Abstract
Objectives
To build a reliable radiomics model from multiregional and multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for pretreatment prediction of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promotor methylation status in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM).
Methods
In this retrospective multicentre study, 1,705 multiregional radiomics features were automatically extracted from multiparametric MRI. A radiomics model with a minimal set of all-relevant features and a radiomics model with univariately-predictive and non-redundant features were built for MGMT methylation prediction from a primary cohort (133 patients) and tested on an independent validation cohort (60 patients). Predictive models combing clinical factors were built and evaluated. Both radiomics models were assessed on subgroups stratified by clinical factors.
Results
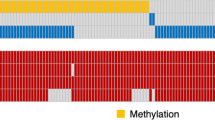
The radiomics model with six all-relevant features allowed pretreatment prediction of MGMT methylation (AUC=0.88, accuracy=80 %), which significantly outperformed the model with eight univariately-predictive and non-redundant features (AUC=0.76, accuracy=70 %). Combing clinical factors with radiomics features did not benefit the prediction performance. The all-relevant model achieved significantly better performance in stratified analysis.
Conclusions
Radiomics model built from multiregional and multiparameter MRI may serve as a potential imaging biomarker for pretreatment prediction of MGMT methylation in GBM. The all-relevant features have the potential of offering better predictive power than the univariately-predictive and non-redundant features.
Key Points
• Multiregional and multiparametric MRI features reliably predicted MGMT methylation in multicentre cohorts.
• All-relevant imaging features predicted MGMT methylation better than univariately-predictive and non-redundant features.
• Combing clinical factors with radiomics features did not benefit the prediction performance.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUC:
-
Area under the ROC curve
- FLAIR:
-
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma multiforme
- GLCM:
-
Grey-level co-occurrence matrix
- GLRLM:
-
Grey-level run length matrix
- GLSZM:
-
Grey level size zone matrix
- KPS:
-
Karnofsky performance score
- MGMT:
-
O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NGTDM:
-
Neighbourhood grey-tone difference matrix
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic curve
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- TCIA:
-
The Cancer Imaging Archive
- VASARI:
-
Visually Accusable Rembrandt Images
References
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Xu J, et al (2016) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2009–2013. Neuro Oncol 18:v1–v75
Reardon DA, Wen PY (2015) Glioma in 2014: unravelling tumour heterogeneity-implications for therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 12:69–70
Weller M, Stupp R, Reifenberger G et al (2010) MGMT promoter methylation in malignant gliomas: ready for personalized medicine? Nat Rev Neurol 6:39–51
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T et al (2005) MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:997–1003
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP et al (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10:459–466
Sottoriva A, Spiteri I, Piccirillo SG et al (2013) Intratumor heterogeneity in human glioblastoma reflects cancer evolutionary dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:4009–4014
Patel AP, Tirosh I, Trombetta JJ et al (2014) Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science 344:1396–1401
Dunn J, Baborie A, Alam F et al (2009) Extent of MGMT promoter methylation correlates with outcome in glioblastomas given temozolomide and radiotherapy. Brit J Cancer 101:124–131
Parker NR, Hudson AL, Khong P et al (2016) Intratumoral heterogeneity identified at the epigenetic, genetic and transcriptional level in glioblastoma. Sci Rep 6:22477
Drabycz S, Roldán G, De Robles P et al (2010) An analysis of image texture, tumor location, and MGMT promoter methylation in glioblastoma using magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 49:1398–1405
Carrillo JA, Lai A, Nghiemphu PL et al (2012) Relationship between tumor enhancement, edema, IDH1 mutational status, MGMT promoter methylation, and survival in glioblastoma. Am J Neuroradiol 33:1349–1355
Moon WJ, Choi JW, Roh HG, Lim SD, Koh YC (2012) Imaging parameters of high grade gliomas in relation to the MGMT promoter methylation status: the CT, diffusion tensor imaging, and perfusion MR imaging. Neuroradiology 54:555–563
Korfiatis P, Kline TL, Coufalova L et al (2016) MRI texture features as biomarkers to predict MGMT methylation status in glioblastomas. Med Phys 43:2835–2844
Kanas VG, Zacharaki EI, Thomas GA, Zinn PO, Megalooikonomou V, Colen RR (2017) Learning MRI-based classification models for MGMT methylation status prediction in glioblastoma. Comput Meth Prog Bio 140:249–257
VASARI Research Project, Available via https://wiki.cancerimagingarchive.net/display/Public/VASARI+Research+Project. Accessed 2 June 2017
Lambin P, Leijenaar RT, Deist TM et al (2017) Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14:749–762
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2015) Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278:563–577
Aerts HJ, Velazquez ER, Leijenaar RT et al (2014) Decoding tumour phenotype by non-invasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat Comm 5
Itakura H, Achrol AS, Mitchell LA et al (2015) Magnetic resonance image features identify glioblastoma phenotypic subtypes with distinct molecular pathway activities. Sci Transl Med 7:303ra138–303ra138
