Abstract
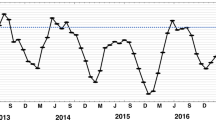
In the Wakatobi region of Indonesia, a prolonged period of elevated water temperature in 2016 caused extensive coral bleaching and mortality. Unusually, bleaching was also observed in the bioeroding sponge Cliona aff. viridis, with affected sponges expelling 99% of their Symbiodinium. Bleaching surveys of C. aff. viridis were conducted 6 weeks apart, coinciding with a 0.8 °C drop in water temperature. Over this period, bleaching prevalence dropped from 73.9% (± 9.9 SE) to 25.7% (± 5.8 SE), and bleaching severity dropped from 25.95% (± 4.5 SE) to 11.54% (± 1.9 SE) of sponge tissue. Over the same period, monitored bleached sponges showed an 81% drop in bleaching severity, but also a 13% reduction in overall sponge size. Our results show that while the clionaid–Symbiodinium relationship is susceptible to break down under thermal stress, rapid recovery can occur, although incurring some partial host mortality.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baird A, Marshall P (2002) Mortality, growth and reproduction in scleractinian corals following bleaching on the Great Barrier Reef. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 237:133–141
Carballo JL, Bautista E, Nava H, Cruz-Barraza JA, Chávez JA (2013) Boring sponges, an increasing threat for coral reefs affected by bleaching events. Ecol Evol 3:872–886
Chaves-Fonnegra A, Riegl B, Zea S, Lopez JV, Smith T, Brandt M, Gilliam DS (2018) Bleaching events regulate shifts from corals to excavating sponges in algae-dominated reefs. Glob Change Biol 24:773–785
Fang JK, Mello-Athayde MA, Schönberg CH, Kline DI, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Dove S (2013) Sponge biomass and bioerosion rates increase under ocean warming and acidification. Glob Change Biol 19:3581–3591
Fang JK, Schönberg CH, Mello-Athayde MA, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Dove S (2014) Effects of ocean warming and acidification on the energy budget of an excavating sponge. Glob Change Biol 20:1043–1054
Fang JK, Schönberg CH, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Dove S (2016) Day–night ecophysiology of the photosymbiotic bioeroding sponge Cliona orientalis Thiele, 1900. Mar Biol 163:1–12
Fang JK, Schönberg CH, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Dove S (2017) Symbiotic plasticity of Symbiodinium in a common excavating sponge. Mar Biol 164:104
Hill M, Walter C, Bartels E (2016) A mass bleaching event involving clionaid sponges. Coral Reefs 35:153
Hoegh-Guldberg O, Mumby PJ, Hooten AJ, Steneck RS, Greenfield P, Gomez E, Harvell CD, Sale PF, Edwards AJ, Caldeira K, Knowlton N, Eakin CM, Iglesias-Prieto R, Muthiga N, Bradbury RH, Dubi A, Hatziolos ME (2007) Coral reefs under rapid climate change and ocean acidification. Science 318:1737–1742
Hoogenboom MO, Frank GE, Chase TJ, Jurriaans S, Alvarez-Noriega M, Peterson K, Critchell K, Berry KL, Nicolet KJ, Ramsby B, Paley AS (2017) Environmental drivers of variation in bleaching severity of Acropora species during an extreme thermal anomaly. Glob Chang Biol 11:2251–2265
Hughes TP, Kerry JT, Álvarez-Noriega M, Álvarez-Romero JG, Anderson KD, Baird AH, Babcock RC, Beger M, Bellwood DR, Berkelmans R (2017) Global warming and recurrent mass bleaching of corals. Nature 543:373–377
Marlow J, Smith D, Werorilang S, Bell J (2018) Sedimentation limits the erosion rate of a bioeroding sponge. Mar Ecol 39:e12483
McMellor S, Smith DJ (2010) Coral reefs of the Wakatobi: Abundance and biodiversity. In: Clifton J, Unsworth RKF, Smith DJ (eds) Marine research and conservation in the Coral Triangle: The Wakatobi National Park. NOVA Science Publishers, New York, pp 11–26
