Abstract
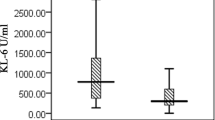
Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) has been described as a promising biomarker in the diagnosis and determining the severity of interstitial lung disease in adults with connective tissue disease. This study was performed to determine whether the serum KL-6 level is useful as a biomarker for detecting the interstitial lung disease (ILD) in pediatric cases of connective tissue disease (CTD). In total, 88 patients [36 patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA), 27 patients with juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus (JSLE), 14 patients with juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM), and 11 patients with juvenile systemic sclerosis (JSSc)] and 68 healthy controls were included in this study. Age, sex, and duration of CTD and ILD (if any) were recorded. Blood samples from all the patients and controls were examined by ELISA. Eleven of the 88 patients with CTD (12.5%) had ILD and all of them were symptomatic. Subgroup analysis indicated that eight patients had JSSc, two had JSLE, and one had systemic JIA. The median serum KL-6 level was 1450.5 U/mL (interquartile range (IQR) 742.9–2603.2) in the CTD with ILD group, 415.9 U/mL (IQR 233.4–748.4) in the CTD without ILD group, and 465.9 U/mL (IQR 273.6–1036) in the control group. KL-6 levels were significantly higher in the CTD with ILD group than the CTD without ILD group and the control group (p = 0.003). At a cut-off of 712.5 U/ml identified by ROC curve, serum KL-6 yielded a sensitivity of 81% and specificity of 72% for CTD with ILD group. There was no significant difference in serum KL-6 level among the disease subgroups (sJIA, JSLE, JSSc, JDM), in either the CTD with ILD group or the CTD without ILD group (p > 0.05). In conclusion, KL-6 is a useful biomarker of CTD with ILD in pediatric patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dell S, Matejka CK, Hagood JS (2012) Diffuse and interstitial lung disease and childhood rheumatologic disorders. Curr Opin Rheumatol 24:530–540
Oguz EO, Kucuksahin O, Turgay M, Yildizgoren MT, Ates A, Demir N, Kumbasar OO, Kinikli G, Duzgun N (2016) Association of serum KL6 levels with interstitial lung disease patients with connective tissue disease: cross sectional study. Clin Rheumatol 35(3):663–666
Satoh H, Kurishima K, Ishikawa H, Ohtsuka M (2006) Increased levels of KL-6 and subsequent mortality in patients with interstitial lung diseases. J Intern Med 260:429–434
Jee AS, Adelstein S, Bleasel J, Keir GJ, Nguyen M, Sahhar J, Youssef P, Corte TJ (2017) Role of autoantibodies in the diagnosis of connective tissue disease ILD (CTD-ILD) and interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF). J Clin Med 6:51
Saper VE, Chen G, Deutsch GH, Guillerman RP, Birgmeler J et al (2019) Emergent high fatality lung disease in systemic juvenile arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216040
Schulert GS, Yasin S, Carey B, Chalk C, Do T, Schapiro AH, Husami A, Watts A, Brunner H, Huggins J, Mellins ED, Morgan EM, Ting T, Trapnell BC, Wikenheiser- Brokamp K, Towe C, Grom AA (2019) Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis–associated lung disease: characterization and risk factors. Arthritis Rheumatol 10.1002/art.41073. (Epub ahead of print)
Fathi M, Helmers SB, Lundberg IE (2012) KL6: a serological biomarker for interstitial lung disease in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. J Intern Med 271:589–597
Fukaya S, Oshima H, Kato K, Komatsu Y, Matsumura H, Ishii K, Miyama H, Nagai T, Tanaka I, Mizutani A, Katayama M, Yoshida S, Torikai K (2000) KL-6 as a novel marker for activities of interstitial pneumonia in connective tissue diseases. Rheumatol Int 19:223–225
Kurland G, Deterding RR, Hagood JS, Young RL, Brody AS, Castile RG, Dell S, Fan LL, Hamvas A, Hilman BC, Langston C, Nogee LM, Redding GJ (2013) An official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline: classification, evaluation, and management of childhood interstitial lung disease in infancy. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 188:376–394
Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P et al (2004) International League of Associations for Rheumatology Classification of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: second revision, Edmonton 2004. J Rheumatol 31(2):390–392
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol 40(9):1725–1734
Zullan F, Woo P, Athreya BH et al (2007) The Pediatric Rheumatology European Society/American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism provisional classification criteria for juvenile systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol 57:203–212
Bohan A, Peter JB (1975) Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 292:344–347
Hu C, Wu C, Yang E, Huang H, Xu D, Hou Y, Zhao J, Li M, Xu Z, Zeng X, Wang Q (2019) Serum KL6 is associated with the severity of interstitial lung disease in Chinese patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol 38(8):1–7
