Abstract
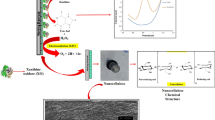
As a comprehensive survey on both health and biosensor technologies, in this study, a non-enzymatic electrochemical biosensor based on kappa-carrageenan/PVA/nano-eggshell (K-carrageenan/PVA/nano-eggshell) biocomposite was prepared to detect low-level urea in phosphate-buffered solution (PBS). Novel K-carrageenan/PVA/nano-eggshell biocomposite was prepared by ultrasonics sonochemistry. The electrochemical biosensor showed a sensitivity of 0.018 μA μM−1 cm−2 in a linear range of [250–1000] μM urea. Urea detection limit of the biosensor was 60 μM at room temperature.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Dutta, S. Chandra, A.K. Swain, D. Bahadur, SnO2 quantum dots-reduced graphene oxide composite for enzyme-free ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of urea. Anal. Chem. 86, 5914–5921 (2014)
A. Sharma, K. Rawat, H.B. Bohidar, P.R. Solankia, Studies on clay-gelatin nanocomposite as urea biosensor. Appl. Clay Sci. 146, 297–305 (2017)
S. Clark, P.S. Francis, X.A. Conlan, N.W. Barnett, Determination of urea using high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection after automated derivation with xanthydrol. J. Chromatogr. A 1161, 207–213 (2007)
K.M. Khan, H. Krishna, S.K. Majumder, P.K. Gupta, Detection of urea adulteration in milk using near-infrared Raman spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 8, 93–102 (2015)
X.C. Hu, N. Takenaka, M. Kitano, H. Bandow, Y. Maeda, M. Hattori, Determination of trace amounts of urea by using flow injection with chemiluminescence detection. Analyst 119, 1829–1833 (1994)
L. Liu, H. Mo, S. Wei, D. Raftery, Quantitative analysis of urea in human urine and serum by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance. Analyst 137, 595–600 (2012)
T.Q. Tran, S.W. Yoon, B.J. Park, H.H. Yoon, J. Electroanal. Chem. 818, 76–83 (2018)
B.E. Raabo, T. Terkildsen, On the enzymatic determination of blood urea. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 12, 402–407 (1960)
R. Wilson, A. Turner, Urea oxidase: an ideal enzyme. Biobiosens. Bioelectron. 7, 165–185 (1992)
A.S.G. Huggett, D. Nixon, Use of urea oxidase, peroxidase, and O-dianisidine in determination of blood and urinary urea. Lancet 270, 368–370 (1957)
J. Luo, S. Jiang, H. Zhang, J. Jiang, X.A. Liu, novel non-enzymatic urea biosensor based on Cu nanoparticle modified graphene sheets electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 709, 47–53 (2012)
S.A. Ansari, Q. Husain, Potential applications of enzymes immobilized on/in nanomaterials: a review. Biotechnol. Adv. 30, 512–523 (2012)
S. Park, H. Boo, T.D. Chung, Electrochemical non-enzymatic urea biosensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 556, 46–57 (2006)
S. Cherevko, C.-H. Chung, Gold nanowire array electrode for non-enzymatic voltammetric and amperometric urea sensing”. Biosens. Actuators B Chem. 142, 216–223 (2009)
J. Ryu, K. Kim, H.-S. Kim, H.T. Hahn, D. Lashmore, Intense pulsed light induced platinum–gold alloy formation on carbon nanotubes for non-enzymatic urea sensing. Biobiosens. Bioelectron. 26, 602–607 (2010)
H.-F. Cui, J.-S. Ye, W.-D. Zhang, C.-M. Li, J.H.T. Luong, F.-S. Sheu, Selective and sensitive electrochemical sensing of urea in neutral solution using platinum-lead alloy nanoparticle/carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Anal. Chim. Acta 594, 175–183 (2007)
F. Gao, F. Zhou, Y. Yao, Y. Zhang, L. Du, D. Geng, P. Wang, Ordered assembly of platinum nanoparticles on carbon nanocubes and their application in the non-enzymatic sensing of urea. J. Electroanal. Chem. 803, 165–172 (2017)
S. Park, T.D. Chung, H.C. Kim, Nonenzymatic urea sensing using mesoporous platinum. Anal. Chem. 75, 3046–3049 (2003)
S. Cherevko, C.-H. Chung, The porous CuO electrode fabricated by hydrogen bubble evolution and its application to highly sensitive non-enzymatic urea sensing. Talanta 80, 1371–1377 (2010)
S.C. Hou, A.Y. Zhang, M. Su, Nanostructures for biosensing applications. Nanostructures 6, 58 (2016)