Cui Y, Tha KK, Terasaka S et al (2015) Prognostic imaging biomarkers in glioblastoma: development and independent validation on the basis of multiregion and quantitative analysis of MR images. Radiology 278:546–553
Li Q, Bai H, Chen Y et al (2017) A Fully-Automatic Multiparametric Radiomics Model: Towards Reproducible and Prognostic Imaging Signature for Prediction of Overall Survival in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Sci Rep 7:14331
Kickingereder P, Götz M, Muschelli J et al (2016) Large-scale radiomic profiling of recurrent glioblastoma identifies an imaging predictor for stratifying anti-angiogenic treatment response. Clin Cancer Res 22:5765–5771
Cui Y, Ren S, Tha KK, Wu J, Shirato H, Li R (2017) Volume of high-risk intratumoral subregions at multi-parametric MR imaging predicts overall survival and complements molecular analysis of glioblastoma. Eur Radiol 27:3583–3592
Yoon RG, Kim HS, Paik W, Shim WH, Kim SJ, Kim JH (2017) Different diagnostic values of imaging parameters to predict pseudoprogression in glioblastoma subgroups stratified by MGMT promoter methylation. Eur Radiol 27:255–266
Prasanna P, Patel J, Partovi S, Madabhushi A, Tiwari P (2017) Radiomic features from the peritumoral brain parenchyma on treatment-naïve multi-parametric MR imaging predict long versus short-term survival in glioblastoma multiforme: Preliminary findings. Eur Radiol 27:4188–4197
Vartanian A, Singh SK, Agnihotri S et al (2014) GBM's multifaceted landscape: highlighting regional and microenvironmental heterogeneity. Neuro-oncology 16:1167–1175
Gatenby RA, Grove O, Gillies RJ (2013) Quantitative imaging in cancer evolution and ecology. Radiology 269:8–14
Lemée JM, Clavreul A, Menei P (2015) Intratumoral heterogeneity in glioblastoma: don't forget the peritumoral brain zone. Neuro-oncology 17:1322–1332
Havik AB, Brandal P, Honne H et al (2012) MGMT promoter methylation in gliomas-assessment by pyrosequencing and quantitative methylation-specific PCR. J Transl Med 10:36
Tustison NJ, Avants BB, Cook PA et al (2010) N4ITK: improved N3 bias correction. IEEE T Med Imaging 29:1310–1320
Lötjönen JM, Wolz R, Koikkalainen JR et al (2010) Fast and robust multi-atlas segmentation of brain magnetic resonance images. NeuroImage 49:2352–2365
Pereira S, Pinto A, Alves V, Silva CA (2016) Brain tumor segmentation using convolutional neural networks in MRI images. IEEE T Med Imaging 35:1240–1251
Menze BH, Jakab A, Bauer S et al (2015) The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE T Med Imaging 34:1993–2024
Abadi M, Agarwal A, Barham P et al (2016) Tensorflow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems. arXiv preprint:1603.04467
Kursa MB, Rudnicki WR (2010) Feature selection with the Boruta package. J Stat Softw 36:1–13
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32
DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL (1988) Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics:837-845
Nilsson R, Peña JM, Björkegren J, Tegnér J (2007) Consistent feature selection for pattern recognition in polynomial time. J Mach Learn Res 8:589–612
Kursa MB (2014) Robustness of Random Forest-based gene selection methods. BMC bioinformatics 15:8
Guo P, Luo Y, Mai G et al (2014) Gene expression profile based classification models of psoriasis. Genomics 103:48–55
Baessler B, Mannil M, Oebel S, Maintz D, Alkadhi H, Manka R (2017) Subacute and Chronic Left Ventricular Myocardial Scar: Accuracy of Texture Analysis on Nonenhanced Cine MR Images. Radiology https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017170213
Yamamoto S, Korn RL, Oklu R et al (2014) ALK molecular phenotype in non–small cell lung cancer: CT radiogenomic characterization. Radiology 272:568–576
Falconer DS, Mackay TFC (1996) Introduction to Genetics, Fourth edn. Addison Wesley Longman, Harlow, Essex, UK
Burrell RA, McGranahan N, Bartek J, Swanton C (2013) The causes and consequences of genetic heterogeneity in cancer evolution. Nature 501:338–345
McCarthy N (2012) Tumour heterogeneity: Darwin's finches. Nat Rev Cancer 12:317–317
Polyak K (2014) Tumor heterogeneity confounds and illuminates: a case for Darwinian tumor evolution. Nat Med 20:344–346
Reifenberger G, Hentschel B, Felsberg J et al (2012) Predictive impact of MGMT promoter methylation in glioblastoma of the elderly. Int J Cancer 131:1342–1350
O'connor JP, Aboagye EO, Adams JE et al (2016) Imaging biomarker roadmap for cancer studies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14:169–186
Funding
This study received funding by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61571432), National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2015CB755500), and Shenzhen Basic Research Program (JCYJ20170413162354654).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Guarantor
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Hairong Zheng.
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Statistics and biometry
One of the authors (Zhi-Cheng Li) has significant statistical expertise.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained from the three local institutions. Institutional Review Board approval for the TCIA data was not required.
Methodology
• Retrospective
• Diagnostic or prognostic study
• Multicentre study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, ZC., Bai, H., Sun, Q. et al. Multiregional radiomics features from multiparametric MRI for prediction of MGMT methylation status in glioblastoma multiforme: A multicentre study. Eur Radiol 28, 3640–3650 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5302-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5302-1