McMurray SE, Blum JE, Leichter JJ, Pawlik JR (2011) Bleaching of the giant barrel sponge Xestospongia muta in the Florida Keys. Limnol Oceanogr 56:2243–2250
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Coral Reef Watch. http://www.ospo.noaa.gov/data/cb/TS_vs/vs_ts_Wakatobi_Indonesia.txt
Nakamura T, van Woesik R (2001) Water-flow rates and passive diffusion partially explain differential survival of corals during the 1998 bleaching event. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 212:301–304
Pineda MC, Strehlow B, Sternel M, Duckworth A, Jones R, Webster NS (2017) Effects of suspended sediments on the sponge holobiont with implications for dredging management. Sci Rep 7:4925
Riesgo A, Peterson K, Richardson C, Heist T, Strehlow B, McCauley M, Cotman C, Hill M, Hill A (2014) Transcriptomic analysis of differential host gene expression upon uptake of symbionts: a case study with Symbiodinium and the major bioeroding sponge Cliona varians. BMC Genomics 15:376
Rützler K (1990) Associations between Caribbean sponge and photosynthetic organisms. In: Rützler K (ed) New perspectives in sponge biology. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington DC, pp 455–466
Schönberg CHL, Ortiz J (2009) Is sponge bioerosion increasing. Proc 11th Int Coral Reef Symp 1:527–530
Schönberg CHL, Suwa R (2007) Why bioeroding sponges may be better hosts for symbiotic dinoflagellates than many corals. In: Custódio MR, Lôbo-Hajdu G, Hajdu E, Muricy G (eds) Porifera research: biodiversity, innovation and sustainability. Museu Nacional, Rio de Janeiro, pp 569–580
Schönberg CH, Suwa R, Hidaka M, Loh WKW (2008) Sponge and coral zooxanthellae in heat and light: preliminary results of photochemical efficiency monitored with pulse amplitude modulated fluorometry. Mar Ecol 29:247–258
Vicente V (1990) Response of sponges with autotrophic endosymbionts during the coral-bleaching episode in Puerto Rico. Coral Reefs 8:199–202
Weisz JB, Massaro AJ, Ramsby BD, Hill MS (2010) Zooxanthellar symbionts shape host sponge trophic status through translocation of carbon. Biol Bull 219:189–197
Wilson JR, Ardiwijaya RL, Prasetia R (2012) A study of the impact of the 2010 coral bleaching event on coral communities in Wakatobi National Park. The Nature Conservancy, Bali
Wisshak M, Schönberg C, Form AU, Freiwald A (2013) Effects of ocean acidification and global warming on reef bioerosion—lessons from a clionaid sponge. Aquat Biol 19:111–127
Wouthuyzen S, Abrar M, Lorwens J (2018) A comparison between the 2010 and 2016 El-Ninō induced coral bleaching in the Indonesian waters. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci 118:012051
Zamoum T, Furla P (2012) Symbiodinium isolation by NaOH treatment. J Exp Biol 215:3875–3880
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by a Victoria University of Wellington doctoral scholarship awarded to Joseph Marlow, the PADI Foundation, and facilitated by Operation Wallacea who provided travel funds and access to research facilities on Hoga, Indonesia. We would like to thank Christine Schönberg and Lisa Woods for their respective advice on sponge taxonomy and statistical analysis. We are also grateful to the reviewers of this manuscript, whose input improved it greatly. Research was conducted under a permit (182/SIP/FRP/E5/Dit.KI/VI/2016) from the Indonesian Ministry of Research and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Topic Editor Morgan S. Pratchett
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marlow, J., Davy, S.K., Shaffer, M. et al. Bleaching and recovery of a phototrophic bioeroding sponge. Coral Reefs 37, 565–570 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-018-1680-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-018-1680-3