Abstract
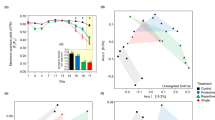
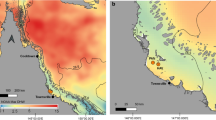
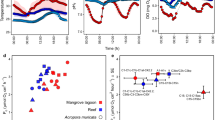
Rapid climate change due to anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions is pushing corals to and past their physiological limits, while their microbiome is being pressed towards dysbiosis. Microbes greatly influence the health and functioning of corals, but thermal anomalies that cause bleaching can affect certain taxa of the host-associated prokaryote and Symbiodiniaceae communities, leading corals towards a disease-prone state. In some coral species, however, even significant thermal stress may not result in visible signs of bleaching. Whether changes in the coral microbiome occur in these resilient species during temperature anomalies is not well described. In the present study, we tagged, visually assessed and sampled 10 colonies of the branching coral Pocillopora acuta on a fringing reef off Orpheus Island in the central Great Barrier Reef for 1 yr, of which the summer coincided with the 2016 mass-bleaching event. No visible signs of bleaching were observed in any of the 10 colonies throughout the study period, despite experiencing two degree heating weeks of thermal stress and observations of bleaching in other coral species on the same reef. Metabarcoding based on the Symbiodiniaceae ITS2 rDNA spacer and the bacterial 16S rRNA gene provided evidence for stability of the overall microbial community structure, although the bacterial community showed increases in a number of potentially beneficial taxa, such as diazotrophs, during the thermal stress event. These findings suggest some flexibility in the microbiome to adjust to higher than average temperatures without disrupting microbiome stability, perhaps contributing to the thermal resilience of P. acuta.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson AF, Lindberg M, Jakobsson H, Bäckhed F, Nyrén P, Engstrand L (2008) Comparative analysis of human gut microbiota by barcoded pyrosequencing. PLoS One 3:
Apprill A, Weber LG, Santoro AE (2016) Distinguishing between Microbial Habitats Unravels Ecological Complexity in Coral Microbiomes. mSystems 1:e00143-16
Arbizu PM (2017) pairwiseAdonis: Pairwise multilevel comparison using Adonis
Arif C, Daniels C, Bayer T, Banguera-Hinestroza E, Barbrook A, Howe CJ, Lajeunesse TC, Voolstra CR (2014) Assessing Symbiodinium diversity in scleractinian corals via next-generation sequencing-based genotyping of the ITS2 rDNA region. Mol Ecol 23:4418–4433
Ben-Haim Y, Rosenberg E (2002) A novel Vibrio sp. pathogen of the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Mar Biol 141:47–55
Berkelmans R, van Oppen MJ (2006) The role of zooxanthellae in the thermal tolerance of corals: a “nugget of hope” for coral reefs in an era of climate change. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 273:2305–2312
Boulotte NM, Dalton SJ, Carroll AG, Harrison PL, Putnam HM, Peplow LM, Oppen MJH Van (2016) Exploring the Symbiodinium rare biosphere provides evidence for symbiont switching in reef-building corals. Nature 1–9
Bourne D, Iida Y, Uthicke S, Smith-Keune C (2008) Changes in coral-associated microbial communities during a bleaching event. ISME J 2:350–363
Cai L, Zhou G, Tong H, Tian R, Zhang W, Ding W, Liu S (2018) Season structures prokaryotic partners but not algal symbionts in subtropical hard corals. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:4963–4973
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13:581
Coenye T, Vandamme P (2003) Diversity and significance of Burkholderia species occupying diverse ecological niches. Environ Microbiol 5:719–729
Cunning R, Silverstein RN, Baker AC (2018) Symbiont shuffling linked to differential photochemical dynamics of Symbiodinium in three Caribbean reef corals. Coral Reefs 37:145–152
De Cáceres M, Legendre P (2009) Associations between species and groups of sites: indices and statistical inference. Ecology 90:3566–3574
Fox J, Weisberg S (2011) An R companion to applied regression, second edition
Glasl B, Webster NS, Bourne DG (2017) Microbial indicators as a diagnostic tool for assessing water quality and climate stress in coral reef ecosystems. Mar Biol 164:1–18
Glynn PW (1984) Widespread Coral Mortality and the 1982–83 El Niño Warming Event. Environ Conserv 11:133
Graves S, Piepho H-P, Selzer L, Dorai-Raj S (2015) multcompView: Visualizations of paired comparisons
