Abstract
Key message
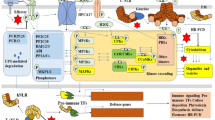
Oomycetes MAMP Pep-13 can trigger SERK3/BAK1-independent PTI. Silencing of SERK3/BAK1 in solanaceous plants resulted in reduced expression of brassinosteroid marker genes and enhanced PTI transcriptional responses to Pep-13 treatment.
Abstract
To prevent disease, pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) are responsible for detecting microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) to switch on plant innate immunity. SOMATIC EMBROYOGENESIS KINASE 3 (SERK3)/BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 1-ASSOCIATED KINASE 1 (BAK1) is a well-characterized receptor-like kinase (RLK) that serves as a pivotal co-receptor with PRRs to activate immunity following recognition of MAMPs including flg22, EF-Tu, INF1 and XEG1. However, the requirement for SERK3/BAK1 in many pattern-triggered immune (PTI) signaling pathways is not yet known. Pep-13 is an oomycete MAMP that consists of a highly conserved motif (an oligopeptide of 13 amino acids) shared in Phytophthora transglutaminases. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis reveals that the transcripts of three PTI marker genes (WRKY7, WRKY8 and ACRE31) rapidly accumulate in response to three different MAMPs: flg22, chitin and Pep-13. Whereas silencing of SERK3/BAK1 in Nicotiana benthamiana or potato compromised transcript accumulation in response to flg22, it did not attenuate WRKY7, WRKY8 and ACRE31 up-regulation in response to chitin or Pep-13. This indicates that Pep-13 triggers immunity in a SERK3/BAK1-independent manner, similar to chitin. Surprisingly, silencing of SERK3/BAK1 led to significantly increased accumulation of PTI marker gene transcripts following Pep-13 or chitin treatment, compared to controls. This was accompanied by reduced expression of brassinosteroid (BR) marker genes StSTDH, StEXP8 and StCAB50 and StCHL1, which is a negative regulator of PTI, supporting previous reports that SERK3/BAK1-dependent BR signaling attenuates plant immunity. We provide Pep-13 as an alternative to chitin as a trigger of SERK3/BAK1-independent immunity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PRRs:
-
Pattern recognition receptors
- MAMPs:
-
Microbe-associated molecular patterns
- BAK1:
-
BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 1-ASSOCIATED KINASE 1
- PTI:
-
Pattern-triggered immune
- ETI:
-
Effector-triggered immunity
- RLK:
-
Receptor-like kinase
References
Albrecht C, Boutrot F, Segonzac C, Schwessinger B, Gimenez-Ibanez S, Chinchilla D, Rathjen JP, de Vries SC, Zipfel C (2012) Brassinosteroids inhibit pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immune signaling independent of the receptor kinase BAK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:303–308
Antolin-Llovera M, Ried MK, Parniske M (2014) Cleavage of the SYMBIOSIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE ectodomain promotes complex formation with Nod factor receptor 5. Curr Biol 24:422–427
Belkhadir Y, Yang L, Hetzel J, Dangl JL, Chory J (2014) The growth-defense pivot: crisis management in plants mediated by LRR-RK surface receptors. Trends Biochem Sci 39:447–456
Ben Khaled S, Postma J, Robatzek S (2015) A moving view: subcellular trafficking processes in pattern recognition receptor-triggered plant immunity. Annu Rev Phytopathol 53:379–402
Bohm H, Albert I, Oome S, Raaymakers TM, Van den Ackerveken G, Nurnberger T (2014) A conserved peptide pattern from a widespread microbial virulence factor triggers pattern-induced immunity in Arabidopsis. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004491
Brodaczewska K, Donskow-Lysoniewska K, Doligalska M (2015) Chitin, a key factor in immune regulation: lesson from infection with fungi and chitin bearing parasites. Acta Parasitol 60:337–344
Brunner F, Rosahl S, Lee J, Rudd JJ, Geiler C, Kauppinen S, Rasmussen G, Scheel D, Nurnberger T (2002) Pep-13, a plant defense-inducing pathogen-associated pattern from Phytophthora transglutaminases. EMBO J 21:6681–6688
Cao Y, Liang Y, Tanaka K, Nguyen CT, Jedrzejczak RP, Joachimiak A, Stacey G (2014) The kinase LYK5 is a major chitin receptor in Arabidopsis and forms a chitin-induced complex with related kinase CERK1. eLife 3:e03766
