Abstract
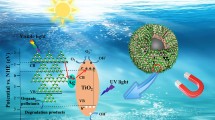
In this paper, we present the design and implementation of a type of yolk-like Fe3O4@C–Au@void@TiO2–Pd hierarchical microspheres with visible light-assisted enhanced photocatalytic degradation of dye and rapid magnetic separation. The resulting composite microspheres exhibited yolk-like hierarchical structures with a 236.3 m2 g−1 surface area and a high-saturation magnetization of 31.5 emu g−1. As an example of applications, the photodegradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) in the presence of NaBH4 was investigated under simulated sunlight irradiation. The results show that the photocatalytic activity of the yolk-like Fe3O4@C–Au@void@TiO2–Pd microcomposites in the RhB photodegradation is higher than the Fe3O4@C–Au@void@TiO2 and Fe3O4@C@TiO2 microcomposites, as they can degrade RhB with 40 min of irradiation time. In addition, by magnetic separation, the as-prepared yolk-like Fe3O4@C–Au@void@TiO2–Pd hierarchical microcomposites can be completely separated and reused for four times.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.T. Gibson, Mesosilica materials and organic pollutant adsorption: part B removal from aqueous solution. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43(15), 5173–5182 (2014)
N. Kannan, M.M.Sundaram, Kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue by adsorption on various carbons-a comparative study. Dyes Pigments. 51(1), 25–40 (2001)
P. Pandit, S. Basu, Removal of ionic dyes from water by solvent extraction using reverse micelles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38(8), 2435–2442 (2014)
B. Neppolian, H.C. Choi, S. Sakthivel, Solar/UV-induced photocatalytic degradation of three commercial textile dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 89(2), 303–317 (2002)
M. Nasrollahzadeh, S.M. Sajadi, M. Rostami-Vartooni, R. Bagherzadeh, Immobilization of copper nanoparticles on perlite: green synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity on aqueous reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J Molec. Catal. A Chem. 400(32), 22–30 (2015)
D. Jana, G. De, Controlled and stepwise generation of Cu2O, Cu2O@Cu and Cu nanoparticles inside the transparent alumina films and their catalytic activity. Rsc Adv. 2(25), 9606–9613 (2012)
A. Chakravarty, K. Bhowmik, A. Mukherjee, Cu2O nanoparticles anchored on amine-functionalized graphite nanosheet: a potential reusable catalyst. Lang. ACS J Surf. Coll. 31(18), 5210–5219 (2015)
M.R. Kim, K.L. Dong, D.J. Jang, Facile fabrication of hollow Pt/Ag nanocomposites having enhanced catalytic properties. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 103(1–2), 253–260 (2011)
K. Satoh, S. Ishihara, S. Nanoparticles, Facile synthesis and their catalytic application for the degradation of dyes. Rsc Adv. 5(33), 25781–25788 (2015)
C. Wang, K. Tang, D. Wang, Z. Liu, L. Wang, Simple self-assembly of HLaNb2O7 nanosheets and Ag nanoparticles/clusters and their catalytic properties. J. Mater. Chem. 22(43), 22929–22934 (2012)
A.H. Lu, E.L. Salabas, F. Schuth, Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 1222–1244 (2007)
N. Nishioka, T.S. Koizumi, Synthesis of novel nitrogen-containing polymers by Pd(0)-catalyzed polycondensation of propargylic carbonates and bifunctional nitrogen nucleophiles. Eur. Polym. J 47(5), 1142–1150 (2011)
W. Zhao, W. Wang, F. Zhang, X. Zhuang, S. Han, X. Feng, One-pot approach to Pd-loaded porous polymers with properties tunable by the oxidation state of the phosphorus core. Polym. Chem. 6(35), 6351–6357 (2015)
G. Liu, H. Ji, X. Yang, Y. Wang, Synthesis of a Au/silica/polymer trilayer composite and the corresponding hollow polymer microsphere with a movable Au core. Langmuir 24(3), 1019–1025 (2008)
M. Tagliazucchi, M.G. Blaber, G.C. Schatz, E.A. Weiss, I. Szleifer, Optical properties of responsive hybrid Au@polymer nanoparticles. Acs Nano. 6(9), 8397–8406 (2012)
Q. Tian, X. Yu, L. Zhang, D. Yu, Monodisperse raspberry-like multihollow polymer/Ag nanocomposite microspheres for rapid catalytic degradation of methylene blue. J Coll. Inter. Sci. 491, 294–304 (2017)
A. Kadir, M. Wu, K. Aslan, M. Wu, J.R. Lakowicz, C.D. Geddes, Fluorescent core-shell Ag@SiO2 nanocomposites for metal-enhanced fluorescence and single nanoparticle sensing platforms. J AM. Chem. Soc. 129(6), 1524–1525 (2007)
