Abstract
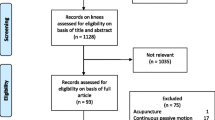
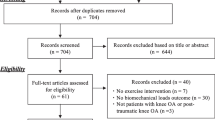
The objective of this study is to construct an evidence synthesis to identify the types of land-based exercises most investigated in the current literature, the intervention duration, frequency of the programs and the exercises which are most frequently implemented. A search was performed on the reference list of included and excluded studies of one systematic review, on land-based exercises for knee osteoarthritis and, an updated search of The Cochrane Library, Embase, CINAHL and PEDro was completed. Two authors independently selected the studies and a third author was consulted for an additional opinion. The inclusion criteria were male or female with tibiofemoral knee osteoarthritis, land-based exercises, non-exercise control group and randomized clinical trials. The exclusion criteria were mixed diagnosis or comparison to other types of exercise. The data were extracted by two authors. Fifty-five full-text articles were included. Strengthening, proprioception and aerobic exercises resulted in significant pain reduction. The intervention durations which were significant for pain reduction were either the period of 8–11 weeks or 12–15 weeks. The frequency of three times per week was found significant in comparison to a non-exercise control group. The results, which formed an evidence synthesis, demonstrate that there is substantial evidence regarding the benefits of strengthening exercises to reduce pain in knee osteoarthritis patients. Based on the included studies analysis, exercises should be performed three times weekly for a duration of 8–11 or 12–15 weeks. Health professionals working with knee osteoarthritis patients can use this evidence synthesis as a fast and pragmatic instrument to obtain information about several effective types of exercises for pain reduction.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- OA:
-
Osteoarthritis
- e.g.:
-
“For example”
- RCTs:
-
Randomized clinical trials
- ACSM:
-
American College of Sports Medicine
- i.e.:
-
“That is”
- PICOTS:
-
Population, intervention, comparator, outcomes, time, and study design
- MDT:
-
Mechanical diagnosis and therapy
- min:
-
Minutes
- TIDieR:
-
Template for intervention description and replication
- CONTENT:
-
Consensus on therapeutic exercise training
References
Carlson NL, Christopherson Z, Arnall E, Mohn S, Holton K, Marshall L et al (2011) 457 a pilot study on the effects of strength and aerobic conditioning in patients with hip osteoarthritis. Osteoarth Cartil 19
Felson DT (2009) Developments in the clinical understanding of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 11(1):203
Kongtharvonskul J, Anothaisintawee T, McEvoy M, Attia J, Woratanarat P, Thakkinstian A (2015) Efficacy and safety of glucosamine, diacerein, and NSAIDs in osteoarthritis knee: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur J Med Res 20:24
Bennell KL, Wrigley TV, Hunt MA, Lim BW, Hinman RS (2013) Update on the role of muscle in the genesis and management of knee osteoarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 39(1):145–176
Maurer BT, Stern AG, Kinossian B, Cook KD, Schumacher HR (1999) Osteoarthritis of the knee: isokinetic quadriceps exercise versus an educational intervention. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 80(10):1293–1299
Bennell KL, Hall M, Hinman RS (2016) Osteoarthritis year in review 2015: rehabilitation and outcomes. Osteoarthr Cartil 24(1):58–70
Slemenda C, Heilman DK, Brandt KD, Katz BP, Mazzuca SA, Braunstein EM et al (1998) Reduced quadriceps strength relative to body weight: a risk factor for knee osteoarthritis in women? Arthritis Rheum 41(11):1951–1959
Hurley MV (1999) The role of muscle weakness in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 25(2):283–298 (vi)
Fisher NM, Pendergast DR (1997) Reduced muscle function in patients with osteoarthritis. Scand J Rehabil Med 29(4):213–221
Pettee Gabriel KK, Morrow JR, Woolsey AL (2012) Framework for physical activity as a complex and multidimensional behavior. J Phys Act Health 9(Suppl 1):S11–S18
Peat G, McCarney R, Croft P (2001) Knee pain and osteoarthritis in older adults: a review of community burden and current use of primary health care. Ann Rheum Dis 60(2):91–97
Zacharias A, Green RA, Semciw AI, Kingsley MI, Pizzari T (2014) Efficacy of rehabilitation programs for improving muscle strength in people with hip or knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Osteoarthr Cartil 22(11):1752–1773
