Abstract
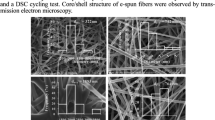
Herein, we fabricated bead-free isotactic poly(4-methyl-1-pentene) (PMP) nanofiber membranes and characterized their thermo-mechanical properties. PMP nanofiber membranes were electrospun and heat-treated at 180 and 220 °C, and thermally treated under load. The report investigates the effect of thermal treatments on the morphology, degree of crystallinity and mechanical properties, improving the mechanical properties of PMP nanofibers. Prepared nanofibers were investigated by SEM, DSC, XRD and mechanical properties. The mechanical properties demonstrate a tensile strength, an elongation (%) and a Young’s modulus of the nanofiber membranes. The DSC and WAXD analysis shows an increase of degree of crystallinity with thermal treatment. Thermally treated nanofibers under load demonstrate 4.1 times higher tensile strength and 14.1 times higher Young’s modulus than PMP fibrous membrane. Thermally treated nanofibers under load at 200 °C did not retain their structure and fuse with neighboring fibers, because it almost reached the melting temperature of (230 °C).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee Y, Kim B-S, Hong JH, Park S, Kim H, Kim I-S (2012) Enhanced mechanical properties and pre-tension effects of polyurethane (PU) nanofiber filaments prepared by electrospinning and dry twisting. J Polym Res 19(2):1–5
Yin C, Jatoi A, Bang H, Gopiraman M, Kim I-S (2016) Fabrication of silk fibroin based three dimensional scaffolds for tissue engineering. Fibers Poly 17(8):1140–1145
Lee H, Koo JM, Sohn D, Kim I-S, Im SS (2016) High thermal stability and high tensile strength terpolyester nanofibers containing biobased monomer: fabrication and characterization. RSC Adv 6(46):40383–40388
Lee H, Kim M, Sohn D, Kim SH, Oh S-G, Im SS, Kim IS (2017) Electrospun tungsten trioxide nanofibers decorated with palladium oxide nanoparticles exhibiting enhanced photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv 7(10):6108–6113
Khatri Z, Jatoi AW, Ahmed F, Kim I-S (2016) Cell adhesion behavior of poly (ε-caprolactone)/poly (l-lactic acid) nanofibers scaffold. Mater Lett 171:178–181
Ke M, Wahab JA, Hyunsik B, Song K-H, Lee JS, Gopiraman M, Kim IS (2016) Allantoin-loaded porous silica nanoparticles/polycaprolactone nanofiber composites: fabrication, characterization, and drug release properties. RSC Adv 6(6):4593–4600
Gopiraman M, Jatoi AW, Hiromichi S, Yamaguchi K, Jeon H-Y, Chung I-M, Soo KI (2016) Silver coated anionic cellulose nanofiber composites for an efficient antimicrobial activity. Carbohyd Polym 149(20):51–59
Mitchell RR, Gallant BM, Thompson CV, Shao-Horn Y (2011) All-carbon-nanofiber electrodes for high-energy rechargeable Li–O 2 batteries. Energy Environ Sci 4(8):2952–2958
Lee H, Phan D-N, Kim M, Sohn D, Oh S-G, Kim S, Kim I (2016) The chemical deposition method for the decoration of palladium particles on carbon nanofibers with rapid conductivity changes. Nanomaterials 6(12):226–235
Sambaer W, Zatloukal M, Kimmer D (2011) 3D modeling of filtration process via polyurethane nanofiber based nonwoven filters prepared by electrospinning process. Chem Eng Sci 66(4):613–623
Kizildag N, Ucar N, Karacan I, Onen A, Demirsoy N (2014) The effect of the dissolution process and the polyaniline content on the properties of polyacrylonitrile–polyaniline composite nanoweb. J Ind Text 45(6):1548–1570
Huang Z-M, Zhang Y-Z, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2003) A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 63(15):2223–2253
Lee H, Nagaishi T, Phan D-N, Kim M, Zhang K-Q, Wei K, Kim IS (2017) Effect of graphene incorporation in carbon nanofiber decorated with TiO2 for photoanode applications. RSC Adv 7(11):6574–6582
Ramakrishna S, Fujihara K, Teo W-E, Yong T, Ma Z, Ramaseshan R (2006) Electrospun nanofibers: solving global issues. Mater Today 9(3):40–50
Lee H, Watanabe K, Kim M, Gopiraman M, Song K-H, Lee JS, Kim IS (2016) Handspinning enabled highly concentrated carbon nanotubes with controlled orientation in nanofibers. Sci Rep 6:37590