J. Lee, C.P. Ji, H. Song, A nanoreactor framework of a Au@SiO2 yolk/shell structure for catalytic reduction of p-nitrophenol. Adv. Mater. 20(8), 1523–1528 (2008)
Y. Lu, Y.D. Yin, Z.Y. Li, Y.N. Xia, Synthesis and self-assembly of Au@SiO2 core-shell colloids. Nano Lett. 2(7), 785–788 (2002)
K. Hareesh, J.F. Williams, N.A. Dhole, K.M. Kodam, V.N. Bhoraskar, S.D. Dhole, Bio-green synthesis of Ag–GO, Au–GO and Ag–Au–GO nanocomposites using azadirachta indica: its application in sers and cell viability. Mater. Res. Exp. 3(7), 075010–075017 (2016)
H.K. He, G. Chao, Graphene nanosheets decorated with Pd, Pt, Au, and Ag nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and catalysis applications. Sci. China Chem. 54(2), 397–404 (2011)
G. Li, Z. Tang, Noble metal nanoparticle@metal oxide core/yolk-shell nanostructures as catalysts: recent progress and perspective. Nanoscale 45(27), 3995–4011 (2014)
B. Liu, Z. Zhao, G. Henkelman, W. Song, Computational design of a CeO2-supported Pd-based bimetallic nanorod for CO oxidation. J Phy. Chem. C 120(10), 5557–5564 (2016)
L. Muñoz-Fernandez, A. Sierra-Fernandez, O. Milošević, M.E. Rabanal, Solvothermal synthesis of Ag/ZnO and Pt/ZnO nanocomposites and comparison of their photocatalytic behaviors on dyes degradation. Adv. Powder Technol. 27(3), 983–993 (2016)
Y. Pang, C. Wang, J. Wang, Z. Sun, R. Xiao, S. Wang, Fe3O4@Ag magnetic nanoparticles for microrna capture and duplex-specific nuclease signal amplification based SERS detection in cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 79, 574–580 (2015)
F.H. Lin, W. Chen, Y.H. Liao, R.A. Dong, Y. Li, Effective approach for the synthesis of monodisperse magnetic nanocrystals and m-Fe3O4, (m = Ag, Au, Pt, Pd) heterostructures. Nano Res. 4(12), 1223–1232 (2011)
G.M. Haselmann, D. Eder, Early-stage deactivation of platinum-loaded TiO2 using in situ photodeposition during photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ACS Catal. 7, 4668–4675 (2017)
Q. Guo, C.Y. Zhou, Z.B. Ma, Z.F. Ren, H.J. Fan, X.M. Yang, Elementary photocatalytic chemistry on TiO2 surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 3701–3730 (2016)
X.M. Zhou, N. Liu, P. Schmuki, Photocatalysis with TiO2 nanotubes: “colorful” reactivity and designing site-specific photocatalytic centers into TiO2 nanotubes. ACS Catal. 7(5), 3210–3235 (2017)
S.L. Wang, J. Li, S. Wang et al., Two-Dimensional C/TiO2 heterogeneous hybrid for noble-metal-free hydrogen evolution. ACS Catal. 7(10), 6892–6900 (2017)
T. Renjis, A. Tom, N. Sreekumaran, S. Navinder, Freely dispersible Au@TiO2, Au@ZrO2, Ag@TiO2, and Ag@ZrO2 core-shell nanoparticles: one-step synthesis, characterization, spectroscopy, and optical limiting properties. Langmuir 19(8), 3439–3445 (2013)
M. Wang, J. Han, H. Xiong, R. Guo, Yolk@shell nanoarchitecture of Au@r-GO/TiO2 hybrids as powerful visible light photocatalysts. Langmuir 31(22), 6220–6228 (2015)
I. Lee, J.B. Joo, Y. Yin, F. Zaera, A yolk@shell nanoarchitecture for Au/TiO2 catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 50(43), 10208–10211 (2015)
D. Xu, G. Yan, M. Gao, C. Deng, X. Zhang, Selective enrichment of glycopeptides/ phosphopeptides using Fe3O4@Au-B(OH)2@mTiO2, core-shell micro-spheres. Talanta 166, 154–161 (2017)
H. Huo, X. Li, X. Zhou, L. Jiao, S. Zhao, L. Zhang, Fabrication of Ag/gamma- Fe2O3@TiO2 hollow magnetic core-shell nanospheres as highly efficient catalysts for the synthesis of beta-enaminones. Rsc Adv. 5(90), 73612–73618 (2015)
M. Shen, S. Chen, W. Jia, G. Fan, Y. Jin, H. Liang, Highly efficient and porous TiO2-coated Ag@Fe3O4@C–Au microspheres for degradation of organic pollutants. J. Nanopart. Res. 18(12), 356–361 (2016)
W. Hu, B. Liu, Q. Wang, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, P. Jing, A magnetic double-shell microsphere as a highly efficient reusable catalyst for catalytic applications. Chem. Commun. 49(69), 7596–7598 (2013)
H. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhou, C. Zhang, Q. Wang, Y. Xu, Synthesis and characterization of a multifunctional nanocatalyst based on a novel type of binary-metal-oxide-coated Fe3O4–Au nanoparticle. Rsc Adv. 6(22), 18685–18694 (2016)
Y. Zhou, Y. Zhu, X. Yang, J. Huang, W. Chen, X. Lv, C.Y. Li, C.Z. Li, Au decorated Fe3O4@TiO2 magnetic composites with visible light-assisted enhanced catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Rsc Adv. 5(62), 50454–50461 (2015)
