Abstract
Objectives
To identify the complication rate associated with US-guided core needle biopsy (CNB) of thyroid lesions using a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
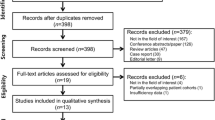
Ovid-MEDLINE and EMBASE databases were searched for studies on US-guided CNB of thyroid lesions from 1 January 1994–13 December 2016. A review of 393 potential papers identified 39 eligible papers including 14,818 patients. The pooled proportions of complications were assessed using random-effects modelling. Subgroup analysis was performed. Among-study heterogeneity was explored using χ2 statistic for pooled estimates and inconsistency index I2. Quality of the studies was evaluated using the Risk of Bias Assessment Tool for Nonrandomized Studies.
Results
The pooled proportion of overall complications after CNB of thyroid lesions was 1.11% (95% CI: 0.64–1.51, I2: 87.2%). The pooled proportion of major complications (0.06% [95% CI: 0.02–0.10], I2: 0.0%) was much lower than that of minor complications (1.08%[95% CI: 0.63–1.53], I2: 93.17%). Subgroup analysis revealed no significant differences between studies on Asian versus non-Asian groups (p=0.7769), radiologist versus non-radiologist groups (p=0.8607), nodule size <20 mm versus nodule size ≥20 mm (p=0.1591) groups, CNB versus CNB-plus-FNA groups (p=0.9281) and studies performed before and after 2012 (p=0.6251). The overall quality of the included studies was moderate with all of the studies satisfying five or more of the eight total domains.
Conclusion
Various complications can occur after US-guided CNB of thyroid lesions. However, the procedure is safe, with a low complication rate.
Key Points
• Various complications occurred after CNB of thyroid lesions, but the pooled complication rate was low (1.11%, I 2 = 87.2%).
• The pooled proportion of major complications (0.06%) was much lower than that of minor complications (1.08%).
• There was no significant differences between studies on Asian vs. non-Asian groups, radiologist vs. non-radiologist groups, nodule size <20 mm vs. nodule size ≥20 mm groups, CNB vs. CNB-plus-FNA groups, or studies performed before 2012 vs. after 2012.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CNB:
-
Core needle biopsy
- FNA:
-
Fine-needle aspiration
- US:
-
Ultrasound
References
Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC et al (2016) 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 26:1–133
Shin JH, Baek JH, Chung J et al (2016) Ultrasonography Diagnosis and Imaging-Based Management of Thyroid Nodules: Revised Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology Consensus Statement and Recommendations. Korean J Radiol 17:370–395
Gharib H, Papini E, Garber JR et al (2016) American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, American College of Endocrinology, and Associazione Medici Endocrinologi Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for the Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Nodules--2016 Update. Endocr Pract 22:622–639
Na DG, Baek JH, Jung SL et al (2017) Core Needle Biopsy of the Thyroid: 2016 Consensus Statement and Recommendations from Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology. Korean J Radiol 18:217–237
Kim SY, Park JE, Lee YJ et al (2013) Testing a tool for assessing the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies showed moderate reliability and promising validity. J Clin Epidemiol 66:408–414
Suh CH, Park SH (2016) Successful Publication of Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy. Korean J Radiol 17:5–6
Lee J, Kim KW, Choi SH, Huh J, Park SH (2015) Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy: A Practical Review for Clinical Researchers-Part II. Statistical Methods of Meta-Analysis. Korean J Radiol 16:1188–1196
Kim KW, Lee J, Choi SH, Huh J, Park SH (2015) Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies Evaluating Diagnostic Test Accuracy: A Practical Review for Clinical Researchers-Part I. General Guidance and Tips. Korean J Radiol 16:1175–1187
Higgins J GS (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from: http://handbook.cochrane.org.
