Abstract
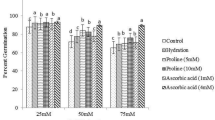
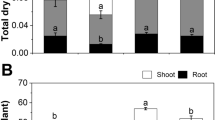
In this study, the effects of seed soaking in proline (12 mM) or Moringa oleifera leaf extract (MLE; 6%) on the biomass, yield, and the antioxidant systems were investigated using wheat plants grown under NaCl stress (120 mM). Shoot fresh and dry weights, yield, K+ ion accumulation, K+/Na+ ration, soluble protein, photosynthetic pigment (that is, carotenoids and chlorophylls) contents, and efficiency (that is, Fv/Fm and performance index; PI) of wheat were decreased at salt-stress treatment. Salinity increased the activity of superoxide dismutase, ascorbate and glutathione peroxidases, and the content of malondialdehyde, H2O2, and Na+ and Cl− contents in leaf compared to control. Additionally, increased magnitudes of proline, soluble sugar, soluble protein, ascorbate, glutathione contents were more pronounced under 120 mM NaCl than those under control. Proline or MLE ameliorated the inhibitory effects of NaCl stress to varying degrees, ensuring significant amelioration on biomass, yield, osmoprotectants and antioxidant systems. In comparison to proline, seed soaking with MLE was more effective in improving wheat growth and yield by mitigating the inhibitory effects of salinity stress. The presented results indicate that seed soaking with 6% MLE can contribute to protecting wheat seedlings/plants against NaCl stress by mitigating the oxidative stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abogadallah GM (2010) Antioxidative defense under salt stress. Plant Signal Behav 5:369–374
Agami RA (2004) Applications of ascorbic acid or proline increase resistance to salt stress in barley seedlings. Biol Plant 58:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-014-0392-y
Ali Q, Daud MK, Haider MZ, Ali S, Rizwan M, Aslam N, Noman A, Iqbal N, Shahzad F, Deeba F, Ali I, Zhu SJ (2017) Seed priming by sodium nitroprusside improves salt tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by enhancing physiological and biochemical parameters. Plant Physiol Biochem 119:50–58
Amini F, Ehsanpour AA (2005) Soluble proteins, proline, carbohydrates and Na+/K+ changes in two tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) cultivars under in vitro salt stress. Am J Biochem Biotechnol 1(4):212–216
Anjum SA, Farooq M, Xie X, Liu XJ, Ijaz MF (2012) Antioxidant defense system and proline accumulation enables hot pepper to perform better under drought. Sci Hortic 140:66–73
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24(1):1–5
Assaha DVM, Ueda A, Saneoka H, Al-Yahyai R (2017) The role of Na+ and K+ transporters in salt stress adaptation in glycophytes. Front Physiol 8:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00509
Azevedo-Neto AD, Prisco JT, Enéas-Filho J, Lacerda CF, Silva JV, Costa PHA, Gomes-Filho E (2004) Effects of salt stress on plant growth, stomatal response and solute accumulation of different maize genotypes. Braz J Plant Physiol 16:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-04202004000100005
Bano S, Ashraf M, Akram NA (2014) Salt stress regulates enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidative defense system in the edible part of carrot (Daucus carota L.). J Plant Interact 9(1):324–329
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39(1):205–207
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44(1):276–287
Ben Ahmed C, Ben Rouina B, Sensoy S, Boukhriss M, Ben Abdullah F (2010) Exogenous proline effects on photosynthetic performance and antioxidant defense system of young olive tree. J Agric Food Chem 58:4216–4222. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9041479
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Chen H, Jiang JG (2010) Osmotic adjustment and plant adaptation to environmental changes related to drought and salinity. Environ Rev 18:309–319. https://doi.org/10.1139/A10-014
Chen Z, Pottosin II, Cuin TA et al (2007) Root plasma membrane transporters controlling K+/Na+ homeostasis in salt-stressed barley. Plant Physiol 145:1714–1725. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.110262
Ching LS, Mohamed S (2001) Alpha-tocopherol content in 62 edible tropical plants. J Agric Food Chem 49(6):3101–3105
Choudhury FK, Rivero RM, Blumwald E, Mittler R (2017) Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J 90(5):856–867
Clark AJ, Landolt W, Bucher JB, Strasser RJ (2000) Beech (Fagus sylvatica) response to ozone exposure assessed with a chlorophyll a fluorescence performance index. Environ Pollut 109(3):501–507