Grottoli AG, Martins PD, Wilkins MJ, Johnston MD, Warner ME, Cai WJ, Melman TF, Hoadley KD, Pettay DT, Levas S, Schoepf V (2018) Coral physiology and microbiome dynamics under combined warming and ocean acidification. PLoS One 13:1–22
Hadaidi G, Röthig T, Yum LK, Ziegler M, Arif C, Roder C, Burt J, Voolstra CR (2017) Stable mucus-associated bacterial communities in bleached and healthy corals of Porites lobata from the Arabian Seas. Sci Rep 7:1–11
Heron SF, Maynard JA, van Hooidonk R, Eakin CM (2016) Warming Trends and Bleaching Stress of the World’s Coral Reefs 1985–2012. Sci Rep 6:38402
Horn M, Harzenetter MD, Linner T, Schmid EN, Muller K-D, Michel R, Wagner M (2001) Members of the Cytophaga-Flavobacterium-Bacteroides phylum as intracellular bacteria of acanthamoebae: proposal of “Candidatus Amoebophilus asiaticus”. Environ Microbiol 3:440–449
Hughes TP, Kerry J, Álvarez-Noriega M, Álvarez-Romero J, Anderson K, Baird A, Babcock R, Beger M, Bellwood D, Berkelmans R, Bridge T, Butler I, Byrne M, Cantin N, Comeau S, Connolly S, Cumming G, Dalton S, Diaz-Pulido G, Eakin CM, Figueira W, Gilmour J, Harrison H, Heron S, Hoey AS, Hobbs J-P, Hoogenboom M, Kennedy E, Kuo C-Y, Lough J, Lowe R, Liu G, Malcolm McCulloch HM, McWilliam M, Pandolfi J, Pears R, Pratchett M, Schoepf V, Simpson T, Skirving W, Sommer B, Torda G, Wachenfeld D, Willis B, Wilson S (2017) Global warming and recurrent mass bleaching of corals. Nature 453:373–377
Huggett MJ, Apprill A (2018) Coral Microbiome Database: Integration of sequences reveals high diversity and relatedness of coral-associated microbes. Environ Microbiol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12686
Jones A, Berkelmans R, van Oppen MJ, Mieog J, Sinclair W (2008) A community change in the algal endosymbionts of a scleractinian coral following a natural bleaching event: field evidence of acclimatization. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 275:1359–1365
Klepac C, Beal J, Kenkel C, Sproles A, Polinski J, Williams M, Matz M, Voss J (2015) Seasonal stability of coral-Symbiodinium associations in the subtropical coral habitat of St. Lucie Reef. Florida. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 532:137–151
Kushmaro A, Banin E, Loya Y, Stackebrandt E, Rosenberg E (2001) Vibrio shiloi sp. nov., the causative agent of bleaching of the coral Oculina patagonica. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1383–1388
Kushmaro A, Loya Y, Fine M, Rosenberg E (1996) Bacterial infection and coral bleaching. Nature 380:396
Kushmaro A, Rosenberg E, Fine M, Loya Y (1997) Bleaching of the coral Oculina patagonica by Vibrio AK-1. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 147:159–165
LaJeunesse TC, Lee S, Bush S, Bruno JF (2005) Persistence of non-caribbean algal symbionts in Indo-Pacific mushroom corals released to Jamaica 35 years ago. Coral Reefs 24:157–159
LaJeunesse TC, Parkinson JE, Gabrielson PW, Jeong HJ, Reimer JD, Voolstra CR, Santos SR (2018) Systematic revision of Symbiodiniaceae highlights the antiquity and diversity of coral endosymbionts. Curr Biol 1–11
Lee MD, Walworth NG, Sylvan JB, Edwards KJ, Orcutt BN (2015) Microbial communities on seafloor basalts at Dorado Outcrop reflect level of alteration and highlight global lithic clades. Front Microbiol 6:1–20
Leite DCA, Leão P, Garrido AG, Lins U, Santos HF, Pires DO, Castro CB, van Elsas JD, Zilberberg C, Rosado AS, Peixoto RS (2017) Broadcast spawning coral Mussismilia Hispida can vertically transfer its associated bacterial core. Front Microbiol 8:1–12
Lema KA, Bourne DG, Willis BL (2014) Onset and establishment of diazotrophs and other bacterial associates in the early life history stages of the coral Acropora millepora. Mol Ecol 23:4682–4695
Lema KA, Willis BL, Bourneb DG (2012) Corals form characteristic associations with symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:3136–3144
Lenth RV (2016) Least-Squares Means: The R Package lsmeans. J Stat Softw 69:1–33
Littman R, Willis BL, Bourne DG (2011) Metagenomic analysis of the coral holobiont during a natural bleaching event on the Great Barrier Reef. Environ Microbiol Rep 3:651–660
Liu G, Rauenzahn J, Heron S, Eakin C, Skirving W, Christensen T, Strong A, Li J (2013) NOAA Technical Report NESDIS 143 NOAA Coral Reef Watch 50 km Satellite Sea Surface Temperature-Based Decision Support System for Coral Bleaching Management. 41
Magalon H, Flot J-F, Baudry E (2007) Molecular identification of symbiotic dinoflagellates in Pacific corals in the genus Pocillopora. Coral Reefs 26:551–558
