Abstract
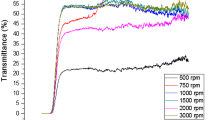
In this study, undoped ZnO and yttrium (Y)-doped ZnO (YZO) nanoparticles having different Y dopant concentrations (Zn1−xYxO; x = 0.005, 0.01, 0.015, 0.02) were successfully synthesized by sol–gel dip-coating method. Structural characterizations of the obtained samples were examined with scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses. SEM analysis shows that the synthesized nanoparticles are mostly dot-like structures. The sizes of nanostructures decrease with increasing Y-doping concentration up to 2 mol % Y and XRD results show that all of samples have wurtzite hexagonal structure of ZnO with (002) c-plane orientation. According to EDS results pure YZO samples are obtained. Optical transmittances of all samples were investigated in the range of 350–750 nm at room temperature. The average optical transmittances of YZO samples in the visible region are approximately over 90%, but the transmittance starts to decrease for Zn0.98Y0.02O sample. Also, it was observed that the optical transmittances of Y-doped samples are higher than that of undoped ZnO. The electrical properties of YZO samples were obtained by resistance measurements at room temperature. The resistivity of samples was found to be 2.25 × 10−3, 1.43 × 10−3, 7.8 × 10−3, and 1.3 × 10−3 Ω-cm for Zn0.995Y0.005O, Zn0.99Y0.01O, Zn0.985Y0.015O and Zn0.98Y0.02O, respectively. All these results show that surface, structural, electrical and optical properties of ZnO samples can be improved with doping Y up to 2 mol % concentrations.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
02 March 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05330-5
References
S.M. W.Park, Yi, Kim,, Park, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 4358 (2003)
Z. Z.Liu, W. Jin, J. Li, Qiu, Mater. Lett. 59, 3620 (2005)
A. Moezzi, A.M. McDonagh, M.B. Cortie, Chem. Eng. J. 1, 185 (2012)
Y. Wang, J. Yang, J. Kong, H. Jia, M. Yu, Superlatt. Microstr. 86, 228–235 (2015)
A. Erdem, Talanta 74, 318 (2007)
G.Q. Wang, Y.Q. Wang, L.X. Chen, J. Choo, Biosens, Bioelectron. 25, 1859 (2010)
M. Ohyama, H. Kozuka, T. Yoko, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81, 1622 (1998)
K.Y. Cheong, N. Muti, S.R. Ramanan, Thin Solid Films 410, 142 (2002)
E.J. Luna-Arredondo, A. Maldonado, R. Asomoza, D.R. Acosta, M.A. Meléndez-Lira, M. de la L. Olvera, Thin Solid Films 490, 132 (2005)
T. Ivanova, A. Harizanova, T. Koutzarova, B. Vertruyen, Journal of Physics: Conference Series 682, 012023, (2016)
H. Ko, W.P. Tai, K.C. Kim, S.H. Kim, S.J. Suh, Y.S. Kim, J. Cryst. Growth 277, 352 (2005)
J.B. Lee, S.H. Kwak, H.J. Kim, Thin Solid Films 423, 262 (2003)
H. Park, Y. Kim, I. Ji, S.H. Lee, J.S. Kim, J.Y. Leem, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 14(11), 833 (2014)
J.L. Zhao, X.M. Li, J.M. Bian, W.D. Yu, X.D. Gao, J. Cryst. Growth 276, 507 (2005)
Y.S. Kim, W.P. Tai, S.J. Shu, Thin Solid Films 491, 153 (2005)
R. Kaur, A.V. Singh, R.M. Mehra, phys. stat. sol. (a) 202(6), 1053–1059 (2005)
Q. Yu, H. Yang, W. Fu, L. Chang, J. Xu, C. Yu, R. Wei, K. Du, H. Zhu, M. Li, G. Zou, Thin Solid Films 515, 3840–3843 (2007)
K. Han, L.Q. Guo, N.D. Shepherd, M. Tao, IEEE 001275 (2011) (2011)
H. Zhou, D. Yi, Z. Yu, L. Xiao, J. Li, Thin Solid Films 515, 6909–6914 (2007)
S.T. Tan, B.J. Chen, X.W. Sun, W.J. Fan, H.S. Kwok, X. Zhang, S.J. Chua, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 013505 (2005)
Q. Yu, W. Fu, C. Yu, H. Yang, R. Wei, Y. Sui, S. Liu, Z. Liu, M. Li, G. Wang, C. Shao, Y. Liu, G. Zou, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40, 5592–5597 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by Research Fund of the Istanbul University in Turkey with project number BEK-26582.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Üzar, N. Enhanced optical and electrical properties of Y-doped ZnO nanoparticles having different Y concentrations. Appl. Phys. A 124, 303 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1725-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1725-z