Abstract
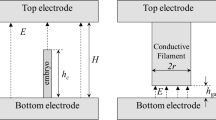
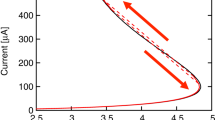
We have shown an exponential increase in the ratio of conductance in the on and off states of switching devices by controlling the surface morphology of the thin films for the device by depositing at different rotational speeds. The pinholes which are preferred topography on the surface at higher rotational speed give rise to higher on–off ratio of current from the devices fabricated at the speed. The lower rotational speed contributes to higher thickness of the film and hence no switching. For thicker films, the domain is formed due to phase segregation between the two components in the film, which also indicates that the film is far from thermal equilibrium. At higher speed, there is very little scope of segregation when the film is drying up. Hence, there are only few pinholes on the surface of the film which are shallow. So, the filamentary mechanism of switching in memory devices can be firmly established by varying the speed of thin film deposition which leads to phase segregation of the materials. Thus, the formation of filament can be regulated by controlling the thickness and the surface morphology.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.W. Tang, S.A. VanSlyke, Appl. Phys. Lett. 51, 913 (1987)
M. Strukelj, R.H. Jordan, A. Dodabalapur, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 1213 (1996)
S.E. Shaheen, C.J. Brabec, N.S. Sariciftci, F. Padinger, T. Fromherz, J.C. Hummelen, Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 841 (2001)
B.A. Gregg, J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 4688 (2003)
P. Peumans, V. Bulović, S.R. Forrest, Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 3855 (2000)
C.D. Dimitrakopoulos, P.R.L. Malenfant, Adv. Mater. 14, 99 (2002)
S.-J. Kim, J.-S. Lee, Nano Lett. 10, 2884 (2010)
K.S. Kumar, M. Ruben, Coord. Chem. Rev. 346, 176 (2017)
M. Suda, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 91, 19 (2017)
J. Zhang, W. Xu, P. Sheng, G. Zhao, D. Zhu, Acc. Chem. Res. 50, 1654 (2017)
Q. Li, G. Mathur, S. Gowda, S. Surthi, Q. Zhao, L. Yu, J.S. Lindsey, D.F. Bocian, V. Misra, Adv. Mater. 16, 133 (2004)
Z. Liu, A.A. Yasseri, J.S. Lindsey, D.F. Bocian, Science (80-.) 302, 1543 (2003)
K.M. Roth, J.S. Lindsey, D.F. Bocian, W.G. Kuhr, Langmuir 18, 4030 (2002)
T. Furukawa, Phase Transit. A Multinatl. J. 18, 143 (1989)
M. Kiguchi, S. Fujii, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 90, 1 (2016)
J. Kevorkian, M.M. Labes, D.C. Larson, D.C. Wu, Discuss. Faraday Soc. 51, 139 (1971)
A. Bandyopadhyay, A.J. Pal, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 1215 (2003)
A. Bandyopadhyay, A.J. Pal, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 999 (2004)
Z. Liu, F. Xue, Y. Su, K. Varahramyan, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 27, 151 (2006)
L. Ma, J. Liu, S. Pyo, Y. Yang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 362 (2002)
L.P. Ma, J. Liu, Y. Yang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 2997 (2002)
G. Vyas, P. Dagar, S. Sahu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 233301 (2016)
F. Zhang, C. Di, N. Berdunov, Y. Hu, Y. Hu, X. Gao, Q. Meng, H. Sirringhaus, D. Zhu, Adv. Mater. 25, 1401 (2013)
S. Walheim, M. Böltau, J. Mlynek, G. Krausch, U. Steiner, Macromolecules 30, 4995 (1997)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Department of Science and Technology (DST) India, through INSPIRE Faculty Program with Project No. IFA12-PH-26. The authors are thankful to IIT Jodhpur for providing all the support. We are thankful to Suresh Dahiya of Department of Electrical Engineering for helping us in programming and interfacing the instruments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vyas, G., Dagar, P. & Sahu, S. Exponential increase in the on–off ratio of conductance in organic memory devices by controlling the surface morphology of the devices. Appl. Phys. A 124, 369 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1791-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1791-2