Marcelino LA, Westneat MW, Stoyneva V, Henss J, Rogers JD, Radosevich A, Turzhitsky V, Siple M, Fang A, Swain TD, Fung J, Backman V (2013) Modulation of Light-Enhancement to Symbiotic Algae by Light-Scattering in Corals and Evolutionary Trends in Bleaching. PLoS One 8:e61492
McMurdie PJ, Holmes S (2013) phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS One 8:e61217
Meistertzheim AL, Lartaud F, Arnaud-Haond S, Kalenitchenko D, Bessalam M, Le Bris N, Galand PE (2016) Patterns of bacteria-host associations suggest different ecological strategies between two reef building cold-water coral species. Deep Res Part I Oceanogr Res Pap 114:12–22
Morrow KM, Bourne DG, Humphrey C, Botté ES, Laffy P, Zaneveld J, Uthicke S, Fabricius KE, Webster NS (2015) Natural volcanic CO2 seeps reveal future trajectories for host-microbial associations in corals and sponges. ISME J 9:894–908
Muscatine L, Porter JW (1977) Reef Corals: Mutualistic Symbioses Adapted to Nutrient-Poor Environments. Bioscience 27:454–460
Neave MJ, Apprill A, Ferrier-Pagès C, Voolstra CR (2016) Diversity and function of prevalent symbiotic marine bacteria in the genus Endozoicomonas. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:8315–8324
Neave MJ, Michell CT, Apprill A, Voolstra CR (2017) Endozoicomonas genomes reveal functional adaptation and plasticity in bacterial strains symbiotically associated with diverse marine hosts. Sci Rep 1–12
Oksanen J, Blanchet G, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin P, O’Hara R, Simpson G, Solymos P, Stevens H, Szoecs E, Wagner H (2018) vegan: Community ecology package
Oliver JK, Berkelmans R, Eakin CM, Coral bleaching in space and time, (2018) In: van Oppen MJH, Lough JM (eds) Coral bleaching: Patterns, processes, causes and consequences. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 21–39
Olson ND, Ainsworth TD, Gates RD, Takabayashi M (2009) Diazotrophic bacteria associated with Hawaiian Montipora corals: Diversity and abundance in correlation with symbiotic dinoflagellates. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 371:140–146
Pantos O, Bongaerts P, Dennis PG, Tyson GW, Hoegh-Guldberg O (2015) Habitat-specific environmental conditions primarily control the microbiomes of the coral Seriatopora hystrix. ISME J 9:1916–1927
Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D, R Core Team (2018) nlme: Linear and nonlinear mixed effects models
Pochon X, Pawlowski J, Zaninetti L, Rowan R (2001) High genetic diversity and relative specificity among Symbiodinium-like endosymbiotic dinoflagellates in soritid foraminiferans. Mar Biol 139:1069–1078
Pogoreutz C, Rädecker N, Cárdenas A, Gärdes A, Meyer JL, Wild C, Voolstra CR (2017) Nitrogen fixation aligns with nifH abundance and expression in two coral trophic functional groups. Front Microbiol. 8:1187
Pogoreutz C, Rädecker N, Cárdenas A, Gärdes A, Wild C, Voolstra CR (2018) Dominance of Endozoicomonas bacteria throughout coral bleaching and mortality suggests structural inflexibility of the Pocillopora verrucosa microbiome. Ecol Evol 8:2240–2252
QIIME2 Development Team (2017) QIIME2. < URL: http://qiime2.org>
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41:590–596
R Core Team (2018) R: A language and environmental for statistical computing
Rädecker N, Pogoreutz C, Voolstra CR, Wiedenmann J, Wild C (2015) Nitrogen cycling in corals: The key to understanding holobiont functioning? Trends Microbiol 23:490–497
Raina J-B, Tapiolas D, Willis BL, Bourne DG (2009) Coral-associated bacteria and their role in the biogeochemical cycling of sulfur. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3492–3501
Reshef L, Koren O, Loya Y, Zilber-Rosenberg I, Rosenberg E (2006) The Coral Probiotic Hypothesis. Environ Microbiol 8:2068–2073
Ritchie KB (2006) Regulation of microbial population by coral surface mucus and mucus-associated bacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 322:1–14
Roder C, Bayer T, Aranda M, Kruse M, Voolstra CR (2015) Microbiome structure of the fungid coral Ctenactis echinata aligns with environmental differences. Mol Ecol 3501–3511
Rognes T, Flouri T, Nichols B, Quince C, Mahé F (2016) VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ Prepr 4:e2409v1
Rosenberg E, Koren O, Reshef L, Efrony R, Zilber-Rosenberg I (2007) The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:355–362
Sampayo EM, Dove S, LaJeunesse TC (2009) Cohesive molecular genetic data delineate species diversity in the dinoflagellate genus Symbiodinium. Mol Ecol 18:500–519