Riebe D, Jonathan K, Ligori G (2016) ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. Philadelphia, PA, 10th edn
Fransen M, McConnell S, Harmer AR, Van der Esch M, Simic M, Bennell KL (2015) Exercise for osteoarthritis of the knee. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD004376
Dong R, Wu Y, Xu S, Zhang L, Ying J, Jin H et al (2018) Is aquatic exercise more effective than land-based exercise for knee osteoarthritis? Medicine (Baltimore) 97(52):e13823
Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, Goode AP, Jordan JM (2014) A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: the chronic osteoarthritis management initiative of the U.S. bone and joint initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum 43(6):701–712
Brosseau L, Rahman P, Toupin-April K, Poitras S, King J, De Angelis G et al (2014) A systematic critical appraisal for non-pharmacological management of osteoarthritis using the appraisal of guidelines research and evaluation II instrument. PLoS One 9(1):e82986
Brosseau L, Taki J, Desjardins B, Thevenot O, Fransen M, Wells GA et al (2017) The Ottawa panel clinical practice guidelines for the management of knee osteoarthritis. Part one: introduction, and mind-body exercise programs. Clin Rehabil 31(5):582–595
Brosseau L, Taki J, Desjardins B, Thevenot O, Fransen M, Wells GA et al (2017) The Ottawa panel clinical practice guidelines for the management of knee osteoarthritis. Part two: strengthening exercise programs. Clin Rehabil 31(5):596–611
Brosseau L, Taki J, Desjardins B, Thevenot O, Fransen M, Wells GA et al (2017) The Ottawa panel clinical practice guidelines for the management of knee osteoarthritis. Part three: aerobic exercise programs. Clin Rehabil 31(5):612–624
Fransen M, McConnell S, Hernandez-Molina G, Reichenbach S (2010) Does land-based exercise reduce pain and disability associated with hip osteoarthritis? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Osteoarthr Cartil 18(5):613–620
Lowe CJ, Davies L, Sackley CM, Barker KL (2015) Effectiveness of land-based physiotherapy exercise following hospital discharge following hip arthroplasty for osteoarthritis: an updated systematic review. Physiotherapy 101(3):252–265
Bartholdy C, Nielsen SM, Warming S, Hunter DJ, Christensen R, Henriksen M (2019) Poor replicability of recommended exercise interventions for knee osteoarthritis: a descriptive analysis of evidence informing current guidelines and recommendations. Osteoarthr Cartil 27(1):3–22
Regnaux JL-C, Trinquart MM, Nguyen L, Boutron C, Brosseau I, Ravaud L (2015) High-intensity versus low-intensity physical activity or exercise in people with hip or knee osteoarthritis.. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (10)
Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, Franklin BA, Lamonte MJ, Lee IM et al (2011) American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43(7):1334–1359
Slade SC, Dionne CE, Underwood M, Buchbinder R, Beck B, Bennell K et al (2016) Consensus on exercise reporting template (CERT): modified Delphi study. Phys Ther 96(10):1514–1524
Knoop J, Steultjens MP, van der Leeden M, van der Esch M, Thorstensson CA, Roorda LD et al (2011) Proprioception in knee osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Osteoarthr Cartil 19(4):381–388
Jagodinsky A, Fox J, Decoux B, Weimar W, Liu W (2015) Biomechanical comparison of frontal plane knee joint moment arms during normal and Tai Chi walking. J Phys Ther Sci 27(9):2959–2961
Rosedale R, Rastogi R, May S, Chesworth BM, Filice F, Willis S et al (2014) Efficacy of exercise intervention as determined by the McKenzie system of mechanical diagnosis and therapy for knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 44(3):173–181, A1-6
Machado LA, de Souza M, Ferreira PH, Ferreira ML (2006) The McKenzie method for low back pain: a systematic review of the literature with a meta-analysis approach. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31(9):E254–E262
Hoffmann TC, Glasziou PP, Boutron I, Milne R, Perera R, Moher D et al (2014) Better reporting of interventions: template for intervention description and replication (TIDieR) checklist and guide. BMJ 348:g1687
Hoogeboom TJ, Oosting E, Vriezekolk JE, Veenhof C, Siemonsma PC, de Bie RA et al (2012) Therapeutic validity and effectiveness of preoperative exercise on functional recovery after joint replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 7(5):e38031
Higgins JPT, GSe (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration. http://www.handbook.cochrane.org.