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Duval S, Tweedie R (2000) Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 56:455–463
Ahn D, Sohn JH, Yeo CK, Jeon JH (2016) Feasibility of surgeon-performed ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy in the thyroid and lymph nodes. Head Neck 38:E1413–E1418
Aysan E, Kiran T, Idiz UO et al (2017) The diagnostic ability of core needle biopsy in nodular thyroid disease. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 99:233–236
Carpi A, Rossi G, Nicolini A, Iervasi G, Russo M, Mechanick J (2013) Does large needle aspiration biopsy add pain to the thyroid nodule evaluation? PLoS One 8:e58016
Chen BT, Jain AB, Dagis A et al (2015) Comparison of the efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy versus fine-needle aspiration for evaluating thyroid nodules. Endocr Pract 21:128–135
Ha EJ, Baek JH, Lee JH et al (2017) Complications following US-guided core-needle biopsy for thyroid lesions: a retrospective study of 6,169 consecutive patients with 6,687 thyroid nodules. Eur Radiol 27:1186–1194
Hahn SY, Shin JH, Han BK, Ko EY, Ko ES (2013) Ultrasonography-guided core needle biopsy for the thyroid nodule: does the procedure hold any benefit for the diagnosis when fine-needle aspiration cytology analysis shows inconclusive results? Br J Radiol 86:20130007
Hahn SY, Shin JH, Lim HK, Jung SL (2017) Follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma: comparison of ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy and ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration in a multicentre study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 86:113–119
Han S, Shin JH, Hahn SY, Oh YL (2016) Modified Core Biopsy Technique to Increase Diagnostic Yields for Well-Circumscribed Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules: A Retrospective Analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37:1155–1159
Harvey JN, Parker D, De P, Shrimali RK, Otter M (2005) Sonographically guided core biopsy in the assessment of thyroid nodules. J Clin Ultrasound 33:57–62
Karstrup S, Balslev E, Juul N, Eskildsen PC, Baumbach L (2001) US-guided fine needle aspiration versus coarse needle biopsy of thyroid nodules. Eur J Ultrasound 13:1–5
Khoo TK, Baker CH, Hallanger-Johnson J et al (2008) Comparison of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy with core-needle biopsy in the evaluation of thyroid nodules. Endocr Pract 14:426–431
Kim HC, Kim YJ, Han HY et al (2017) First-Line Use of Core Needle Biopsy for High-Yield Preliminary Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 38:357–363
Kim SY, Lee HS, Moon J et al (2017) Fine-needle aspiration versus core needle biopsy for diagnosis of thyroid malignancy and neoplasm: a matched cohort study. Eur Radiol 27:801–811
Lee KH, Shin JH, Oh YL, Hahn SY (2014) Atypia of undetermined significance in thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology: prediction of malignancy by US and comparison of methods for further management. Ann Surg Oncol 21:2326–2331
Lee SH, Kim MH, Bae JS, Lim DJ, Jung SL, Jung CK (2014) Clinical outcomes in patients with non-diagnostic thyroid fine needle aspiration cytology: usefulness of the thyroid core needle biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol 21:1870–1877
Lee SH, Park GS, Jung SL et al (2016) Core-needle biopsy for the preoperative diagnosis of follicular neoplasm in thyroid nodule screening: a validation study. Pathology – Research and Practice
Liu Q, Castelli M, Gattuso P, Prinz RA (1995) Simultaneous fine-needle aspiration and core-needle biopsy of thyroid nodules. Am Surg 61:628–632 discussion 632-623
Mehrotra P, Hubbard JG, Johnson SJ, Richardson DL, Bliss R, Lennard TW (2005) Ultrasound scan-guided core sampling for diagnosis versus freehand FNAC of the thyroid gland. Surgeon 3:1–5
Min HS, Kim JH, Ryoo I, Jung SL, Jung CK (2014) The role of core needle biopsy in the preoperative diagnosis of follicular neoplasm of the thyroid. Apmis 122:993–1000
Na DG, Min HS, Lee H, Won JK, Seo HB, Kim JH (2015) Role of Core Needle Biopsy in the Management of Atypia/Follicular Lesion of Undetermined Significance Thyroid Nodules: Comparison with Repeat Fine-Needle Aspiration in Subcategory Nodules. Eur Thyroid J 4:189–196
Na DG, Kim DS, Kim SJ, Ryoo JW, Jung SL (2016) Thyroid nodules with isolated macrocalcification: malignancy risk and diagnostic efficacy of fine-needle aspiration and core needle biopsy. Ultrasonography 35:212–219
Nasrollah N, Trimboli P, Rossi F et al (2014) Patient's comfort with and tolerability of thyroid core needle biopsy. Endocrine 45:79–83