W-x Zhang, Y-z Wang, C-f Sun (2007) Characterization on oxidative stabilization of polyacrylonitrile nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. J Polym Res 14(6):467–474
Saligheh O, Forouharshad M, Arasteh R, Eslami-Farsani R, Khajavi R, Roudbari BY (2013) The effect of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on morphology, crystallinity and mechanical properties of PBT/MWCNT composite nanofibers. J Polym Res 20(2):1–6
He B, Tian L, Li J, Pan Z (2013) Effect of hot-stretching on morphology and mechanical properties of electrospun PMIA nanofibers. Fibers Poly 14(3):405–408
Baji A, Mai Y-W, Wong S-C, Abtahi M, Chen P (2010) Electrospinning of polymer nanofibers: effects on oriented morphology, structures and tensile properties. Compos Sci Technol 70(5):703–718
Liu LQ, Tasis D, Prato M, Wagner HD (2007) Tensile mechanics of electrospun multiwalled nanotube/poly (methyl methacrylate) nanofibers. Adv Mater 19(9):1228–1233
Sun W, Cai Q, Li P, Deng X, Wei Y, Xu M, Yang X (2010) Post-draw PAN–PMMA nanofiber reinforced and toughened Bis-GMA dental restorative composite. Dental Mat 26(9):873–880
You Y, Lee SW, Lee SJ, Park WH (2006) Thermal interfiber bonding of electrospun poly (l-lactic acid) nanofibers. Mater Lett 60(11):1331–1333
Tsai H, Ciou Y, Hu C, Lee K, Yu D, Lai J (2005) Heat-treatment effect on the morphology and pervaporation performances of asymmetric PAN hollow fiber membranes. J Membr Sci 255(1):33–47
Hou X, Yang X, Zhang L, Waclawik E, Wu S (2010) Stretching-induced crystallinity and orientation to improve the mechanical properties of electrospun PAN nanocomposites. Mater Des 31(4):1726–1730
Griffith JH, Rånby B (1960) Dilatometric measurements on poly (4-methyl-1-pentene) glass and melt transition temperatures, crystallization rates, and unusual density behavior. J Poly Sci 44(144):369–381
Lee K-H, Givens S, Chase DB, Rabolt JF (2006) Electrostatic polymer processing of isotactic poly (4-methyl-1-pentene) fibrous membrane. Polymer 47(23):8013–8018
Lee K-H, Givens SR, Snively CM, Chase B, Rabolt JF (2008) Crystallization behavior of electrospun PB/PMP blend fibrous membranes. Macromolecules 41(9):3144–3148
Fong H, Chun I, Reneker D (1999) Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer 40(16):4585–4592
Bryant GM (1967) Fibers from crystalline hydrocarbon polymers1. Text Res J 37(7):552–563
Hayes HJ, McCarthy TJ (1998) Maleation of poly (4-methyl-1-pentene) using supercritical carbon dioxide. Macromolecules 31(15):4813–4819
Jalili R, Morshed M, Ravandi SAH (2006) Fundamental parameters affecting electrospinning of PAN nanofibers as uniaxially aligned fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 101(6):4350–4357
Esrafilzadeh D, Jalili R, Morshed M (2008) Crystalline order and mechanical properties of as-electrospun and post-treated bundles of uniaxially aligned polyacrylonitrile nanofiber. J Appl Polym Sci 110(5):3014–3022
Charlet G, Delmas G (1984) Effect of solvent on the polymorphism of poly (4-methylpentene-1): 2. crystallization in semi-dilute solutions. Polymer 25(11):1619–1625
De Rosa C (2003) Crystal structure of form II of isotactic poly (4-methyl-1-pentene). Macromolecules 36(16):6087–6094
Miyoshi T, Pascui O, Reichert D (2004) Large-amplitude motions of form III of isotactic poly (4-methyl-1-pentene) crystallites prior to crystal-crystal transformation. Macromolecules 37(17):6653–6656
Chen S, Jin J, Zhang J (2010) Non-isothermal crystallization behaviors of poly (4-methyl-pentene-1). J Therm Anal Calorim 103(1):229–236
Aharoni SM, Charlet G, Delmas G (1981) Investigation of solutions and gels of poly (4-methyl-1-pentene) in cyclohexane and decalin by viscosimetry, calorimetry, and X-ray diffraction. A new crystalline form of poly (4-methyl-1-pentane) from gels. Macromolecules 14(5):1390–1394
Acknowledgements
The research project was supported by Wataya Co., Ltd., Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wahab, J.A., Lee, H., Wei, K. et al. Post-electrospinning thermal treatments on poly(4-methyl-1-pentene) nanofiber membranes for improved mechanical properties. Polym. Bull. 74, 5221–5230 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-017-2004-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-017-2004-4