Deeks JJHJ, Altman DG (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0. http://www.handbook.cochrane.org: The Cochrane Collaboration
Fransen M, Crosbie J, Edmonds J (2001) Physical therapy is effective for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Rheumatol 28(1):156–164
Huang MH, Lin YS, Yang RC, Lee CL (2003) A comparison of various therapeutic exercises on the functional status of patients with knee osteoarthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 32(6):398–406
Jan MH, Lin JJ, Liau JJ, Lin YF, Lin DH (2008) Investigation of clinical effects of high- and low-resistance training for patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Phys Ther 88(4):427–436
Salli A, Sahin N, Baskent A, Ugurlu H (2010) The effect of two exercise programs on various functional outcome measures in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Isokinetics Exercise Science 18(4):201–209
Samut G, Dinçer F, Özdemir O (2015) The effect of isokinetic and aerobic exercises on serum interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha levels, pain, and functional activity in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Mod Rheumatol 25(6):919–924
Simão AP, Avelar NC, Tossige-Gomes R, Neves CD, Mendonça VA, Miranda AS et al (2012) Functional performance and inflammatory cytokines after squat exercises and whole-body vibration in elderly individuals with knee osteoarthritis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 93(10):1692–1700
Topp R, Woolley S, Hornyak J, Khuder S, Kahaleh B (2002) The effect of dynamic versus isometric resistance training on pain and functioning among adults with osteoarthritis of the knee. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 83(9):1187–1195
Wortley MZ, Paquette S, Byrd M, Baumgartnerb E, Klippled L, Krusenklause G, Brownb J (2013) L. Effects of resistance and Tai Ji training on mobility and symptoms in knee osteoarthritis patients. J Sport Health Sci 2(4):209–214
Lim BW, Hinman RS, Wrigley TV, Sharma L, Bennell KL (2008) Does knee malalignment mediate the effects of quadriceps strengthening on knee adduction moment, pain, and function in medial knee osteoarthritis? A randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 59(7):943–951
Baker KR, Nelson ME, Felson DT, Layne JE, Sarno R, Roubenoff R (2001) The efficacy of home based progressive strength training in older adults with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. J Rheumatol 28(7):1655–1665
Bennell KL, Hunt MA, Wrigley TV, Hunter DJ, McManus FJ, Hodges PW et al (2010) Hip strengthening reduces symptoms but not knee load in people with medial knee osteoarthritis and varus malalignment: a randomised controlled trial. Osteoarthr Cartil 18(5):621–628
Bezalel T, Carmeli E, Katz-Leurer M (2010) The effect of a group education programme on pain and function through knowledge acquisition and home-based exercise among patients with knee osteoarthritis: a parallel randomised single-blind clinical trial. Physiotherapy 96(2):137–143
Bruce-Brand RA, Walls RJ, Ong JC, Emerson BS, O’Byrne JM, Moyna NM (2012) Effects of home-based resistance training and neuromuscular electrical stimulation in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 13:118
Chang KV, Chen SY, Chen WS, Tu YK, Chien KL (2012) Comparative effectiveness of focused shock wave therapy of different intensity levels and radial shock wave therapy for treating plantar fasciitis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 93(7):1259–1268
Chen TW, Lin CW, Lee CL, Chen CH, Chen YJ, Lin TY et al (2014) The efficacy of shock wave therapy in patients with knee osteoarthritis and popliteal cyamella. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 30(7):362–370
Christensen R, Leeds M, Gudbergsen AR, Christensen H, Sørensen P, Bartels TJ, Riecke EM, Aaboe BF, Frederiksen J, Boesen R, Lohmander M, Astrup LS, Bliddal AH (2015) Effect of weight maintenance on symptoms of knee osteoarthritis in obese patients: a twelve-month randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Care Research (Hoboken) 67(5):640–650
Doi T, Akai M, Fujino K, Iwaya T, Kurosawa H, Hayashi K et al (2008) Effect of home exercise of quadriceps on knee osteoarthritis compared with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 87(4):258–269
Foley A, Halbert J, Hewitt T, Crotty M (2003) Does hydrotherapy improve strength and physical function in patients with osteoarthritis—a randomised controlled trial comparing a gym based and a hydrotherapy based strengthening programme. Ann Rheum Dis 62(12):1162–1167