de Freitas PAF, de Souza Miranda R, Marques EC, Prisco JT, Gomes-Filho E (2018) Salt tolerance induced by exogenous proline in maize is related to low oxidative damage and favorable ionic homeostasis. J Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9787-x
Desoky EM, Merwad AM, Rady MM (2018) Natural biostimulants improve saline soil characteristics and salt stressed-sorghum performance. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 49(8):967–983
Dubey RS, Rani M (1989) Influence of NaCl salinity on growth and metabolic statusof protein and amino acids in rice seedlings. J Agron Crop Sci 162:97–106
Elkoca E (2007) Priming: pre-treatment before sowing. Ataturk Univ Agric Fac J 38:113–120
Elzaawely AA, Ahmed ME, Maswada HF, Xuan TD (2017) Enhancing growth, yield, biochemical, and hormonal contents of snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) sprayed with moringa leaf extract. Arch Agron Soil Sci 63(5):687–699
Farhangi-Abriz S, Torabian S (2017) Antioxidant enzyme and osmotic adjustment changes in bean seedlings as affected by biochar under salt stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 137:64–70
Farooq M, Basra SMA, Rehman H, Saleem BA (2008) Seed priming enhances the performance of late sown wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by improving chilling tolerance. J Agron Crop Sci 194:55–60
Foidl N, Makkar HPS, Becker K (2001) The potential of Moringa oleifera for agricultural and industrial uses. In: Proceedings of the International Workshop “What development potential for Moringa products?” pp 47–67
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2011) Ascorbate and glutathione: the heart of the redox hub. Plant Physiol 155:2–18. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.167569
Gaines TP, Parker MB, Gascho GJ (1984) Automated determination of chlorides in soil and plant tissue by sodium nitrate extraction 1. Agron J 76(3):371–374
Griffith OW (1980) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal Biochem 106(1):207–212
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Anee TI, Fujita M (2017) Exogenous silicon attenuates cadmium-induced oxidative stress in Brassica napus L. by modulating AsA-GSH pathway and glyoxalase system. Front Plant Sci 8:1061
Havir EA, McHale NA (1987) Biochemical and developmental characterization of multiple forms of catalase in tobacco leaves. Plant Physiol 84:450–455. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.84.2.450
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125(1):189–198
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water culture method for growing plants without soil. University of California, College of Agriculture, Agricultural Experiment Station, Baltimore
Howladar SM (2014) A novel Moringa oleifera leaf extract can mitigate the stress effects of salinity and cadmium in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 100:69–75
Huang Y, Bie Z, Liu Z, Zhen A, Wang W (2009) Protective role of proline against salt stress is partially related to the improvement of water status and peroxidase enzyme activity in cucumber. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 55:698–704. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2009.00412.x
Irigoyen JJ, Einerich DW, Sánchez-Díaz M (1992) Water stress induced changes in concentrations of proline and total soluble sugars in nodulated alfalfa (Medicago sativa) plants. Physiol Plant 84(1):55–60
Kampfenkel K, Van Montagu M (1995) Extraction and determination of ascorbate and dehydroascorbate from plant tissue. Anal Biochem 225:165–167
Konings EJ, Roomans HH, Beljaars PR (1996) Liquid chromatographic determination of tocopherols and tocotrienols in margarine, infant foods, and vegetables. J AOAC Int 79(4):902–906
Kosovà K, Pràšil IT, Vitàmvàs P (2013) Protein contribution to plant salinity response and tolerance acquisition. Int J Mol Sci 14:6757–6789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14046757
Kusvuran S, Dasgan HY, Abak K (2013) Citrulline is an important biochemical indicator in tolerance to saline and drought stresses in melon. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/253414
Lachica M, Aguilar A, Yanez J (1973) Analisis foliar: Métodos Utilizados enla estaciln experimental del zaidin. Anales Edafologia Agrobiologia 32:1033–1047
Lavrich RJ, Hays MD (2007) Validation studies of thermal extraction-GC/MS applied to source emissions aerosols. 1. Semivolatile analyte-nonvolatile matrix interactions. Anal Chem 79:3635–3645
Lee SC, Kim JH, Jeong SM, Kim DR, Ha JU, Nam KC (2003) Effect of far-infrared radiation on the antioxidant activity of rice hulls. J Agric Food Chem 51:4400–4403