Caplan J, Padmanabhan M, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2008) Plant NB-LRR immune receptors: from recognition to transcriptional reprogramming. Cell Host Microbe 3:126–135
Chaparro-Garcia A, Wilkinson RC, Gimenez-Ibanez S, Findlay K, Coffey MD, Zipfel C, Rathjen JP, Kamoun S, Schornack S (2011) The receptor-like kinase SERK3/BAK1 is required for basal resistance against the late blight pathogen Phytophthora infestans in Nicotiana benthamiana. PloS One 6:e16608
Chinchilla D, Zipfel C, Robatzek S, Kemmerling B, Nürnberger T, Jones JDG, Felix G, Boller T (2007) A flagellin induced complex of the receptor FLS2 and BAK1 initiates plant defense. Nature 448:497–500
Cikos S, Bukovska A, Koppel J (2007) Relative quantification of mRNA: comparison of methods currently used for real-time PCR data analysis. BMC Mol Biol 8:113
Couto D, Zipfel C (2016) Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signalling in plants. Nat Rev Immunol 16:537–552
Desaki Y, Miyata K, Suzuki M, Shibuya N, Kaku H (2018) Plant immunity and symbiosis signaling mediated by LysM receptors. Innate Immun 24:92–100
Du J, Verzaux E, Chaparro-Garcia A, Bijsterbosch G, Keizer LC, Zhou J, Liebrand TW, Xie C, Govers F, Robatzek S, van der Vossen EA, Jacobsen E, Visser RG, Kamoun S, Vleeshouwers VG (2015) Elicitin recognition confers enhanced resistance to Phytophthora infestans in potato. Nat Plants 1:15034
Elieh Ali Komi D, Sharma L, Dela Cruz CS (2018) Chitin and its effects on inflammatory and immune responses. Clin Rev Allergy Immun 54:213–223
Fellbrich G, Romanski A, Varet A, Blume B, Brunner F, Engelhardt S, Felix G, Kemmerling B, Krzymowska M, Nürnberger T (2002) NPP1, a Phytophthora-associated trigger of plant defense in parsley and Arabidopsis. Plant J 32:375–390
Gómez-Gómez L, Boller T (2000) FLS2: an LRR receptor-like kinase involved in the perception of the bacterial elicitor flagellin in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 5:1003–1011
Gopalakannan A, Aru V (2006) Immunomodulatory effects of dietary intake of chitin, chitosan and levamisole on the immune system of Cyprinus carpio and control of Aeromonas hydrophila infection in pond. Aquaculture 255:179–187
Halim VA, Altmann S, Ellinger D, Eschen-Lippold L, Miersch O, Scheel D, Rosahl S (2009) PAMP-induced defense responses in potato require both salicylic acid and jasmonic acid. Plant J 57:230–242
He Q, McLellan H, Boevink PC, Sadanandom A, Xie C, Birch PR, Tian Z (2015) U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase PUB17 acts in the nucleus to promote specific immune pathways triggered by Phytophthora infestans. J Exp Bot 66:3189–3199
Heese A, Hann DR, Gimenez-Ibanez S, Jones AM, He K, Li J, Schroeder JI, Peck SC, Rathjen JP (2007) The receptor-like kinase SERK3/BAK1 is a central regulator of innate immunity in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:12217–12222
Hein I, Gilroy EM, Armstrong MR, Birch PR (2009) The zig-zag-zig in oomycete-plant interactions. Mol Plant Pathol 10:547–562
Jones J, Dangl J (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–329
Jones JD, Vance RE, Dangl JL (2016) Intracellular innate immune surveillance devices in plants and animals. Science 354:6316
Jung WJ, Park RD (2014) Bioproduction of chitooligosaccharides: present and perspectives. Mar Drugs 12:5328–5356
Kemmerling B, Halter T, Mazzotta S, Mosher S, Nurnberger T (2011) A genome-wide survey for Arabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor kinases implicated in plant immunity. Front Plant Sci 2:88
Kroj T, Rudd JJ, Nürnberger T, Gäbler Y, Lee J, Scheel D (2003) Mitogen-activated protein kinases play an essential role in oxidative burst-independent expression of pathogenesis-related genes in parsley. J Biol Chem 278:2256–2264
Lee J, Rudd JJ, Macioszek VK, Scheel D (2004) Dynamic changes in the localization of MAPK cascade components controlling pathogenesis-related (PR) gene expression during innate immunity in parsley. J Biol Chem 279:22440–22448
Lee CG, Da Silva CA, Lee JY, Hartl D, Elias JA (2008) Chitin regulation of immune responses: an old molecule with new roles. Curr Opin Immunol 20:684–689
Li J, Wen J, Lease KA, Dorke JT, Tax FE, Walker JC (2002) BAK1, an Arabidopsis LRR receptor-like kinase, interacts with BRI1 and modulates brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 110:213–222
