Abstract
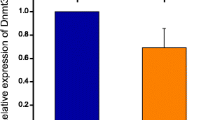
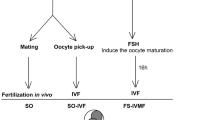
In vitro fertilization (IVF) and zona pellucida laser microdissection-facilitated IVF (Laser-IVF) are presently routine procedures in human assisted reproduction. The safety of these methods at the epigenetic level is not fully understood. Studies on mouse Laser-IVF embryos provide evidence that the use of Laser-IVF leads to reduced birth rate, indicating a potential harm of this technique for the embryo. Hence, the aim of this study was to examine the difference in DNA methylation pattern between IVF- and Laser-IVF-derived mouse zygotes. We examined two experimental groups of C3HeB/FeJ oocytes: (1) zona-intact and (2) laser-microdissected oocytes that were fertilized in vitro with freshly collected spermatozoa. Zygotes were fixed 5, 8, and 12 h after fertilization, and indirect immunofluorescence staining was studied using an anti-5-methylcytidine (5-MeC) antibody. The fluorescence intensities of paternal and maternal pronuclei were evaluated using the computer-assisted analysis of digital images. In addition, we performed a semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of the presence of transcripts of three developmental marker genes, Oct4, Dab2, and Dnmt3b, in IVF- and Laser-IVF-derived blastocysts. We observed no significant differences in methylation status of the paternal genome and in the transcripts of the developmental marker genes after IVF and Laser-IVF. In conclusion, epigenetic patterns and early embryonic development are not altered by laser-assisted IVF techniques and another explanation must be sought for the poor implantation rates observed in mice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adenot PG, Mercier Y, Renard JP, Thompson EM (1997) Differential H4 acetylation of paternal and maternal chromatin precedes DNA replication and differential transcriptional activity in pronuclei of 1-cell mouse embryos. Development 124:4615–4625
Boersma A, Marschall S, Hrabe de Angelis M (2007) Laser-assisted IVF—an alternative approach for successful cryopreservation of mutant mouse lines on C57BL/6 background. International Mouse Genome Conference, Kyoto, Japan, October 28 - November 1, 2007, P77
Depypere HT, McLaughlin KJ, Seamark RF, Warnes GM, Matthews CD (1988) Comparison of zona cutting and zona drilling as techniques for assisted fertilization in the mouse. J Reprod Fertil 84:205–211
Doherty AS, Mann MR, Tremblay KD, Bartolomei MS, Schultz RM (2000) Differential effects of culture on imprinted H19 expression in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Biol Reprod 62:1526–1535
el-Danasouri I, Westphal LM, Neev Y, Gebhardt J, Louie D et al (1993) Zona opening with 308 nm XeCl excimer laser improves fertilization by spermatozoa from long-term vasectomized mice. Hum Reprod 8:464–466
Enginsu ME, Schutze K, Bellanca S, Pensis M, Campo R et al (1995) Micromanipulation of mouse gametes with laser microbeam and optical tweezers. Hum Reprod 10:1761–1764
Fulka H, Fulka J (2006) No differences in the DNA methylation pattern in mouse zygotes produced in vivo, in vitro, or by intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil Steril 86:1534–1536
Germond M, Nocera D, Senn A, Rink K, Delacretaz G et al (1995) Microdissection of mouse and human zona pellucida using a 1.48-microns diode laser beam: efficacy and safety of the procedure. Fertil Steril 64:604–611
Germond M, Nocera D, Senn A, Rink K, Delacretaz G et al (1996) Improved fertilization and implantation rates after non-touch zona pellucida microdrilling of mouse oocytes with a 1.48 microm diode laser beam. Hum Reprod 11:1043–1048
Hirasawa R, Sasaki H (2009) Dynamic transition of Dnmt3b expression in mouse pre- and early post-implantation embryos. Gene Expr Patterns 9:27–30
Hollis A, Rastegar S, Descloux L, Delacretaz G, Rink K (1997) Zona pellucida microdrilling with a 1.48-micron diode laser. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag 16:43–47
Howlett SK, Reik W (1991) Methylation levels of maternal and paternal genomes during preimplantation development. Development 113:119–127
Hrabe de Angelis M, Balling R (1998) Large scale ENU screens in the mouse: genetics meets genomics. Mutat Res 400:25–32
Hrabe de Angelis MH, Flaswinkel H, Fuchs H, Rathkolb B, Soewarto D et al (2000) Genome-wide, large-scale production of mutant mice by ENU mutagenesis. Nat Genet 25:444–447
Kawase Y, Iwata T, Ueda O, Kamada N, Tachibe T et al (2002) Effect of partial incision of the zona pellucida by piezo-micromanipulator for in vitro fertilization using frozen-thawed mouse spermatozoa on the developmental rate of embryos transferred at the 2-cell stage. Biol Reprod 66:381–385
Kawase Y, Aoki Y, Kamada N, Jishage K, Suzuki H (2004) Comparison of fertility between intracytoplasmic sperm injection and in vitro fertilization with a partial zona pellucida incision by using a piezo-micromanipulator in cryopreserved inbred mouse spermatozoa. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci 43:21–25
Khosla S, Dean W, Brown D, Reik W, Feil R (2001a) Culture of preimplantation mouse embryos affects fetal development and the expression of imprinted genes. Biol Reprod 64:918–926
Khosla S, Dean W, Reik W, Feil R (2001b) Culture of preimplantation embryos and its long-term effects on gene expression and phenotype. Hum Reprod Update 7:419–427