Makkar HPS, Francis G, Becker K (2007) Bioactivity of phytochemicals in some lesser-known plants and their effects and potential applications in livestock and aquaculture production systems. Animal 1(9):1371–1391
Martinez V, Nieves-Cordones M, Lopez-Delacalle M, Rodenas R, Mestre TC, Garcia-Sanchez F, Rubio F, Nortes PA, Mittler R, Rivero RM (2018) Tolerance to stress combination in tomato plants: new insights in the protective role of melatonin. Molecules 23:535
Maxwell K, Johnson GN (2000) Chlorophyll fluorescence—a practical guide. J Exp Bot 51(345):659–668
Miller G, Honig A, Stein H (2009) Unraveling ∆1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate-proline cycle in plants by uncoupled expression of proline oxidation enzymes. J Biol Chem 284:26482–26492
Morsy MR, Jouve L, Hausman JF, Hoffmann L, Stewart JM (2007) Alteration of oxidative and carbohydrate metabolism under abiotic stress in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes contrasting in chilling tolerance. J Plant Physiol 164:157–167
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22(5):867–880
Noctor G, Reichheld JP, Foyer CH (2017) ROS-related redox regulation and signaling in plants. Semin Cell Dev Biol https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.07.013
Nouman W, Siddiqui MT, Basra SMA, Afzal I, Rehman HU (2012) Enhancement of emergence potential and stand establishment of Moringa oleifera Lam. by seed priming. Turk J Agric For 36(2):227–235
Nounjan N, Theerakulpisut P (2012) Effects of exogenous proline and trehalose on physiological responses in rice seedlings during salt-stress and after recovery. Plant Soil Environ 2012:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.01.004
Nounjan N, Nghia PT, Theerakulpisut P (2012) Exogenous proline and trehalose promote recovery of rice seedlings from salt-stress and differentially modulate antioxidant enzymes and expression of related genes. J Plant Physiol 169:596–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.01.004
Rady MM, Mohamed GF (2015) Modulation of salt stress effects on the growth, physio-chemical attributes and yields of Phaseolus vulgaris L. plants by the combined application of salicylic acid and Moringa oleifera leaf extract. Sci Hortic 193:105–113
Rady MM, Varma B, Howladar SM (2013) Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seedlings overcome NaCl stress as a result of presoaking in Moringa oleifera leaf extract. Sci Hortic 162:63–70
Rady MM, Mohamed GF, Abdalla AM, Ahmed YH (2015) Integrated application of salicylic acid and Moringa oleifera leaf extract alleviates the salt-induced adverse effects in common bean plants. Int J Agric Technol 11(7):1595–1614
Ranjbarfordoei A, Samson R, Van Damme P (2006) Chlorophyll fluorescence performance of sweet almond [Prunus dulcis (Miller) D. Webb] in response to salinity stress induced by NaCl. Photosynthetica 44(4):513–522
Rehman H, Nawaz Q, Basra SMA, Afzal I, Yasmeen A (2014) Seed priming influence on early crop growth, phenological development and yield performance of linola (Linum usitatissimum L.). J Integr Agric 13(5):990–996
Rezende RALS, Rodrigues FA, Soares JDR, Silveira HRDO, Pasqual M, Dias GDMG (2018) Salt stress and exogenous silicon influence physiological and anatomical features of in vitro-grown cape gooseberry. Ciência Rural. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20170176
Rhodes D, Nadolska-Orczyk A, Rich PJ (2002) Salinity, osmolytes and compatible solutes. Salinity: environment-plant-molecules. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 181–204
Saadia M, Jamil A, Akram NA, Ashraf M (2012) A study of proline metabolism in canola (Brassica napus L.) seedlings under salt stress. Molecules 17:5803–5815. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17055803
Safi-naz S, Rady MM (2015) Moringa oleifera leaf extract improves growth, physio-chemical attributes, antioxidant defence system and yields of salt-stressed Phaseolus vulgaris L. plants. Int J ChemTech Res 8(11):120–134
Sairam RK, Rao KV, Srivastava GC (2002) Differential response of wheat genotypes to long term salinity stress in relation to oxidative stress, antioxidant activity and osmolyte concentration. Plant Sci 163(5):1037–1046
Sakuraba H, Takamatsu Y, Satomura T, Kawakami R (2001) Purification, characterization, and application of a novel dye-linked l-proline dehydrogenase from a hyperthermophilic archaeon, Thermococcus profundus. Appl Environ Microb 67:1470–1475. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.4.1470
Semida WM, Rady MM (2014) Presoaking application of propolis and maize grain extracts alleviates salinity stress in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Sci Hortic 168:210–217
