Reinert RA, Eason G (1995) Loblolly pine needle nutrient and soil enzyme activity as influenced by ozone and acid rain chemistry. Soil Biol Biochem 27:1059–1064
Renaud JP, Allard GB, Mauffette Y (1997) Effects of ozone on yield, growth, and root starch concentration of two alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars. Environ Pollut 95:273–281
Scagel CF, Andersen CP (1997) Seasonal changes in root and soil respiration of ozone-exposed ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa) grown in different substrates. New Phytol 136:627–643
Schloter M, Winkler JB, Aneja M, Koch N, Fleischmann F, Pritsch K, Heller W, Stich S, Grans TEE, Göttlein A, Matyssek R, Munch JC (2005) Short term effects of ozone on the plant–rhizosphere–bulk soil system of young beech trees. Plant Biol 7:728–736
Schöler A, Jacquiod S, Vestergaard G, Schulz S, Schloter M (2017) Analysis of soil microbial communities based on amplicon sequencing of marker genes. Biol Fertil Soils 53:485–489
Tabatabai MA (1982) Soil enzymes in methods of soil analysis. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science of America, Madison, pp 903–947
Tang J, Wang R, Niu X, Zhou Q (2010) Enhancement of soil petroleum remediation by using a combination of ryegrass (Lolium perenne) and different microorganisms. Soil Tillage Res 110:87–93
Van der Heijden MGA, Bardgett RD, van Straalen NM (2008) The unseen majority: soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 11:296–310
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Vestal JR, White DC (1989) Lipid analysis in microbial ecology-quantitative approaches to the study of microbial communities. Bioscience 39:535–541
Vestergaard G, Schulz S, Schöler A, Schloter M (2017) Making big data smart—how to use metagenomics to understand soil quality. Biol Fertil Soils 53:479–484
Wang JJ, Li XY, Zhu AN, Zhang XK, Zhang HW, Liang WJ (2012) Effects of tillage and residue management on soil microbial communities in North China. Plant Soil Environ 58:28–33
Wardle DA (1992) A comparative assessment of factors which influence microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen levels in soil. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 67:321–358
White D, Stair J, Ringelberg D (1996) Quantitative comparisons of in situ microbial biodiversity by signature biomarker analysis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 17:185–196
Wilson GW, Rice CW, Rillig MC, Springer A, Hartnett DC (2009) Soil aggregation and carbon sequestration are tightly correlated with the abundance of mycorrhizal arbuscular fungi: results from long-term field experiments. Ecol Lett 12:452–461
Wu H, Li Q, Lu C, Zhang L, Zhu J, Dijkstra FA, Yu Q (2016) Elevated ozone effects on soil nitrogen cycling differ among wheat cultivars. Appl Soil Ecol 108:187–194
Xiang D, Verbruggen E, Hu YJ, Veresoglou SD, Rillig MC, Zhou W, Zhou W, Xu T, Li H, Hao Z, Chen Y (2014) Land use influences arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in the farming-pastoral ecotone of northern China. New Phytol 204:968–978
Zak DR, Kubiske ME, Pregitzer KS, Burton AJ (2012) Atmospheric CO2 and O3 alter competition for soil nitrogen in developing forests. Glob Chang Biol 18:1480–1488
Zelles L (1997) Phospholipid fatty acid profiles in selected members of soil microbial communities. Chemosphere 35:275–294
Zelles L (1999) Fatty acid patterns of phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides in the characterisation of microbial communities in soil: a review. Biol Fertil Soils 29:111–129
Zhang W, He H, Li Q, Lu C, Zhang X, Zhu J (2014) Soil microbial residue dynamics after 3-year elevated O3 exposure are plant species-specific. Plant Soil 376:139–149
Zhao Q, Classen AT, Wang WW, Zhao XR, Mao B, Zeng DH (2017) Asymmetric effects of litter removal and litter addition on the structure and function of soil microbial communities in a managed pine forest. Plant Soil 414:81–93
Zheng H, Ouyang ZY, Wang XK, Fang ZG, Zhao TQ, Miao H (2005) Effects of regenerating forest cover on soil microbial communities: a case study in hilly red soil region, Southern China. Forest Ecol Manag 217:244–254
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30970448; 31570404) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016M601342). We thank editor, three anonymous referees, Gui-Gang Lin PhD and De-Hui Zeng professor for their valuable comments and suggestions that greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1210 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, B., Wang, Y., Zhao, TH. et al. Effects of O3 stress on physico-chemical and biochemical properties and composition of main microbial groups of a soil cropped to soybean. Biol Fertil Soils 54, 965–976 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-018-1318-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-018-1318-1