Kishigami S, Van Thuan N, Hikichi T, Ohta H, Wakayama S et al (2006) Epigenetic abnormalities of the mouse paternal zygotic genome associated with microinsemination of round spermatids. Dev Biol 289:195–205
Landel CP (2005) Archiving mouse strains by cryopreservation. Lab Anim 34:50–57
Liow SL, Bongso A, Ng SC (1996) Fertilization, embryonic development and implantation of mouse oocytes with one or two laser-drilled holes in the zona, and inseminated at different sperm concentrations. Hum Reprod 11:1273–1280
Marschall S, Hrabe de Angelis M (1999) Cryopreservation of mouse spermatozoa: double your mouse space. Trends Genet 15:128–131
Marschall S, Huffstadt U, Balling R, Hrabe de Angelis M (1999) Reliable recovery of inbred mouse lines using cryopreserved spermatozoa. Mamm Genome 10:773–776
Mayer W, Niveleau A, Walter J, Fundele R, Haaf T (2000) Demethylation of the zygotic paternal genome. Nature 403:501–502
McGrath J, Solter D (1984) Completion of mouse embryogenesis requires both the maternal and paternal genomes. Cell 37:179–183
Nagy A, Gertsenstein M, Vintersten K, Behringer R (2003) Manipulating the mouse embryo. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Nakagata N (2000) Cryopreservation of mouse spermatozoa. Mamm Genome 11:572–576
Nakagata N, Takeshima T (1993) Cryopreservation of mouse spermatozoa from inbred and F1 hybrid strains. Jikken Dobutsu 42:317–320
Nakagata N, Okamoto M, Ueda O, Suzuki H (1997) Positive effect of partial zona-pellucida dissection on the in vitro fertilizing capacity of cryopreserved C57BL/6 J transgenic mouse spermatozoa of low motility. Biol Reprod 57:1050–1055
Nicklas W, Baneux P, Boot R, Decelle T, Deeny AA (2002) Recommendations for the health monitoring of rodent and rabbit colonies in breeding and experimental units. Lab Anim 36:20–42
Nolan PM, Peters J, Strivens M, Rogers D, Hagan J et al (2000) A systematic, genome-wide, phenotype-driven mutagenesis programme for gene function studies in the mouse. Nat Genet 25:440–443
Obruca A, Strohmer H, Sakkas D, Menezo Y, Kogosowski A et al (1994) Use of lasers in assisted fertilization and hatching. Hum Reprod 9:1723–1726
Oswald J, Engemann S, Lane N, Mayer W, Olek A et al (2000) Active demethylation of the paternal genome in the mouse zygote. Curr Biol 10:475–478
Payne D (1995) Micro-assisted fertilization. Reprod Fertil Dev 7:831–839
Peters DD, Marschall S, Mahabir E, Boersma A, Heinzmann U et al (2006) Risk assessment of mouse hepatitis virus infection via in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer by the use of zona-intact and laser-microdissected oocytes. Biol Reprod 74:246–252
Quinn P, Kerin JF, Warnes GM (1985) Improved pregnancy rate in human in vitro fertilization with the use of a medium based on the composition of human tubal fluid. Fertil Steril 44:493–498
Reik W, Walter J (2001) Genomic imprinting: parental influence on the genome. Nat Rev Genet 2:21–32
Reik W, Dean W, Walter J (2001) Epigenetic reprogramming in mammalian development. Science 293:1089–1093
Ribas RC, Taylor JE, McCorquodale C, Mauricio AC, Sousa M et al (2006) Effect of zona pellucida removal on DNA methylation in early mouse embryos. Biol Reprod 74:307–313
Santos F, Hendrich B, Reik W, Dean W (2002) Dynamic reprogramming of DNA methylation in the early mouse embryo. Dev Biol 241:172–182
Scholer HR, Dressler GR, Balling R, Rohdewohld H, Gruss P (1990) Oct-4: a germline-specific transcription factor mapping to the mouse t-complex. EMBO J 9:2185–2195
Szczygiel MA, Kusakabe H, Yanagimachi R, Whittingham DG (2002) Intracytoplasmic sperm injection is more efficient than in vitro fertilization for generating mouse embryos from cryopreserved spermatozoa. Biol Reprod 67:1278–1284
Sztein JM, Farley JS, Mobraaten LE (2000) In vitro fertilization with cryopreserved inbred mouse sperm. Biol Reprod 63:1774–1780
Thornton CE, Brown SD, Glenister PH (1999) Large numbers of mice established by in vitro fertilization with cryopreserved spermatozoa: implications and applications for genetic resource banks, mutagenesis screens, and mouse backcrosses. Mamm Genome 10:987–992
Wrenzycki C, Herrmann D, Carnwath JW, Niemann H (1999) Alterations in the relative abundance of gene transcripts in preimplantation bovine embryos cultured in medium supplemented with either serum or PVA. Mol Reprod Dev 53(1):8–18
Yanagimachi R (1998) Intracytoplasmic sperm injection experiments using the mouse as a model. Hum Reprod 13(Suppl 1):87–98
Yang DH, Smith ER, Roland IH, Sheng Z, He J et al (2002) Disabled-2 is essential for endodermal cell positioning and structure formation during mouse embryogenesis. Dev Biol 251:27–44
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the European Commission under FP6, by EMMA inf (RII3-CT-2004-506455) to MHdA and by a grant from the National Genome Research Network, NGFN + (01GS0850), to MHdA. We thank Stefanie Dunst, Monika Beschorner, Andrea Bäßler, Alexander Huber, and Bernhard Rey for excellent technical assistance. We are grateful to John Favor for valuable comments on this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peters, D.D., Lepikhov, K., Rodenacker, K. et al. Effect of IVF and laser zona dissection on DNA methylation pattern of mouse zygotes. Mamm Genome 20, 664–673 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-009-9227-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-009-9227-0