Sharma P, Jha AB, Dubey RS, Pessarakli M (2012) Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. J Bot. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/217037
Sheng M, Tang M, Chen H, Yang B, Zhang F, Huang Y (2008) Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizae on photosynthesis and water status of maize plants under salt stress. Mycorrhiza 18(6–7):287–296
Siringam K, Juntawong N, Cha-Um S, Kirdmanee C (2011) Salt stress induced ion accumulation, ion homeostasis, membrane injury and sugar contents in salt-sensitive rice (Oryza sativa L. spp. indica) roots under isoosmotic conditions. Afr J Biotechnol 10:1340–1346
Sobahan MA, Akter N, Ohno M, Okuma E, Hirai Y, Mori IC, Nakamura Y, Murata Y (2012) Effects of exogenous proline and glycinebetaine on the salt tolerance of rice cultivars. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76:1568–1570. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.120233
Soliman AS, Shanan NT (2017) The role of natural exogenous foliar applications in alleviating salinity stress in Lagerstroemia indica L. seedlings. J Appl Hortic 19(1):35–45
Srinieng K, Saisavoey T, Karnchanatat A (2015) Effect of salinity stress on antioxidative enzyme activities in tomato cultured in vitro. Pak J Bot 47(1):1–10
Sundstrom FJ, Reader RB, Edwards RL (1987) Effect of seed treatment and planting method on Tabasco pepper. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 112:641–644
Taha RS (2016) Improving salt tolerance of Helianthus annuus (L.) plants by Moringa oleifera leaf extract. Egypt J Agron 38(1):117–140
Tamimi SM (2016) Effect of seed priming on growth and physiological traits of five Jordanian wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) landraces under salt stress. J Biosci Agric Res 11(01):906–922
Teh CY, Noor CT, Shaharuddin A, Maziah CH (2016) Exogenous proline significantly affects the plant growth and nitrogen assimilation enzymes activities in rice (Oryza sativa) under salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 38:10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2163-1
Valero E, Marcià H, De la Fuente IM, Henandez J-A, Gonzàles-Sànchez M-I, Garcia-Carmona F (2016) Modeling the ascorbateglutathione cycle in chloroplasts under light/dark conditions. BMC Syst Biol 10:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12918-015-0239-y
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants. Plant Sci 151:59–66
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14
Wang K, Liu Y, Dong K, Dong J, Kang J, Yang Q, Sun Y (2011) The effect of NaCl on proline metabolism in Saussurea amara seedlings. Afr J Biotechnol 10(15):2886–2893
Wu GQ, Feng RJ, Li SL, Du YY (2017) Exogenous application of proline alleviates salt-induced toxicity in sainfoin seedlings. J Anim Plant Sci 27:246–251. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2013.11512989
Yan Z, Guo S, Shu S, Sun J, Tezuka T (2011) Effects of proline on photosynthesis, root reactive oxygen species (ROS) metabolism in two melon cultivars (Cucumis melo L.) under NaCl stress. Afr J Biotechnol 10:18381–18390. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.1073
Yasmeen A (2011) Exploring the potential of moringa (Moringa oleifera) leaf extract as natural plant growth enhancer. Dissertation, University of Faisalabad
Yasmeen A, Basra SMA, Ahmad R, Wahid A (2012) Performance of late sown wheat in response to foliar application of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaf extract. Chil J Agric Res 72(1):92
Yemm EW, Cocking EC, Ricketts RE (1955) The determination of amino-acids with ninhydrin. Analyst 80(948):209–214
Zhou Y, Wen Z, Zhang J, Chen X, Cui J, Xu W, Liu HY (2017) Exogenous glutathione alleviates salt-induced oxidative stress in tomato seedlings by regulating glutathione metabolism, redox status, and the antioxidant system. Sci Hortic 220:90–101
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: MMR and HFA. Performed the experiments: AK, HFA, YA, SK, and MMR. Analyzed the data: AK, HFA, and YA. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: HFA and SK. Wrote the paper: AK and SK. Revised the paper: MMR, HFA, and YA. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rady, M.M., Kuşvuran, A., Alharby, H.F. et al. Pretreatment with Proline or an Organic Bio-stimulant Induces Salt Tolerance in Wheat Plants by Improving Antioxidant Redox State and Enzymatic Activities and Reducing the Oxidative Stress. J Plant Growth Regul 38, 449–462 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9860-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9860-5