Abstract
Key message
OsEXPA10 gene coordinates the balance between rice development and biotic resistance.
Abstract
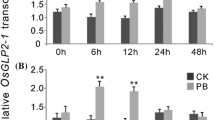
Expansins are proteins that can loosen the cell wall. Previous studies have indicated that expansin-encoding genes were involved in defense against abiotic stress, but little is known about the involvement of expansins in biotic stress. Brown planthopper (BPH) is one of the worst insect pests of rice in the Asia-Pacific planting area, and many efforts have been made to identify and clone BPH-resistance genes for use in breeding resistant cultivars. At the same time, rice blast caused by Magnaporthe grisea is one of the three major diseases that severely affect rice production worldwide. Here, we demonstrated that one rice expansin-encoding gene, OsEXPA10, functions in both rice growth and biotic resistance. Over expression of OsEXPA10 improved rice growth but also increased susceptibility to BPH infestation and blast attack, while knock-down OsEXPA10 gene expression resulted in reduced plant height and grain size, but also increased resistance to BPH and the blast pathogen. These results imply that OsEXPA10 mediates the balance between rice development and biotic resistance.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BPH:
-
Brown planthopper
- OE:
-
Over expression
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- JA:
-
Jasmonic acid
- MeJA:
-
Methyl jasmonic acid
References
Abuqamar S, Ajeb S, Sham A et al (2013) A mutation in the expansin-like A2 gene enhances resistance to necrotrophic fungi and hypersensitivity to abiotic stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant Pathol 14:813–827
Ba LJ, Shan W, Xiao YY et al (2014) A ripening-induced transcription factor MaBSD1 interacts with promoters of MaEXP1/2 from banana fruit. Plant Cell Rep 33:1913–1920
Bae JM, Kwak MS, Noh SA et al (2014) Overexpression of sweetpotato expansin cDNA (IbEXP1) increases seed yield in Arabidopsis. Transgenic Res 23:657–667
Balestrini R, Cosgrove D, Bonfante P (2005) Differential location of α-expansin proteins during the accommodation of root cells to an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. Planta 220:889–899
Cheng X, Zhu L, He G (2013) Towards understanding of molecular interactions between rice and the brown planthopper. Mol Plant 6:621–634
Cho HT, Kende H (1997) Expression of expansin genes is correlated with growth in deepwater rice. Plant cell 9:1661–1671
Cosgrove DJ (1997) Assembly and enlargement of the prim ary cell wall in plants. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol 13:171–201
Cosgrove DJ (2000) Loosening of plant cell walls by expansins. Nature 407:321–326
Cosgrove DJ, Li LC, Cho HT et al (2002) The growing world of expansins. Plant Cell Physiol 43:1436–1444
Dai F, Zhang C, Jiang X et al (2012) RhNAC2 and RhEXPA4 are involved in the regulation of dehydration tolerance during the expansion of rose petals. Plant Physiol 160:2064–2082
Ding X, Cao Y, Huang L et al (2008) Activation of the indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase GH3-8 suppresses expansin expression and promotes salicylate- and jasmonate-independent basal immunity in rice. Plant Cell 20:228–240
Du B, Zhang W, Liu B et al (2009) Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:22163–22168
Gal TZ, Aussenberg ER, Burdman S et al (2006) Expression of a plant expansin is involved in the establishment of root knot nematode parasitism in tomato. Planta 224:155–162
Han Y, Chen Y, Yin S et al (2015) Over-expression of TaEXPB23, a wheat expansin gene, improves oxidative stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco plants. J Plant Physiol 173:62–71
Han YC, Kuang JF, Chen JY et al (2016) Banana transcription factor MaERF11 recruits histone deacetylase MaHDA1 and represses the expression of MaACO1 and expansins during fruit ripening. Plant Physiol 171:1070–1084
Hayashi T, Wong YS, Maclachlan G (1984) Pea xyloglucan and cellulose: II. Hydrolysis by pea endo-1,4-beta-glucanases. Plant Physiol 75:605–610
Helliwell EE, Yang Y (2013) Molecular strategies to improve rice disease resistance. Methods Mol Biol 956:285–309
Hematy K, Cherk C, Somerville S (2009) Host-pathogen warfare at the plant cell wall. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:406–413
Herms DA, Mattson WJ (1992) The dilemma of plants: to grow or defend. Quart Rev Biol 67:283–335
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T et al (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J 6:271–282
Hu J, Xiao C, He Y (2016) Recent progress on the genetics and molecular breeding of brown planthopper resistance in rice. Rice 9:30
Jiang X, Zhang C, Lu P et al (2014) RhNAC3, a stress-associated NAC transcription factor, has a role in dehydration tolerance through regulating osmotic stress-related genes in rose petals. Plant Biotechnol J 12:38–48
Karasov TL, Chae E, Herman JJ et al (2017) Mechanisms to mitigate the trade-off between growth and defense. Plant Cell 29:666–680
Kende H, Bradford K, Brummell D et al (2004) Nomenclature for members of the expansin superfamily of genes and proteins. Plant Mol Biol 55:311–314