R. Malik, V. Chaudhary, V.K. Tomer, P.S. Rana, S.P. Nehra, S. Duhan, Visible light-driven mesoporous Au–TiO2/SiO2, photocatalysts for advanced oxidation process. Ceram. Int. 42(9), 10892–10901 (2016)
M.M. Khan, J. Lee, M.H. Cho, Au@TiO2, nanocomposites for the catalytic degradation of methyl orange and methylene blue: an electron relay effect. J Ind. Eng. Chem. 20(4), 1584–1590 (2014)
D. Qi, H. Zhang, J. Tang, C. Deng, X. Zhang, Facile synthesis of mercaptophenylboronic acid-functionalized core-shell structure Fe3O4@C@Au magnetic microspheres for selective enrichment of glycopeptides and glycoproteins. J Phy. Chem. C 114(20), 9221–9226 (2010)
X. Ji, X. Song, J. Li, Y. Bai, W. Yang, X. Peng, Size control of gold nanocrystals in citrate reduction: the third role of citrate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129(45), 13939–13948 (2007)
C. Li, R. Younesi, Y. Cai, Y. Zhu, M. Ma, J. Zhu, Photocatalytic and antibacterial properties of Au-decorated Fe3O4@mTiO2, core–shell microspheres. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 156–157(9), 314–322 (2014)
G. Chen, Y. Wang, J. Zhang, C.L. Wu, H.D. Liang, H. Yang, Preparation and characterization of visible-light-driven TiO2 photocatalyst Co-doped with nitrogen and erbium. J Nanosci. Nanotechno 12(5), 3799–3805 (2012)
H. Khojasteh, M. Salavatiniasari, M.P. Mazhari, M. Hamadanian, Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2@Pd and Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2@Pd–Ag nano composites and their utilization in enhanced degradation systems and rapid magnetic separation. Rsc Adv. 6(89), 86385–86385 (2016)
S. Liu, M.X. Guo, F. Shao, Y.H. Peng, S.W. Bian, Water-dispersible and magnetically recoverable Fe3O4/Pd@nitrogen-doped carbon composite catalysts for the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Rsc Adv. 6(80), 76128–76131 (2016)
M. Zhang, J. Zheng, Y. Zheng, J. Xu, X. He, L. Chen, Preparation, characterization and catalytic activity of core-satellite Au/pdop/SiO2/Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposites. Rsc Adv. 3(33), 13818–13824 (2013)
Y. Jin, J. Zhao, F. Li, W. Jia, D. Liang, H. Chen, Nitrogen-doped graphene supported palladium-nickel nanoparticles with enhanced catalytic performance for formic acid oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 220, 83–90 (2016)
P. Xu, Z. Shen, B. Zhang, J. Wang, R. Wu, Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as calcium-responsive MRI contrast agents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 289(15), 560–566 (2016)
S. Kesavan, D.R. Kumar, M.L. Baynosa, J.J. Shim, Potentiodynamic formation of diaminobenzene films on an electrochemically reduced graphene oxide surface: determination of nitrite in water samples. Mater. Sci. Engin. C 85(1), 97–106 (2018)
M. Zhou, J. Zhang, B. Cheng, H. Yu, Enhancement of visible-light photocatalytic activity of mesoporous Au-TiO2 nanocomposites by surface Plasmon resonance. Int. J Photoenergy (1110-662X), 2058–2069 (2012)
J.Q. Ma, S.B. Guo, X.H. Guo, H.G. Ge, Liquid-phase deposition of TiO2, nanoparticles on core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2, spheres: preparation, characterization, and photocatalytic activity. J. Nanopart. Res. 17(7), 1–11 (2015)
L. Sun, H.E. Jiang, A.N. Song, J. Zhang, J. Zheng, D. Ren, Recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2–Ag magnetic nanospheres for the rapid decolorizing of dye pollutants. Chin. J Catal. 34(7), 1378–1385 (2013)
S.K. Lee, A. Mills, C.O. Rourke, Action spectra in semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46(16), 4877–4894 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support for this research from the General research project of Zhejiang Provincial Department of Education (Y201636639) and the Scientific Research Fund of Zhejiang Provincial Education Department (Y201224099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Liang, H., Shen, M. et al. Yolk-like Fe3O4@C–Au@void@TiO2–Pd hierarchical microspheres with visible light-assisted enhanced photocatalytic degradation of dye. Appl. Phys. A 124, 305 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1724-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1724-0