Abstract
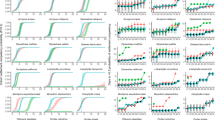
Coral settlement is a key process for the recovery and maintenance of coral reefs, yet interspecific variations in density-dependent settlement are unknown. Settlement of the submassive Goniastrea retiformis and corymbose Acropora digitifera and A. millepora was quantified at densities ranging from 1 to 50 larvae per 20 mL from 110 to 216 h following spawning. Settlement patterns were distinct for each species. Goniastrea settlement was rapid and increased linearly with time, whereas both Acropora spp. hardly settled until crustose coralline algae was provided. Both Goniastrea and A. digitifera showed positive density-dependent settlement, but the relationship was exponential for Goniastrea but linear for A. digitifera. Settlement was highest but density independent in A. millepora. Our results suggest that larval density can have significant effects on settler replenishment, and highlight variability in density-dependent settlement among corals with distinct functional traits as well as those with similar functional forms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez-Noriega M, Baird AH, Dornelas M, Madin JS, Cumbo VR, Connolly SR (2016) Fecundity and the demographic strategies of coral morphologies. Ecology 97:3485–3493
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software 67:1–48
Connell JH, Keough MJ (1985) Disturbance and patch dynamics of subtidal marine animals on hard substrata. In: Pickett STA, White PS (eds) The ecology of natural disturbance and patch dynamics. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 125–152
Connolly SR, Baird AH (2010) Estimating dispersal potential for marine larvae: dynamic models applied to scleractinian corals. Ecology 91:3572–3583
Courchamp F, Clutton-Brock T, Grenfell B (1999) Inverse density dependence and the Allee effect. Trends Ecol Evol 14:405–410
Darling ES, Alvarez-Filip L, Oliver TA, McClanahan TR, Cote IM (2012) Evaluating life-history strategies of reef corals from species traits. Ecol Lett 15:1378–1386
Done TJ (1982) Patterns in the distribution of coral communities across the central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 1:95–107
Doropoulos C, Ward S, Roff G, González-Rivero M, Mumby PJ (2015) Linking demographic processes of juvenile corals to benthic recovery trajectories in two common reef habitats. PLoS One 10:e0128535
Doropoulos C, Roff G, Bozec Y-M, Zupan M, Werminghausen J, Mumby PJ (2016) Characterizing the ecological trade-offs throughout the early ontogeny of coral recruitment. Ecol Monogr 86:20–44
Doropoulos C, Evensen NR, Gómez-Lemos LA, Babcock RC (2017) Density-dependent coral recruitment displays divergent responses during distinct early life-history stages. R Soc Open Sci 4:170082
Edwards AJ, Guest JR, Heyward AJ, Villanueva RD, Baria MV, Bollozos IS, Golbuu Y (2015) Direct seeding of mass-cultured coral larvae is not an effective option for reef rehabilitation. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 525:105–116
Figueiredo J, Baird AH, Connolly SR (2013) Synthesizing larval competence dynamics and reef-scale retention reveals a high potential for self-recruitment in corals. Ecology 94:650–659
Heyward AJ, Negri AP (1999) Natural inducers for coral larval metamorphosis. Coral Reefs 18:273–279
Hughes TP, Baird AH, Dinsdale EA, Moltschaniwskyj NA, Pratchett MS, Tanner JE, Willis BL (1999) Patterns of recruitment and abundance of corals along the Great Barrier Reef. Nature 397:59–63
Mason B, Beard M, Miller M (2011) Coral larvae settle at a higher frequency on red surfaces. Coral Reefs 30:667–676
Miller K, Mundy C (2003) Rapid settlement in broadcast spawning corals: implications for larval dispersal. Coral Reefs 22:99–106
Morse ANC, Iwao K, Baba M, Shimoike K, Hayashibara T, Omori M (1996) An ancient chemosensory mechanism brings new life to coral reefs. Biol Bull 191:149–154
Nozawa Y, Harrison PL (2005) Temporal settlement patterns of larvae of the broadcast spawning reef coral Favites chinensis and the broadcast spawning and brooding reef coral Goniastrea aspera from Okinawa, Japan. Coral Reefs 24:274–282
Oliver JK, Willis BL (1987) Coral-spawn slicks in the Great Barrier Reef—preliminary observations. Mar Biol 94:521–529
Pawlik JR (1992) Chemical ecology of the settlement of benthic marine invertebrates. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 30:273–335
R Development Core Team (2017) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Ritson-Williams R, Arnold SN, Paul VJ (2016) Patterns of larval settlement preferences and post-settlement survival for seven Caribbean corals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 548:127–138
Suzuki G, Arakaki S, Suzuki K, Iehisa Y, Hayashibara T (2012) What is the optimal density of larval seeding in Acropora corals? Fish Sci 78:801–808
Therneau TM (2015) coxme: Mixed effects Cox models. R package version 2:3
Wilson J, Harrison P (1998) Settlement-competency periods of larvae of three species of scleractinian corals. Mar Biol 131:339–345
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the Gorgon Barrow Island Net Conservation Benefits Fund administered by the Western Australian Department of Parks and Wildlife awarded to RCB and a CSIRO Office of the Chief Executive Postdoctoral Fellowship to CD. We thank Megan Huggett and Rachele Bernasconi from Edith Cowan University for field support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Biology Editor Dr. Anastazia Banaszak
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doropoulos, C., Gómez-Lemos, L.A. & Babcock, R.C. Exploring variable patterns of density-dependent larval settlement among corals with distinct and shared functional traits. Coral Reefs 37, 25–29 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-017-1629-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-017-1629-y