Santos HF, Carmo FL, Duarte G, Dini-Andreote F, Castro CB, Rosado AS, van Elsas JD, Peixoto RS (2014) Climate change affects key nitrogen-fixing bacterial populations on coral reefs. ISME J 8:2272–2279
Schmitz-Esser S, Tischler P, Arnold R, Montanaro J, Wagner M, Rattei T, Horn M (2010) The genome of the amoeba symbiont “Candidatus Amoebophilus asiaticus” reveals common mechanisms for host cell interaction among amoeba-associated bacteria. J Bacteriol 192:1045–1057
Smith H, Epstein H, Torda G (2017) The molecular basis of differential morphology and bleaching thresholds in two morphs of the coral Pocillopora acuta. Sci Rep 7:1–12
Stat M, Pochon X, Cowie ROM, Gates RD (2009a) Specificity in communities of Symbiodinium in corals from Johnston Atoll. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 386:83–96
Stat M, Loh WKW, LaJeunesse TC, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Carter DA (2009b) Stability of coral–endosymbiont associations during and after a thermal stress event in the southern Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 28:709–713
Swain TD, DuBois E, Gomes A, Stoyneva VP, Radosevich AJ, Henss J, Wagner ME, Derbas J, Grooms HW, Velazquez EM, Traub J, Kennedy BJ, Grigorescu AA, Westneat MW, Sanborn K, Levine S, Schick M, Parsons G, Biggs BC, Rogers JD, Backman V, Marcelino LA (2016) Skeletal light-scattering accelerates bleaching response in reef-building corals. BMC Ecol 16:15–19
Thornhill DJ, Fitt WK, Schmidt GW (2006a) Highly stable symbioses among western Atlantic brooding corals. Coral Reefs 25:515–519
Thornhill DJ, Fitt WK, Schmidt GW (2006b) Highly stable symbioses among western Atlantic brooding corals. Coral Reefs 25:515–519
Tonk L, Bongaerts P, Sampayo EM, Hoegh-Guldberg O (2013) SymbioGBR: a web-based database of Symbiodinium associated with cnidarian hosts on the Great Barrier Reef. BMC Ecol 13:7
Torda G, Donelson JM, Aranda M, Barshis DJ, Bay L, Berumen ML, Bourne DG, Cantin N, Foret S, Matz M, Miller DJ, Moya A, Putnam HM, Ravasi T, Van Oppen MJH, Thurber RV, Vidal-Dupiol J, Voolstra CR, Watson SA, Whitelaw E, Willis BL, Munday PL (2017) Rapid adaptive responses to climate change in corals. Nat Clim Chang 7:627–636
Valliappan K, Sun W, Li Z (2014) Marine actinobacteria associated with marine organisms and their potentials in producing pharmaceutical natural products. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:7365–7377
van Oppen MJH, Oliver JK, Putnam HM, Gates RD (2015) Building coral reef resilience through assisted evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1–7
Vega Thurber R, Willner-Hall D, Rodriguez-Mueller B, Desnues C, Edwards RA, Angly F, Dinsdale E, Kelly L, Rohwer F (2009) Metagenomic analysis of stressed coral holobionts. Environ Microbiol 11:2148–2163
Webster NS, Negri AP, Botté ES, Laffy P, Flores F, Noonan S, Schmidt C, Uthicke S (2016) Host-associated coral reef microbes respond to the cumulative pressures of ocean warming and ocean acidification. Sci Rep 19324
Wickham H (2009) ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York
Wilson K, Li Y, Whan V, Lehnert S, Byrne K, Moore S, Ballment E, Fayazi Z, Swan J, Kenway M, Benzie J (2002) Genetic mapping of the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon with amplified fragment length polymorphism. Aquaculture 204:297–309
Ziegler M, Roik A, Porter A, Zubier K, Mudarris MS, Ormond R, Voolstra CR (2016) Coral microbial community dynamics in response to anthropogenic impacts near a major city in the central Red Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 105:629–640
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Coral Health Group at the Australian Institute of Marine Science for initial coral tagging, and K. Damjanovic, A. Hernandez-Agreda and H. Smith for statistical advice. This study was funded by Paul G. Allen Philanthropies and AIMS@JCU, the joint venture between James Cook University and the Australian Institute of Marine Science, as part of H.E.E’s PhD research. H.E.E acknowledges receipt of an AIMS@JCU Postgraduate Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Topic Editor Morgan S. Pratchett
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Epstein, H.E., Torda, G. & van Oppen, M.J.H. Relative stability of the Pocillopora acuta microbiome throughout a thermal stress event. Coral Reefs 38, 373–386 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-019-01783-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-019-01783-y