Abstract.
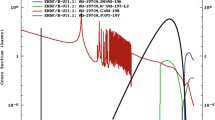
The Resonant Detector Technique (RDT) is a very promising technique for neutron spectroscopy in the epithermal energy region above 1 eV at spallation neutron sources. In this technique, using the (n,γ) reactions, the energy of the scattered neutrons is assigned by revealing the prompt γ ray cascade from the absorbing foil through a γ detector. The advantages of this technique, as compared to the Single Difference Technique (SDT) currently used on eVS spectrometer at ISIS, are presented. Different choices of converter foils and γ detectors will be compared and discussed, especially in terms of their efficiency and background insensitivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 July 2001 / Accepted: 24 October 2001
RID="*"
ID="*"Corresponding author. (Fax: +39-06/2023507, E-mail: antonino.pietropaolo@roma2.infn.it)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pietropaolo, A., Andreani, C., D’Angelo, A. et al. γ detectors for Deep Inelastic Neutron Scattering in the 1–100 eV energy region . Appl Phys A 74 (Suppl 1), s189–s190 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390101089
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390101089