Abstract
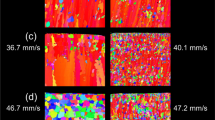
In the excimer laser carburizing process reported here, aluminum alloy samples have been treated in a propylene atmosphere, producing aluminum carbide surface layers. The layers have been characterized by nuclear reaction analysis that has shown carbon incorporation. X-ray diffraction at grazing incidence has evidenced aluminum carbide (Al4C3) phase. This study helps the understanding of the incorporation mechanisms of carbon in a surface. A micro-thermocapillary effect induced by heterogeneous surface formation has been evidenced. This original mass-transport phenomenon is very efficient in improving the carbon incorporation yield and hence in obtaining carbide layers several μm in thickness with a reduced laser pulse number. In order to obtain this micro-thermocapillary effect, the binary diagram of ceramic compounds must contain a peritectic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belmonte T, Lefèvre L, Czerwiec T, Michel H, Ricard A (1999) Thin Solid Films 341:27
Hermann J, Boulmer-Leborgne C, Mihailescu I, Dubreuil B (1993) J. Appl. Phys. 73:3
Thomann AL, Sicard E, Boulmer-Leborgne C, Vivien C, Hermann J, Andreazza-Vignolle C, Andreazza P, Meneau C (1997) Surf. Coat. Technol. 97:448
Sicard E, Boulmer-Leborgne C, Andreazza-Vignolle C, Andreazza P, Langlade C, Vannes B (1998) Surf. Coat. Technol. 100–101:440
Sicard E, Boulmer-Leborgne C, Sauvage T (1998) Appl. Surf. Sci. 127–129:726
Fariaut F, Boulmer-Leborgne C, Le Menn E, Sauvage T, Andreazza C, Andreazza P, Langlade C (2002) Appl. Surf. Sci. 186:105
Illgner C, Schaaf P, Lieb KP, Queitsch R, Barnickel J (1998) J. Appl. Phys. 83:2907
Schaaf P, Landry F, Lieb KP (1999) Appl. Phys. Lett. 74:153
Landry F, Lieb KP, Schaaf P (1999) J. Appl. Phys. 86:168
Carpene E, Landry F, Schaaf P (2000) Appl. Phys. Lett. 77:2412
Schaaf P (2002) Prog Mater Sci 47:1
Carpene E, Schaaf P (2002) Phys. Rev. B 65:224111
Morvan D, Cipriani FD, Bournot P (1994) Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 37:1973
Cipriani FD, Morvan D, Bournot P, Garino A (1990) in Proceedings of the First International Conference on Advanced Computational Methods in Heat Transfer, Southampton, UK, 17–20 July 1990, vol. 3, p. 15
R. Pawlak, M. Tomczyk, M. Walczak, Tranport mechanisms in the Laser aloying of metals, in Laser Technology VII: Applications of Lasers, ed. by W.L. Wolinski, Z. Jankiewitcz, R. Romaniuk, Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 5229, Technical Univ. of Lodz (Poland), pp. 255–259
Fariaut F, Boulmer-Leborgne C, Le Menn E, Sauvage T, Andreazza C, Andreazza P, Langlade C (2001) Surf. Coat. Technol. 146–147:324
Mayer M (1997) SIMNRA User’s Guide, Tech. Rep. IPP 9/113, Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, Garching, Germany
Bäuerle D (1996) Laser Processing and Chemistry. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Bin Mansoor S, Yilbas BS, Shuja SZ (2005) Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 32:822
Sarou-Kanian V, Millot F, Rifflet J-C (2003) Int J Thermophys 24:277
Lide PR (1993) Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 73rd edn. CRC, London
Drezet J-M, Pellerin S, Bezençon C, Mokadem S (2004) J. Phys. IV 120:299
Kalyon M, Yilbas BS (2003) Opt. Laser Eng. 39:109
Sim B-C, Kim W-S (2005) Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 48:1137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
65.20.+w; 52.38.Mf; 52.50.Jm
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fariaut, F., Boulmer-Leborgne, C., Semmar, N. et al. High-speed mass-transport phenomena during carburization of aluminum alloy by laser plasma treatment. Appl. Phys. A 83, 95–101 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-005-3461-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-005-3461-4