Foroughi N, Smith RM, Lange AK, Baker MK, Fiatarone Singh MA, Vanwanseele B (2011) Lower limb muscle strengthening does not change frontal plane moments in women with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Biomech (Bristol Avon) 26(2):167–174
Huang MH, Yang RC, Lee CL, Chen TW, Wang MC (2005) Preliminary results of integrated therapy for patients with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 53(6):812–820
Jorge RT, Souza MC, Chiari A, Jones A, Fernandes AaR, Lombardi Júnior I et al (2015) Progressive resistance exercise in women with osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil 29(3):234–243
Kao MJ, Wu MP, Tsai MW, Chang WW, Wu SF (2012) The effectiveness of a self-management program on quality of life for knee osteoarthritis (OA) patients. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 54(2):317–324
Lin DH, Lin CH, Lin YF, Jan MH (2009) Efficacy of 2 non-weight-bearing interventions, proprioception training versus strength training, for patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized clinical trial. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 39(6):450–457
Mikesky AE, Mazzuca SA, Brandt KD, Perkins SM, Damush T, Lane KA (2006) Effects of strength training on the incidence and progression of knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 55(5):690–699
O’Reilly SC, Muir KR, Doherty M (1999) Effectiveness of home exercise on pain and disability from osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomised controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 58(1):15–19
Thorstensson CA, Roos EM, Petersson IF, Ekdahl C (2005) Six-week high-intensity exercise program for middle-aged patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial [ISRCTN20244858]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 6:27
An B, Dai K, Zhu Z, Wang Y, Hao Y, Tang T et al (2008) Baduanjin alleviates the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis. J Altern Complement Med 14(2):167–174
Brismée JM, Paige RL, Chyu MC, Boatright JD, Hagar JM, McCaleb JA et al (2007) Group and home-based tai chi in elderly subjects with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil 21(2):99–111
Cheung C, Wyman JF, Resnick B, Savik K (2014) Yoga for managing knee osteoarthritis in older women: a pilot randomized controlled trial. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:160
Lee HJ, Park HJ, Chae Y, Kim SY, Kim SN, Kim ST et al (2009) Tai Chi Qigong for the quality of life of patients with knee osteoarthritis: a pilot, randomized, waiting list controlled trial. Clin Rehabil 23(6):504–511
Song R, Lee EO, Lam P, Bae SC (2003) Effects of tai chi exercise on pain, balance, muscle strength, and perceived difficulties in physical functioning in older women with osteoarthritis: a randomized clinical trial. J Rheumatol 30(9):2039–2044
Tsai PF, Chang JY, Beck C, Kuo YF, Keefe FJ (2013) A pilot cluster-randomized trial of a 20-week Tai Chi program in elders with cognitive impairment and osteoarthritic knee: effects on pain and other health outcomes. J Pain Symptom Manage 45(4):660–669
Yip YB, Sit JW, Fung KK, Wong DY, Chong SY, Chung LH et al (2007) Impact of an Arthritis Self-Management Programme with an added exercise component for osteoarthritic knee sufferers on improving pain, functional outcomes, and use of health care services: an experimental study. Patient Educ Couns 65(1):113–121
Bautch JC, Malone DG, Vailas AC (1997) Effects of exercise on knee joints with osteoarthritis: a pilot study of biologic markers. Arthritis Care Res 10(1):48–55
Deyle GD, Henderson NE, Matekel RL, Ryder MG, Garber MB, Allison SC (2000) Effectiveness of manual physical therapy and exercise in osteoarthritis of the knee. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 132(3):173–181
Hay EM, Foster NE, Thomas E, Peat G, Phelan M, Yates HE et al (2006) Effectiveness of community physiotherapy and enhanced pharmacy review for knee pain in people aged over 55 presenting to primary care: pragmatic randomised trial. BMJ 333(7576):995
Hughes SL, Seymour RB, Campbell RT, Huber G, Pollak N, Sharma L et al (2006) Long-term impact of Fit and Strong! on older adults with osteoarthritis. Gerontologist 46(6):801–814
Jenkinson CM, Doherty M, Avery AJ, Read A, Taylor MA, Sach TH et al (2009) Effects of dietary intervention and quadriceps strengthening exercises on pain and function in overweight people with knee pain: randomised controlled trial. BMJ 339:b3170
