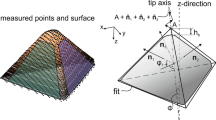
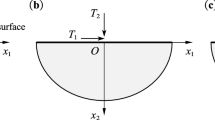
Abstract
Manipulation of the biological particles by atomic force microscopy is used to transfer these particles inside body’s cells, diagnosis and destruction of the cancer cells and drug delivery to damaged cells. According to the impossibility of simultaneous observation of this process, the importance of modeling and simulation can be realized. The contact of the tip with biological particle is important during manipulation, therefore, the first step of the modeling is choosing appropriate contact model. Most of the studies about contact between atomic force microscopy and biological particles, consider the biological particle as an elastic material. This is not an appropriate assumption because biological cells are basically soft and this assumption ignores loading history. In this paper, elastic and viscoelastic JKR theories were used in modeling and simulation of the 3D manipulation for three modes of tip–particle sliding, particle–substrate sliding and particle–substrate rolling. Results showed that critical force and time in motion modes (sliding and rolling) for two elastic and viscoelastic states are very close but these magnitudes were lower in the viscoelastic state. Then, three friction models, Coulomb, LuGre and HK, were used for tip–particle sliding mode in the first phase of manipulation to make results closer to reality. In both Coulomb and LuGre models, critical force and time are very close for elastic and viscoelastic states but in general critical force and time prediction of HK model was higher than LuGre and the LuGre model itself had higher prediction than Coulomb.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Yang, S. Ji, K. Xie, W. Du, B. Liu, Y. Hu, Y. Li, G. Zhao, D. Wu, W. Huang, S. Liu, H. Jiang, J. Chu, High efficiency fabrication of complex microtube arrays by scanning focused femtosecond laser Bessel beam for trapping/releasing biological cells. Opt. Express 25(7), 8144–8157 (2017)
A.S. Nain, C. Amant, M. Sitti, Three-Dimensional Nanoscale Manipulation and Manufacturing using Proximal Probes: Controlled Pulling of Polymer Micro/Nanofibers, in Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on mechatronics, ISSN: 1050–4729. https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2004.1307188 2004
M.L. Rodriguez, P.J. McGarry, N.J. Sniadecki, Review on cell mechanics: experimental and modeling approaches. Appl. Mech. Rev. 65(6), e060801 (2013)
A.H. Korayem, M. Taheri, M.H. Korayem, Dynamic modeling and simulation of nanoparticle motion in different environments using AFM nano–robot. Modares Mech. Eng. 15(1), 294–300 (2013)
C.T. Lim, E. H.Zhou, S.T. Quek, Mechanical models for living cells. Biomechanics 39(2), 195–216 (2004)
M.H. Korayem, M. Taheri, Modeling of various contact theories for the manipulation of different biological micro–nanoparticles based on AFM. Nanoparticle Res. 16(1), 1–13 (2013)
M.H. Korayem, M. Zakeri, Dynamic modeling of manipulation of micro/nano particles on rough surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257(15), 6503–6513 (2011)
W. Ding, A.J. Howard, M.D.M. Peri, C. Cetinkaya, Rolling resistance moment of micro spheres on surfaces: contact measurements. Phil. Mag. 87(36), 5685–5696 (2007)
M. Moradi, A.H. Fereidon, S. Sadeghzadeh, Dynamic modeling for nanomanipulation of polystyrene nanorod by atomic force microscope. Sci Iran. 18(3), 808–815 (2011)
M.H. Korayem, A. Motaghi, M. Zakeri, Dynamic modelling of submerged nanoparticle pushing based on atomic force microscopy in liquid medium. Nanoparticle Res. 13(10), 5009–5019 (2011)
M.H. Korayem, M. Geramizadeh, M. Taheri, Dynamic manipulation of spherical yeast cells based on atomic force microscopy. Lat. Am. Appl. Res. 43, 295–299 (2013)
M.R. Falvo, S. Washburn, R. Superfine et al., Manipulation of individual viruses: friction and mechanical properties. Biophysical 72(3), 1396–1403 (1997)
A. Ikai, R. Afrin, H. Sekiguchi, T. Okajima, M.T. Alam, Nano-mechanical methods in biochemistry using atomic force microscopy. Curr. Nanosci. 4(3), 181–193 (2003)
M.H. Korayem, A.K. Hoshiar, Dynamic 3-D modeling and simulation of nanoparticles using an AFM nanorobot. Robotica 32(4), 625–641 (2014)
M.H. Korayem, Z. Mahmoodi, M. Taheri, M.B. Saraee, Three-dimensional modeling and simulation of the AFM-based manipulation of spherical biological micro/nanoparticles with the consideration of contact mechanics theories. Multi Body Dyn. 229(4), 370–382 (2015)
W.H. Yang, The contact problem for viscoelastic bodies. Appl. Mech. 33(2), 395–395 (1966)
C.Y. Hui, J.M. Baney, E.J. Kramer, Contact mechanics and adhesion of viscoelastic spheres. Langmuir 14(22), 6570–6578 (1998)
M.H. Korayem, Z. Rastegar, M. Taheri, Application of Johnson–Kendall–Roberts model in nano-manipulation of biological cell. Micro Nano Lett. 7(6), 576–580 (2012)
K.L. Johnson, K. Kendall, A.D. Roberts, Surface energy and the contact of elastic solids. Math. Phys. Sci. 324(1558), 301–313 (1971)
Q.S. Li, G.Y.H. Lee, C.N. Ong, C.T. Lim, AFM indentation study of breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 374(4), 609–613 (2008)
C.C. Wong, J. Reboud, J. Soon, P. Neuzil, K. Liao, Detachment Dynamics of Cancer Cells. Exp. Appl. Mech. 6:881–882 (2011)
M.H. Korayem, H. Badkoobeh Hezaveh, M. Taheri, Dynamic modeling and simulation of rough cylindrical micro/nanoparticle manipulation with atomic force microscopy. Microsc. Microanal. 20(6), 1692–1707 (2014)
M.H. Korayem, M. Taheri, S.D. Ghahnaviyeh, Sobol method application in sensitivity analysis of LuGre friction model during 2D manipulation. Mod. Phys. Lett. 29, e1550123 (2015)
AdamsGG,MuftuS,AzharNM.Scale-dependent model for multi-asperity contact and friction. ASME J. Tribol. 125(4), e1550123 (2003)
C.D. Wit, H. Olsson, K.J. Astrom, P. Lischinsky, A new model for control of systems with friction. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 40(3), 419–425 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korayem, M.H., Habibi Sooha, Y. & Rastegar, Z. Modeling and simulation of viscoelastic biological particles’ 3D manipulation using atomic force microscopy. Appl. Phys. A 124, 392 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1772-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1772-5