Abstract
Purpose
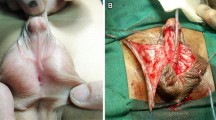
Severe hypospadias repair still presents a great challenge. We evaluated a novel approach of using a specially shaped buccal mucosa graft for simultaneous ventral tunica grafting and new urethral plate creation, in combination with longitudinal dorsal island skin flap, as a one-stage repair of severe hypospadias.
Methods
Between July 2014 and September 2017, 26 patients (aged from 12 to 22 months) underwent scrotal hypospadias repair. Short and non-elastic urethral plate is divided. Buccal mucosa graft is harvested from the inner cheek, and designed in a special “watch” shape, with the spherical part in the middle and two rectangular parts on both sides. Tunica albuginea is opened ventrally for penile straightening and grafted to the spherical part of the “watch-shaped” buccal mucosa with 6–8 “U-shape” stitches. The rectangular parts are fixed to the tip of the glans distally and native urethral meatus proximally. Longitudinal dorsal skin flap is harvested, button-holed ventrally and joined with buccal graft. Penile skin reconstruction is performed using available penile skin.
Results
The mean follow-up was 22 months (range from 9 to 46 months). Satisfactory results were achieved in 22 patients. Two urethral fistulas were successfully repaired by minor surgery after 3 months, while one meatal stenosis and one urethral diverticulum were successfully treated by temporary urethral dilation. There were no cases of residual curvature.
Conclusion
Specially shaped buccal mucosa graft for simultaneous curvature correction and urethroplasty could be a good choice for single-stage repair of scrotal hypospadias with severe curvature.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snodgrass W (1994) Tubularized, incised plate urethroplasty for distal hypospadias. J Urol 151:464–465
Snodgrass WT (2005) Snodgrass technique for hypospadias repair. BJU Int 95:683–693
Djordjevic ML, Perovic SV, Slavkovic Z, Djakovic N (2006) Longitudinal dorsal dartos flap for prevention of fistula after a Snodgrass hypospadias procedure. Eur Urol 50:53–57
Tijani KH, Idiodi-Thomas HO, Elebute OA, Alakaloko FM, Ojewola RW, Ademuyiwa AO (2017) Two-stage flap repair of severe hypospadias: usefulness of the tubularized incised plate urethroplasty. J Pediatr Urol 13:483.e1–483.e5
Bracka A (1995) Hypospadias repair: the two stage alternative. Br J Urol 76:31–41
Djordjevic ML, Majstorovic M, Stanojevic D, Bizic M, Kojovic V, Vukadinovic V, Korac G, Krstic Z, Perovic SV (2008) Combined buccal mucosa graft and dorsal penile skin flap for repair of severe hypospadias. Urology 71:821–825
Shaeer O (2011) Trans-corporal incision of Peyronie’s plaques. J Sex Med 8:589–593
Perovic S, Djordjevic M (2001) Penile disassembly technique to surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Br J Urol 88:731–739
Markiewicz MR, Margarone JE III, Barbagli G, Scaannapieco FA (2007) Oral mucosa harvest: an overview of anatomic and biologic considerations. EAU-EBU Update Ser 5:179–187
Snodgrass W, Bush N (2016) TIP hypospadias repair: a pediatric urology indicator operation. J Pediatr Urol 12:11–18
Gong EM, Cheng EY (2017) Current challenges with proximal hypospadias: we have a long way to go. J Pediatr Urol 13:457–467
Dubey D, Kumar A, Mandhani A, Srivastava A, Kapoor R, Bhandari M (2005) Buccal mucosa urethroplasty: a versatile technique for all urethral segments. BJU Int 95:625–629
Hayashi Y, Kojima Y (2008) Current concepts in hypospadias surgery. Int J Urol 15:651–654
Castellan M, Gosalbez R, Devendra J, Bar-Yosef Y, Labbie A (2011) Ventral corporal body grafting for correcting severe penile curvature associated with single or two-stage hypospadias repair. J Pediatr Urol 7:289–293
Hayashi Y, Kojima Y, Mizuno K, Nakane A, Kato T, Kurokawa S, Kamisawa H, Maruyama T, Kohri K (2010) Demonstration of postoperative effectiveness in ventral lengthening using a tunica vaginalis flap for severe penile curvature with hypospadias. Urology 76:101–106
Dessanti A, Iannuccelli M, Ginesu G, Feo C (2003) Reconstruction of hypospadias and epispadias with buccal mucosa free graft as primary surgery: more than 10 years of experience. J Urol 168:1600–1602
Hensle TW, Kearney MC, Bingham JB (2002) Buccal mucosa grafts for hypospadias surgery: long-term results. J Urol 168:1734–1736
Cormio L, Zucchi A, Lorusso F, Selvaggio O, Fioretti F, Porena M, Carrieri G (2009) Surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease by plaque incision and grafting with buccal mucosa. Eur Urol 55:1469–1475
Hatzichristodoulou G, Osmonov D, Kübler H, Hellstrom WJG, Yafi FA (2017) Contemporary review of grafting techniques for the surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Sex Med Rev 5:544–552
Perovic S, Vukadinovic V (1992) Penoscrotal transposition with hypospadias: 1-stage repair. J Urol 148:1510–1513
Acknowledgements
This paper is supported by Ministry of Science and Technical Development, Republic of Serbia, Project no. 175048.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DML: project development, data collection, and manuscript writing. BM: data collection and analysis. SB: data collection and manuscript editing. BM: data analysis. KV: manuscript editing. KG: project development.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of human rights
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Formal consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants (parents or legal guardians) included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djordjevic, M.L., Bizic, M., Stojanovic, B. et al. Buccal mucosa graft for simultaneous correction of severe chordee and urethroplasty as a one-stage repair of scrotal hypospadias (watch technique). World J Urol 37, 613–618 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2517-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2517-y