Keefe FJ, Blumenthal J, Baucom D, Affleck G, Waugh R, Caldwell DS et al (2004) Effects of spouse-assisted coping skills training and exercise training in patients with osteoarthritic knee pain: a randomized controlled study. Pain 110(3):539–549
Messier SP, Loeser RF, Miller GD, Morgan TM, Rejeski WJ, Sevick MA et al (2004) Exercise and dietary weight loss in overweight and obese older adults with knee osteoarthritis: the Arthritis, Diet, and Activity Promotion Trial. Arthritis Rheum 50(5):1501–1510
Messier SP, Mihalko SL, Legault C, Miller GD, Nicklas BJ, DeVita P et al (2013) Effects of intensive diet and exercise on knee joint loads, inflammation, and clinical outcomes among overweight and obese adults with knee osteoarthritis: the IDEA randomized clinical trial. JAMA 310(12):1263–1273
Péloquin L, Bravo G, Gauthier P, Lacombe G, Billiard JS (1999) Effects of a cross-training exercise program in persons with osteoarthritis of the knee a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Rheumatol 5(3):126–136
Wang TJ, Lee SC, Liang SY, Tung HH, Wu SF, Lin YP (2011) Comparing the efficacy of aquatic exercises and land-based exercises for patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Clin Nurs 20(17–18):2609–2622
Bennell KL, Hinman RS, Metcalf BR, Buchbinder R, McConnell J, McColl G et al (2005) Efficacy of physiotherapy management of knee joint osteoarthritis: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 64(6):906–912
Kim H, Suzuki T, Saito K, Kim M, Kojima N, Ishizaki T et al (2013) Effectiveness of exercise with or without thermal therapy for community-dwelling elderly Japanese women with non-specific knee pain: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 57(3):352–359
Lund H, Weile U, Christensen R, Rostock B, Downey A, Bartels EM et al (2008) A randomized controlled trial of aquatic and land-based exercise in patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Rehabil Med 40(2):137–144
Røgind H, Bibow-Nielsen B, Jensen B, Møller HC, Frimodt-Møller H, Bliddal H (1998) The effects of a physical training program on patients with osteoarthritis of the knees. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 79(11):1421–1427
da Silva FS, de Melo FE, do Amaral MM, Caldas VV, Pinheiro Í, Abreu BJ et al (2015) Efficacy of simple integrated group rehabilitation program for patients with knee osteoarthritis: single-blind randomized controlled trial. J Rehabil Res Dev 52(3):309–322
Skou SR, Laursen S, Rathleff MB, Arendt-Nielsen MS, Simonsen L, Roos O (2015) EM. The efficacy of 12 weeks non-surgical treatment for patients not eligible for total knee replacement: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Osteoarthr Cartil 23(9):1465–1475
Chang TF, Liou TH, Chen CH, Huang YC, Chang KH (2012) Effects of elastic-band exercise on lower-extremity function among female patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Disabil Rehabil 34(20):1727–1735
Henriksen M, Klokker L, Graven-Nielsen T, Bartholdy C, Schjødt Jørgensen T, Bandak E et al (2014) Association of exercise therapy and reduction of pain sensitivity in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 66(12):1836–1843
Salacinski AJ, Krohn K, Lewis SF, Holland ML, Ireland K, Marchetti G (2012) The effects of group cycling on gait and pain-related disability in individuals with mild-to-moderate knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 42(12):985–995
Segal NA, Glass NA, Teran-Yengle P, Singh B, Wallace RB, Yack HJ (2015) Intensive gait training for older adults with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 94(10 Suppl 1):848–858
Kovar PA, Allegrante JP, MacKenzie CR, Peterson MG, Gutin B, Charlson ME (1992) Supervised fitness walking in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 116(7):529–534
Jan MH, Lin CH, Lin YF, Lin JJ, Lin DH (2009) Effects of weight-bearing versus nonweight-bearing exercise on function, walking speed, and position sense in participants with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 90(6):897–904
Rogind H, Bibow-Nielsen B, Jensen B, Møller HC, Frimodt-Møller H, Bliddal H (1998) The effects of a physical training program on patients with osteoarthritis of the knees. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 79(11):1421–1427
Foroughi N, Smith RM, Lange AK, Singh MA, Vanwanseele B (2011) Progressive resistance training and dynamic alignment in osteoarthritis: a single-blind randomised controlled trial. Clin Biomech (Bristol Avon) 26(1):71–77
