Abstract
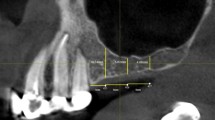
The accuracy of panoramic radiography (RX) and ultrasound (US) in the evaluation of both the length of the osteotomic gap and the quality of new bone formation in patients undergoing mandibular distraction osteogenesis (DO) was assessed, verifying the results against intraoperative and histologic findings. In 31 patients, three RX and three US examinations were performed after DO. RX and US findings were each independently compared, at the time of distractor removal, to the direct intraoperative measurement of the osteotomic gap and to the histologic evaluation of the maturity of a resected specimen. No significant differences (P > 0.1) resulted at any step between RX (average length: 18.19 mm) and US (18.29 mm) measurement of the osteotomic gap. In the assessment of the callus maturity the difference between RX and US (P < 0.001) was statistically significant: at the final control the maturity score averaged 0.612 at RX, 3 at US and 3 at histology. RX and US are equally reliable in the measurement of the osteotomic gap, while US is much more accurate than RX in the evaluation of the callus maturity. US-based follow-up might allow a safe shortening of the fixation period.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ilizarov GA, Soibel’man LM (1969) Some clinical and experimental data on the bloodless lengthening of lower extremities. Eksp Khir Anesteziol 14:27–32
McCarthy JG, Schreiber J, Karp N, Thorne CH, Grayson BH (1992) Lengthening the human mandible by gradual distraction. Plast Reconstr Surg 89:1–8
McTavish J, Marucci DD, Bonar SF, Walsh WR, Poole MD (2000) Does the sheep mandible relapse following lengthening by distraction osteogenesis? J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:251–257
Troulis MJ, Perrott DH, Kaban LB (1999) Endoscopic mandibular osteotomy, and placement and activation of a semiburied distractor. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 57:1110–1113
Castano FJ, Troulis MJ, Glowacki J, Kaban LB, Yates KE (2001) Proliferation of masseter myocytes after distraction osteogenesis of the porcine mandible. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 59:302–307
Tavakoli K, Walsh WR, Bonar F, Smart R, Wulf S, Poole MD (1998) The role of latency in mandibular osteodistraction. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 26:209–219
Ilizarov GA (1989) The tension-stress effect on the genesis and growth of tissues. Part II: the influence of the rate and frequency of distraction. Clin Orthop 238:263–285
Padwa BL, Kearns GJ, Todd R, Troulis MJ, Mulliken JB, Kaban LB (1999) Simultaneous maxillary and mandibular distraction osteogenesis: a technique and case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 28:2–8
Mofid MM, Manson PM, Robertson BC, Tufaro AP, Elias JJ, Vanderkolk CA (2001) Craniofacial distraction osteogenesis: a review of 3278 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 108:1103–1114
Troulis MJ, Glowacki J, Perrott DH, Kaban LB (2000) Effects of latency and rate on bone formation in a porcine mandibular distraction model. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:507–513
Maffulli N, Hughes TH, Fixsen JA (1992) Ultrasonographic monitoring of limb lengthening. J Bone Joint Surg 74:130–132
Nicholls PJ, Berg E, Bliven FE, Kling JM (1979) X-ray diagnosis of healing fractures in rabbits. Clin Orthop 142:234–236
Derbyshire ND, Simpson AH (1992) A role for ultrasound in limb lengthening. Br J Radiol 65:576–580
Malde HM, Hemmadi SS, Chadda D, Parihar ML, Bhosale PB, Kedar RP (1993) The role of skeletal sonography in limb lengthening procedures. J Postgrad Med 39:127–129
Troulis MJ, Coppe C, O’Neill MJ, Kaban LB (2003) Ultrasound: assessment of the distraction osteogenesis wound in patients undergoing mandibular lengthening. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:1144–1149
Juenger TH, Klingmueller V, Howaldt HP (1999) Application of ultrasound in callus distraction of the hypoplastic mandible: an additional method for the follow-up. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 27:160–167
Nocini PF, Albanese M, Wangerin K, Fior A, Trevisiol L, Kretschmer W (2002) Distraction osteogenesis of the mandible: evaluation of callus distraction by B-scan ultrasonography. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 30:286–291
Hughes TH, Maffulli N, Green V, Fixsen JA (1994) Imaging in bone lengthening. Clin Orthop 308:50–53
Smith SW, Sachdeva RC, Cope JB (1999) Evaluation of the consolidation period during osteodistraction using computed tomography. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 116:254–263
Young JW, Kostrubiak IS, Resnik CS, Paley D (1990) Sonographic evaluation of bone production at the distraction site in Ilizarov limb-lengthening procedures. AJR Am J Roentgenol 154:125–128
Friedrich RE, Hellner D, Plambeck K, Schmelzle R (1997) Application of B-scan ultrasonography for analysis of callus distraction in vascularized fibular grafts of the mandible: a report of three patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55:635–640
Nocini PF, Wangerin K, Albanese M, Kretschmer W, Cortelazzi R (2000) Vertical distraction of a free vascularized fibula flap in a reconstructed hemimandible: case report. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 28:20–24
Hirai T, Manders EK, Nagamoto K, Saggers GC (1996) Ultrasonic observation of facial bone fractures: report of cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 54:776–779
Thurmueller P, Troulis MJ, O’Neill MJ, Kaban LB (2002) Use of ultrasound to assess healing of a mandibular distraction wound. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1038–1044
Blane CE, Herzenberg JE, Di Pietro MA (1991) Radiographic imaging for Ilizarov lengthening in children. Pediatr Radiol 21:117–120
Moed BR, Kim EC, Van Holsbeeck M, Schaffler MB, Subramanian S, Bouffard JA, Craig JG (1998) Ultrasound for the early diagnosis of tibial fracture healing after static interlocked nailing without reaming: histologic correlation using a canine model. J Orthop Trauma 12:200–205
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruno, C., Minniti, S., Buttura-da-Prato, E. et al. Gray-scale ultrasonography in the evaluation of bone callus in distraction osteogenesis of the mandible: initial findings. Eur Radiol 18, 1012–1017 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0856-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0856-6