C.E. Rowland, C.W. Brown, J.B. Delehanty, I.L. Medintz, Nanostructure-based biosensors for the sensing of biological threat agents. Mater. Today 19, 464–477 (2016)
S. SoYoon, A. Ramadoss, B. Saravanakumar, S.J. Kim, Novel Cu/CuO/ZnO hybrid hierarchical nanostructures for non-enzymatic urea biosensor application. J. Electroanal. Chem. 717, 90–95 (2014)
K. Zhang, J. Xu, K.Y. Wang, L. Cheng, J. Wang, B. Lıu, Preparation and characterization of chitosan nanocomposites with vermiculite of different modification. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 94(12), 2121–2127 (2009)
R. Jayakumar, M. Prabaharan, R.L. Reis, J.F. Mano, Graft copolymerized chitosan-present status and applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 62(2), 142–158 (2005)
R.D. Joerger, Antimicrobial films for food applications: a quantitative analysis of their effectiveness. Packag. Technol. Sci. 20(4), 231–273 (2007)
N. Vıswanathan, S. Meenakshı, Enriched fluoride sorption using alumina/chitosan composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 178(1–3), 226–232 (2010)
M. Huleıhel, V. Pavlov, V. Erukhımovıtch, The use of FTIR microscopy for the evaluation of anti-bacterial agents activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 96, 17–23 (2009)
L. Luo, L. Zhu, Z. Wang, Nonenzymatic amperometric determination of urea by CuO nanocubes–graphene nanocomposite modified electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 88, 156–163 (2009)
N.R. Stradiotto, H. Yamanaka, M.V.B. Zanoni, Electrochemical biosensors: a powerful tool in analytical chemistry. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 14, 159–173 (2003)
Q. Wang, J.B. Zheng, H.F. Zhang, A novel formaldehyde biosensor containing AgPd alloy nanoparticles transducer posited on an ionic liquid-chitosan composite film. J. Electroanal. Chem. 674, 1–6 (2012)
I. Švancara, K. Vytřas, K. Kalcher, A. Walcarius, J. Wang, Carbon paste electrodes in facts, numbers, and notes: a review on the occasion of the 50-years jubilee of carbon paste in electrochemistry and electroanalysis. Electroanalysis 21, 7–28 (2009)
J. Zima, I. Švancara, J. Barek, K. Vytřas, Recent advances in electroanalysis of organic compounds at carbon paste electrodes. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 39, 204–227 (2009)
V. Vyskocil, J. Barek, Mercury electrodes-possibilities and limitations in environmental electroanalysis. J. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 39, 189–203 (2009)
J.R. Stetter, J. Li, Amperometric gas biosensors—a review. Chem. Rev. 108, 352–366 (2008)
U. Yogeswaran, S.M. Chen, A review on the electrochemical biosensors and biobiosensors composed of nanowires as sensing material. Biosensors 8, 290–313 (2008)
D.E. Mays, A. Hussam, Voltammetric methods for determination and speciation of inorganic arsenic in the environment—a review. Anal Chim. Acta 646, 6–16 (2008)
A. Bobrowski, A. Królicka, J. Zarębski, Characteristics of voltammetric determination and speciation of chromium—a review. Electroanalysis 12, 1449–1458 (2009)
C. Amatore, A. Oleinick, I. Svir, Theoretical analysis of microscopic ohmic drop effects on steady-state and transient voltammetry at the disk microelectrode: a quasi-conformal mapping modeling and simulation. Anal. Chem. 80, 7947–7956 (2008)
C. Amatore, A.I. Oleinick, I. Svir, Numerical simulation of diffusion processes at recessed disk microelectrode arrays using the quasi-conformal mapping approach. Anal. Chem. 81, 4397–4405 (2009)
J.D. Guo, E. Lindner, Cyclic voltammograms at coplanar and shallow recessed microdisk electrode arrays: guidelines for design and experiment. Anal. Chem. 81, 130–138 (2009)
E.F. Douglass, P.F. Driscoll, D. Liu, N.A. Burnham, C.R. Lambert, W.G. McGimpsey, Effect of electrode roughness on the capacitive behavior of self-assembled monolayers. Anal. Chem. 80, 7670–7677 (2008)
D. Menshykau, R.G. Compton, The influence of electrode porosity on diffusional cyclic voltammetry. Electroanalysis 20, 2387–2394 (2008)
J.H. Bae, Y.R. Lim, W. Jung, R.J. Silbey, J. Sung, Practical model for imperfect conductometric molecular wire biosensors. Anal. Chem. 81, 578–583 (2009)