Fitzgerald GK, Piva SR, Irrgang JJ, Bouzubar F, Starz TW (2004) Quadriceps activation failure as a moderator of the relationship between quadriceps strength and physical function in individuals with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 51(1):40–48
Lewek M, Stevens J, Snyder-Mackler L (2001) The use of electrical stimulation to increase quadriceps femoris muscle force in an elderly patient following a total knee arthroplasty. Phys Ther 81(9):1565–1571
Krauss I, Katzmarek U, Rieger MA, Sudeck G (2017) Motives for physical exercise participation as a basis for the development of patient-oriented exercise interventions in osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional study. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 53(4):590–602
Juhl C, Christensen R, Roos EM, Zhang W, Lund H (2014) Impact of exercise type and dose on pain and disability in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(3):622–636
Bartholdy C, Juhl C, Christensen R, Lund H, Zhang W, Henriksen M (2017) The role of muscle strengthening in exercise therapy for knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis of randomized trials. Semin Arthritis Rheum 47(1):9–21
Naugle KM, Naugle KE, Riley JL (2016) Reduced modulation of pain in older adults after isometric and aerobic exercise. J Pain 17(6):719–728
Lesinski M, Hortobágyi T, Muehlbauer T, Gollhofer A, Granacher U (2015) Effects of balance training on balance performance in healthy older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med 45(12):1721–1738
Hasanpour-Dehkordi A, Dehghani A, Solati K (2017) A comparison of the effects of pilates and Mckenzie training on pain and general health in men with chronic low back pain: a randomized trial. Indian J Palliat Care 23(1):36–40
Bowser A, Swanson BT (2016) Evaluation and treatment of a patient diagnosed with adhesive capsulitis, classified as a derangement using the mckenzie method. A case report. Int J Sports Phys Ther 11(4):627–636
Lewis JS (2009) Rotator cuff tendinopathy/subacromial impingement syndrome: is it time for a new method of assessment? Br J Sports Med 43(4):259–264
Heidar Abady A, Rosedale R, Chesworth BM, Rotondi MA, Overend TJ (2018) Consistency of commonly used orthopedic special tests of the shoulder when used with the McKenzie system of mechanical diagnosis and therapy. Musculoskelet Sci Pract 33:11–17
Willis S, Rosedale R, Rastogi R, Robbins SM (2017) Inter-rater reliability of the McKenzie System of mechanical diagnosis and therapy in the examination of the knee. J Man Manip Ther 25(2):83–90
Kwak CJ, Kim YL, Lee SM (2016) Effects of elastic-band resistance exercise on balance, mobility and gait function, flexibility and fall efficacy in elderly people. J Phys Ther Sci 28(11):3189–3196
Ledingham A, Cohn ES, Baker KR, Keysor JJ. Exercise adherence: beliefs of adults with knee osteoarthritis over 2 years. Physiother Theory Pract. 2019:1–16
Funding
The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: this article was funded by the University of Ottawa Research Chair (salary support for graduate students).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AMI: Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. JPP: substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. LB: Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. JT: substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. OT: substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. EF: substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. SP: Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Aline Mizusaki Imoto declares that she has no conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Author Jordi Pardo Pardo declares that he has no conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Author Lucie Brosseau declares that she has no conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Author Jade Taki declares that he has no conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Author Brigit Desjardins declares that she has no conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Author Eduardo Franco declares that he has no conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Author Stella Peccin declares that she has no conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imoto, A.M., Pardo, J.P., Brosseau, L. et al. Evidence synthesis of types and intensity of therapeutic land-based exercises to reduce pain in individuals with knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatol Int 39, 1159–1179 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04289-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04289-6