Kwasniewski M, Szarejko I (2006) Molecular cloning and characterization of β-expansin gene related to root hair formation in barley. Plant Physiol 141:1149–1158
Lee Y, Choi D, Kende H (2001) Expansins: ever-expanding numbers and functions. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:527–532
Li LC, Bedinger PA, Volk C et al (2003a) Purification and characterization of four β-expansins (Zea m 1 isoforms) from maize pollen. Plant Physiol 132:2073–2085
Li Y, Jones L, McQueen-Mason S (2003b) Expansins and cell growth. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:603–610
Li X, Zhao J, Tan Z et al (2015) GmEXPB2, a cell wall β-expansin, affects soybean nodulation through modifying root architecture and promoting nodule formation and development. Plant Physiol 169:2640–2653
Liu L, Tong H, Xiao Y et al (2015) Activation of Big Grain1 significantly improves grain size by regulating auxin transport in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:11102–11107
Lu J, Li J, Ju H et al (2014) Contrasting effects of ethylene biosynthesis on induced plant resistance against a chewing and a piercing-sucking herbivore in rice. Mol Plant 7:1670–1682
Lü P, Kang M, Jiang X et al (2013) RhEXPA4, a rose expansin gene, modulates leaf growth and confers drought and salt tolerance to Arabidopsis. Planta 237:1547–1559
Marowa P, Ding A, Kong Y (2016) Expansins: roles in plant growth and potential applications in crop improvement. Plant Cell Rep 35:949–965
McNeil M, Darvill AG, Fry SC et al (1984) Structure and function of the primary cell walls of plants. Ann Rev Biochem 53:625–663
McQueen-Mason S, Durachko DM, Cosgrove DJ (1992) Two endogenous proteins that induce cell wall extension in plants. Plant Cell 4:1425–1433
Muller B, Bourdais G, Reidy B et al (2007) Association of specific expansins with growth in maize leaves is maintained under environmental, genetic, and developmental sources of variation. Plant Physiol 143:278–290
Noh SA, Lee H-S, Kim Y-S et al (2013) Down-regulation of the IbEXP1 gene enhanced storage root development in sweetpotato. J Exp Bot 64:129–142
Palapol Y, Kunyamee S, Thongkhum M et al (2015) Expression of expansin genes in the pulp and the dehiscence zone of ripening durian (Durio zibethinus) fruit. J Plant Physiol 182:33–39
Qin L, Kudla U, Roze EH et al (2004) Plant degradation: a nematode expansin acting on plants. Nature 427:30–30
Rose JK, Lee HH, Bennett AB (1997) Expression of a divergent expansin gene is fruit-specific and ripening-regulated. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:5955–5960
Shin JH, Jeong DH, Park MC et al (2005) Characterization and transcriptional expression of the alpha-expansin gene family in rice. Mol Cells 20:210–218
Skamnioti P, Gurr SJ (2009) Against the grain: safeguarding rice from rice blast disease. Trends Biotechnol 27:141–150
Underwood W (2012) The plant cell wall: a dynamic barrier against pathogen invasion. Front Plant Sci 3:85
Wang Y, Wang L, Zou Y et al (2014) Soybean miR172c targets the repressive AP2 transcription factor NNC1 to activate ENOD40 expression and regulate nodule initiation. Plant Cell 26:4782–4801
Wilson RA, Talbot NJ (2009) Under pressure: investigating the biology of plant infection by Magnaporthe oryzae. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:185–195
Won S-K, Choi S-B, Kumari S et al (2010) Root hair-specific EXPANSIN B genes have been selected for Graminaceae root hairs. Mol Cells 30:369–376
Xia XJ, Zhou YH, Shi K et al (2015) Interplay between reactive oxygen species and hormones in the control of plant development and stress tolerance. J Exp Bot 66:2839–2856
Xu J, Tian J, Belanger FC et al (2007) Identification and characterization of an expansin gene AsEXP1 associated with heat tolerance in C3 Agrostis grass species. J Exp Bot 58:3789–3796
Xu B, Gou J-Y, Li F-G et al (2013) A cotton BURP domain protein interacts with α-expansin and their co-expression promotes plant growth and fruit production. Mol Plant 6:945–958
Yang YX, Ahammed GJ, Wu C et al (2015) Crosstalk among jasmonate, salicylate and ethylene signaling pathways in plant disease and immune responses. Curr Protein Peptide Sci 16:450–461
Zhao M-r, Li F, Fang Y et al. (2011) Expansin-regulated cell elongation is involved in the drought tolerance in wheat. Protoplasma 248:313–332
Zust T, Agrawal AA (2017) Trade-offs between plant growth and defense against insect herbivory: an emerging mechanistic synthesis. Ann Rev Plant Biol 68:513–534
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFD0100603), the National Transgenic Great Subject from the Ministry of Agriculture of China (2016ZX08009-003-001) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371949). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Da-Bing Zhang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, J., Wang, M., Shi, Z. et al. OsEXPA10 mediates the balance between growth and resistance to biotic stress in rice. Plant Cell Rep 37, 993–1002 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-018-2284-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-018-2284-7