C.Y. Lee, A.M. Bond, Evaluation of levels of defect sites present in highly ordered pyrolytic graphite electrodes using capacitive and faradaic current components derived simultaneously from large-amplitude Fourier transformed ac voltammetric experiments. Anal. Chem. 81, 584–594 (2009)
D.B. Sheth, R. Diefes, M. Gratzl, Spatially averaging electrodes. Anal. Chem. 81, 2129–2134 (2009)
V.I. Ogurtsov, V. Beni, J. Strutwolf, D.W.M. Arrigan, Study of the effects of nonlinear potential sweeps on voltammetry. Electroanalysis 21, 68–76 (2009)
N.G. Rajendra, K.G. Vinod, B. Neeta, A.S. Ram, Electrochemical biosensor for the determination of dopamine in presence of high concentration of ascorbic acid using a Fullerene-C60 coated gold electrode. Electroanalysis 20(7), 757–764 (2008)
A. Saxena, M. Kaloti, H.B. Bohidar, Rheological properties of binary and ternary protein polysaccharide co-hydrogels and comparative release kinetics of salbutamol sulphate from their matrices. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 48(2), 263–270 (2011)
S. Selvakumaran, I.I. Muhamad, S.I. AbdRazak, Evaluation of kappa carrageenan as potential carrier for floating drug delivery system: effect of pore forming agents. Carbohydr. Polym. 135, 207–214 (2016)
J. Zhao, C. Sun, H. Li, X. Dong, X. Zhang, Studies on the physicochemical properties, gelling behavior and drug release performance of agar/κ-carrageenan mixed hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 154, 878–887 (2020)
N.N. Mobarak, N. Ramli, A. Ahmad, M.Y.A. Rahman, Chemical interaction and conductivity of carboxymethyl κ-carrageenan based green polymer electrolyte. Solid State Ion. 224, 51–57 (2012)
M. Nithya, M. Alagar, B. Sundaresan, Eco-friendly biopolymer kappa carrageenan with NH4Br application in energy saving battery. Mater. Lett. 263, 127295 (2020)
R. Zamora-Sequeira, I. Ardao, R. Starbird, C.A. García-González, Conductive nanostructured materials based on poly-(3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)(PEDOT) and starch/κ-carrageenan for biomedical applications. Carbohyd. Polym. 189, 304–312 (2018)
S. Rudhziah, A. Ahmad, I. Ahmad, N.S. Mohamed, Biopolymer electrolytes based on blend of kappa-carrageenan and cellulose derivatives for potential application in dye sensitized solar cell. Electrochim. Acta 175, 162–168 (2015)
S. Sriram, I.M. Nambi, R. Chetty, Hexavalent chromium reduction through redox electrolytic cell with urea and cow urine as anolyte”. J. Environ. Manag. 232, 554–563 (2019)
W. Wang, D. Chai, J. Zhang, S. Xue, Y. Wang, Z. Lei, Ni5Sm-P/C ternary alloyed catalyst as highly efficient electrocatalyst for urea electrooxidation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 80, 326–332 (2017)
Z.P. Yang, X. Liu, C.J. Zhang, B.Z. Liu, A high-performance nonenzymatic piezoelectric sensor based on molecularly imprinted transparent TiO2 film for detection of urea. Biosens. Bioelectron. 74, 85–90 (2015)
R. Ahmad, N. Tripathy, Y.B. Hahn, Highly stable urea sensor based on ZnO nanorods directly grown on Ag/glass electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 194, 290–295 (2014)
H. Yin, Z. Cui, L. Wang, Q. Nie, In situ reduction of the Cu/Cu2O/carbon spheres composite for enzymaticless glucose sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 222, 1018–1023 (2016)
E. Muthusankar, V.K. Ponnusamy, D. Ragupathy, Electrochemically sandwiched poly (diphenylamine)/phosphotungstic acid/graphene nanohybrid as highly sensitive and selective urea biosensor. Synth. Metals 254, 134–140 (2019)
T.Q.N. Tran, G. Das, H.H. Yoon, Nickel-metal organic framework/MWCNT composite electrode for non-enzymatic urea detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 243, 78–83 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by TUBITAK Project 216M421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taşaltın, N., Aydın, E., Karakuş, S. et al. K-carrageenan/PVA/nano-eggshell biocomposite-based non-enzymatic electrochemical biosensor for low-level urea detection. Appl. Phys. A 126, 827 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03960-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03960-1