Paja M, del Cura JL, Zabala R et al (2016) Ultrasound-guided core-needle biopsy in thyroid nodules. A study of 676 consecutive cases with surgical correlation. Eur Radiol 26:1–8
Park KT, Ahn SH, Mo JH et al (2011) Role of core needle biopsy and ultrasonographic finding in management of indeterminate thyroid nodules. Head Neck 33:160–165
Pisani T, Bononi M, Nagar C, Angelini M, Bezzi M, Vecchione A (2000) Fine needle aspiration and core needle biopsy techniques in the diagnosis of nodular thyroid pathologies. Anticancer Res 20:3843–3847
Quinn SF, Nelson HA, Demlow TA (1994) Thyroid biopsies: fine-needle aspiration biopsy versus spring-activated core biopsy needle in 102 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol 5:619–623
Renshaw AA, Pinnar N (2007) Comparison of thyroid fine-needle aspiration and core needle biopsy. Am J Clin Pathol 128:370–374
Samir AE, Vij A, Seale MK et al (2012) Ultrasound-guided percutaneous thyroid nodule core biopsy: clinical utility in patients with prior nondiagnostic fine-needle aspirate. Thyroid 22:461–467
Screaton NJ, Berman LH, Grant JW (2003) US-guided core-needle biopsy of the thyroid gland. Radiology 226:827–832
Stangierski A, Wolinski K, Martin K, Leitgeber O, Ruchala M (2013) Core needle biopsy of thyroid nodules - evaluation of diagnostic utility and pain experience. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 34:798–801
Strauss EB, Iovino A, Upender S (2008) Simultaneous fine-needle aspiration and core biopsy of thyroid nodules and other superficial head and neck masses using sonographic guidance. AJR Am J Roentgenol 190:1697–1699
Sung JY, Na DG, Kim KS et al (2012) Diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration versus core-needle biopsy for the diagnosis of thyroid malignancy in a clinical cohort. Eur Radiol 22:1564–1572
Taki S, Kakuda K, Kakuma K et al (1997) Thyroid nodules: evaluation with US-guided core biopsy with an automated biopsy gun. Radiology 202:874–877
Trimboli P, Guidobaldi L, Amendola S et al (2016) Galectin-3 and HBME-1 improve the accuracy of core biopsy in indeterminate thyroid nodules. Endocrine 52:39–45
Yi KS, Kim JH, Na DG et al (2015) Usefulness of Core Needle Biopsy for Thyroid Nodules with Macrocalcifications: Comparison with Fine-Needle Aspiration. Thyroid 25:657–664
Yousaf U, Christensen LH, Rasmussen AK et al (2008) Immunohistochemical staining for thyroid peroxidase (TPO) of needle core biopsies in the diagnosis of scintigraphically cold thyroid nodules. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 68:996–1001
Yunker WK, Hassan SF, Ferrell LB et al (2013) Needle core biopsy in the diagnosis of pediatric thyroid neoplasms: a single institution retrospective review. Pediatr Surg Int 29:437–443
Zhang M, Zhang Y, Fu S, Lv F, Tang J (2014) Thyroid nodules with suspicious ultrasound findings: the role of ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy. Clin Imaging 38:434–438
Zhang S, Ivanovic M, Nemcek AA Jr, Defrias DV, Lucas E, Nayar R (2008) Thin core needle biopsy crush preparations in conjunction with fine-needle aspiration for the evaluation of thyroid nodules: a complementary approach. Cancer 114:512–518
Jun YK, Jung SL, Byun HK, Baek JH, Sung JY, Sim JS (2016) Radiofrequency Ablation for Iatrogenic Thyroid Artery Pseudoaneurysm: Initial Experience. J Vasc Interv Radiol 27:1613–1617
Polyzos SA, Anastasilakis AD (2009) Clinical complications following thyroid fine-needle biopsy: a systematic review. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 71:157–165
Ha EJ, Baek JH, Lee JH (2015) Ultrasonography-Based Thyroidal and Perithyroidal Anatomy and Its Clinical Significance. Korean J Radiol 16:749–766
Funding
The authors state that this work has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Jung Hwan Baek.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
Chong Hyun Suh performed statistical analysis for this paper.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was not required for this study because this study was designed as a systematic review with meta-analysis.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was not required because this study was designed as a systematic review with meta-analysis.
Methodology
• systematic review with meta-analysis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ha, E.J., Suh, C.H. & Baek, J.H. Complications following ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy of thyroid nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 28, 3848–3860 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5367-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5367-5