Kumanovics G, Gorbe E, Minier T, Simon D, Berki T, Czirjak L (2014) Follow up serum KL6 lung fibrosis biomarker levels in 173 patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 32:138–144
Salazar GA, Kuwana M, Wu M, Estrada-Y-Martin RM, Ying J et al (2018) KL-6 but not CCL-18 is a predictor of early progression in systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol 45(8):1153–1158
Benyamine A, Heim X, Resseguier N, Bertin D, Gomez C, Ebbo M, Harle JR, Kaplanski G, Rossi P, Bardin N, Granel B (2018) Elevated serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 in systemic sclerosis: a marker of lung fibrosis and severity of the disease. Rheumatol Int 38(5):813–819
Hanaoka M, Katsumata Y, Kawasumi H, Kawaguchi Y, Yamanaka H (2019) KL-6 is a long-term disease-activity biomarker for interstitial lung disease associated with polymyositis/dermatomyositis, but is not a short-term disease-activity biomarker. Mod Rheumatol 29(4):625–632
Hu Y, Wang LS, Jin YP, Du SS, Du YK, He X, Weng D, Zhou Y, Li QH, Shen L, Zhang F, Su YL, Sun XL, Ding JJ, Zhang WH, Cai HR, Dai HP, Dai JH, Li HP (2017) Serum Krebs von den Lungen- 6 level as a diagnostic biomarker for interstitial lung disease in Chinese patients. Clin Respir J 11:337–345
Ishikawa N, Hattori N, Yokoyama A et al (2012) Utility of KL-6/ MUC1 in the clinical management of interstitial lung diseases. Respir Investig 50:3–13
Kinoshita F, Hamano H, Harada H, Kinoshita T, Igıshı T, Hagino H, Ogawa T (2004) Role of KL6 in evaluating the disease severity of rheumatoid lung disease: comparision with HRCT. Respir Med 98:1131–1137
Bonella F, Volpe A, Caramaschi P, Nava C, Ferrari P, Schenk K, Ohshimo S, Costabel U, Ferrari M (2011) Surfactant protein D and KL-6 serum levels in systemic sclerosis: correlation with lung and systemic involvement. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 28:27–33
Yamakawa H, Hagiwara E, Kitamura H, Yamanaka Y, Ikeda S, Sekine A, Baba T, Okudela K, Iwasawa T, Takemura T, Kuwano K, Ogura T (2017) Serum KL6 and surfactant protein- D as monitoring and predictive markers of interstitial lung disease in patient with systemic sclerosis and mixed connective tissue disease. J Thorac Dis 9:362–371
Cao XY, Hu SS, Xu D, Li M, Wang Q, Hou Y, Zeng X (2019) Serum levels of Krebs von den Lungen-6 as a promising marker for predicting occurrence and deterioration of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease from a Chinese cohort. Int J Rheum Dis. 22(1):108–115
Lee JS, Lee YE, Ha YJ, Kang EH, Lee YJ, Song YW (2019) Serum KL-6 levels reflect the severity of interstitial lung disease associated with connective tissue disease. Arthritis Res Ther 21:58
Barut K, Adrovic A, Şahin S, Kasapcopur O (2017) Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Balkan Med J 34(2):90–101
Kimura Y, Weiss JE, Haroldson KL, Lee T, Punaro M, Oliveira S et al (2013) Pulmonary hypertension and other potentially fatal pulmonary complications in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Care Res 65:745–752
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All co-authors contributed substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work; the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data for the work. All co-authors made drafting for the work and revising it critically for important intellectual content and made final approval of the version to be published. All co-authors contributed to agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that the questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. All co-authors are familiar and take full responsibility for all aspects of the study and the final manuscript. AAK, HC, AA, and OK contributed to the conception and design of the study, data analysis, and manuscript writing. AAK, AA, AA, and MY had substantially contributed to conception and design of the study and to data analysis. AA, MY, and MK contributed to data collection and data input. HC, KB, OK, and AA contributed to data analysis and manuscript writing. SS, AA, and KB contributed to data analysis and critical revisions. AAK, HC, and OK made final contributions to the conception and design, revision of draft manuscript, and approval of the manuscript to be submitted for publication. All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors of this paper has a conflict of interest, including specific financial interests, relationships, and/or affiliations relevant to the subject matter or materials included.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilinc, A.A., Arslan, A., Yildiz, M. et al. Serum KL-6 level as a biomarker of interstitial lung disease in childhood connective tissue diseases: a pilot study. Rheumatol Int 40, 1701–1706 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04485-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04485-4