Liu T, Liu Z, Song C, Hu Y, Han Z, She J, Fan F, Wang J, Jin C, Chang J, Zhou JM, Chai J (2012) Chitin-induced dimerization activates a plant immune receptor. Science 336:1160–1164
Lozano-Duran R, Macho AP, Boutrot F, Segonzac C, Somssich IE, Zipfel C (2013) The transcriptional regulator BZR1 mediates trade-off between plant innate immunity and growth. eLife 2:e00983
Ma Z, Song T, Zhu L, Ye W, Wang Y, Shao Y, Dong S, Zhang Z, Dou D, Zheng X, Tyler BM, Wang Y (2015) A Phytophthora sojae glycoside hydrolase 12 protein is a major virulence factor during soybean infection and is recognized as a PAMP. Plant Cell 27:2057–2072
McLellan H, Boevink PC, Armstrong MR, Pritchard L, Gomez S, Morales J, Whisson SC, Beynon JL, Birch PRJ (2013) An RxLR effector from Phytophthora infestans prevents re-localisation of two plant NAC transcription factors from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003670
Miya A, Albert P, Shinya T, Desaki Y, Ichimura K, Shirasu K, Narusaka Y, Kawakami N, Kaku H, Shibuya N (2007) CERK1, a LysM receptor kinase, is essential for chitin elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19613–19618
Nam KH, Li (2002) BRI1/BAK1, a receptor kinase pair mediating brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 110:203–212
Nürnberger T, Nennstiel D, Jabs T, Sacks WR, Hahlbrock K, Scheel D (1994) High affinity binding of a fungal oligopeptide elicitor to parsley plasma membranes triggers multiple defense responses. Cell 78:449–460
Ranf S, Eschen-Lippold L, Pecher P, Lee J, Scheel D (2011) Interplay between calcium signalling and early signalling elements during defence responses to microbe- or damage-associated molecular patterns. Plant J 68:100–113
Schwessinger B, Roux M, Kadota Y, Ntoukakis V, Sklenar J, Jones A, Zipfel C (2011) Phosphorylation-dependent differential regulation of plant growth, cell death, and innate immunity by the regulatory receptor-like kinase BAK1. PLoS Genet 7:e1002046
Shan L, He P, Li J, Heese A, Peck SC, Nurnberger T, Martin GB, Sheen J (2008) Bacterial effectors target the common signaling partner BAK1 to disrupt multiple MAMP receptor-signaling complexes and impede plant immunity. Cell Host Microbe 4:17–27
Sun Y, Li L, Macho AP, Han Z, Hu Z, Zipfel C, Zhou JM, Chai J (2013) Structural basis for flg22-induced activation of the Arabidopsis FLS2-BAK1 immune complex. Science 342:624–628
Tang D, Wang G, Zhou JM (2017) Receptor kinases in plant–pathogen interactions: more than pattern recognition. Plant Cell 29:618–637
Turnbull D, Yang L, Naqvi S, Breen S, Welsh L, Stephens J, Morris J, Boevink PC, Hedley PE, Zhan J, Birch PRJ, Gilroy EM (2017) RXLR Effector AVR2 up-regulates a brassinosteroid-responsive bHLH transcription factor to suppress immunity. Plant Physiol 174:356–369
Acknowledgements
This work was support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31761143007, 31171603) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2662017PY069) for funding ZT’s lab. We thank the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) for funding PRJB’s lab (BB/L026880/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Roger Thilmony.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
299_2018_2359_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Figure S1 Expression time courses of flg22 induced transcripts in potato and Nicotiana benthamiana. Figure S2 Expression time course of chitin induced transcripts in potato and N. benthamiana. Figure S3 Expression time courses of Pep13 induced transcripts in potato and N. benthamiana. Figure S4 Alignment of Solanum tuberosum (potato) and Nicotiana benthamiana SERK3/BAK1 full-length nucleotide sequences. Figure S5 The silencing of BAK1 in Solanum tuberosum. Figure S6 Virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) of BAK1 in Nicotiana benthamiana. Table S1. Primer sequences used in this study (DOCX 2759 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., He, H., Qi, Y. et al. The oomycete microbe-associated molecular pattern Pep-13 triggers SERK3/BAK1-independent plant immunity. Plant Cell Rep 38, 173–182 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-018-2359-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-018-2359-5