Abstract
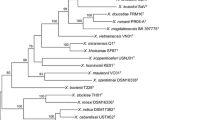
Xenorhabdus species are normally closely associated with entomopathogenic nematodes of the family Steinernematidae. Strain F2, isolated from Steinernema nguyeni, was identified as Xenorhabdus bovienii and strains J194 and SB10, isolated from Steinernema jeffreyense and Steinernema sacchari as Xenorhabdus khoisanae, based on phenotypic characteristics and sequencing of 16S rRNA and housekeeping genes dnaN, gltX, gyrB, infB and recA. All three strains produced antimicrobial compounds that inhibited the growth of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This is the first report of associations between strains of the symbiotic bacteria X. bovienii with S. nguyeni, and X. khoisanae with S. jeffreyense and S. sacchari. This provides evidence that strains of Xenorhabdus spp. may switch between nematode species within the same clade and between different clades.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams BJ, Nguyen KB (2002) Taxonomy and systematics. In: Gaugler R (ed) Entomopathogenic nematology. CAB International, London, pp 1–33
Akhurst RJ (1980) Morphological and functional dimorphism in Xenorhabdus spp., bacteria symbiotically associated with the insect pathogenic nematodes Neoplectana and Heterorhabditis. J Gen Microbiol 212:303–309
Akhurst RJ, Boemare NE (2005) Xenorhabdus. In: Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity GM (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 2B, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 831–838
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477
Boemare NE, Akhurst RJ (1988) Biochemical and physiological characterization of colony form variants in Xenorhabdus spp. (Enterobacteriaceae). J Gen Microbiol 134:751–761
Boemare NE, Boyer-Giglio M-H, Thaler J-O, Akhurst RJ, Brehelin M (1992) Lysogeny and bacteriocinogeny in Xenorhabdus nematophilus and other Xenorhabdus spp. Appl Environ Microb 58(9):3032–3037
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, Madden TL (2009) BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform 10:421
Çimen H, Půža V, Nermu J, Hatting H, Ramakuwela T, Faktorová L, Hazir S (2016) Steinernema beitlechemi n. sp., a new entomopathogenic nematode (Nematoda: Steinernematidae) from South Africa. Nematology 18:439–453
Crouse J, Amorese D (1987) Ethanol precipitation: ammonium acetate as an alternative to sodium acetate. Focus 9:3–5
Ferreira T, Van Reenen CA, Endo A, Dicks LMT, Malan AP, Spröer C (2013) Description of Xenorhabdus khoisanae sp. nov., a symbiont of the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema khoisanae. Int J Syst Evol Micribiol 63:3220–3224
Ferreira T, Van Reenen CA, Pagès S, Tailliez P, Malan AP, Dicks LMT (2013) Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. noenieputensis subsp. nov., a symbiotic bacterium associated with a novel Heterorhabditis species related to Heterorhabditis indica. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1853–1858
Ferreira T, Addison MF, Malan AP (2016) Development and population dynamics of Steinernema yirgalemense (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae) and growth characteristics of its associated Xenorhabdus indica symbiont in liquid culture. J Helminthol 90:364–371
Kaya HK, Stock SP (1997) Techniques in insect nematology. In: Lawrence L (ed) Manual of techniques in insect pathology. Academic Press, London, pp 281–322
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Lee MM, Stock SP (2010) A multigene approach for accessing evolutionary relationships of Xenorhabdus spp. (gamma-Proteobacteria), the bacterial symbionts of entomopathogenic Steinernema nematodes. J Invertebr Pathol 104:67–74
Magoc T, Pabinger S, Canzar S, Liu X, Su Q, Puiu D, Tallon LJ, Salzberg SL (2013) GAGE-B: an evaluation of genome assemblers for bacterial organisms. Bioinformatics 29(14):1718–1725
Malan AP, Knoetze R, Tiedt TR (2016) Steinernema nguyeni n. sp. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae), a new entomopathogenic nematode from South Africa. Nematology 18:571–590
Malan AP, Knoetze R, Tiedt LR (2016) Steinernema jeffreyense n. sp. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae), a new entomopathogenic nematode from South Africa. J Helminthol 90:262–278
Naidoo S, Featherston J, Gray VM (2015) Draft whole-genome sequence and annotation of the entomopathogenic bacterium Xenorhabdus khoisanae strain MCB. Genome Announc 3(4):e00872-15. doi:10.1128/genomeA.00872-15
Nthenga I, Knoetze R, Berry S, Tiedt LR, Malan AP (2014) Steinernema sacchari n. sp. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae), a new entomopathogenic nematode from South Africa. Nematology 16:475–494
Poinar GO, Hess R, Thomas GM (1980) Isolation of defective bacteriophages form Xenorhabdus spp. (Enterobacteriaceae). IRCS. J Med Sci 8:141
Spiridonov SE, Reid AP, Podrucka K, Subbotin SA, Moens M (2004) Phylogenetic relationships within the genus Steinernema (Nematoda: Rhabditida) as inferred from analyses of sequences of the ITSI-5.8S-ITS2 region of rDNA and morphological features. Nematology 6:547–566
Stock P (2015) Diversity, biology and evolutionary relationships. In: Campos-Herrera R (ed) Sustainability in plant and crop protection: ecology and applied technologies for sustainable plant and crop protection. Springer, Basel, pp 3–27
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Thomas GM, Poinar JR (1979) Xenorhabdus gen. nov., a genus of entomopathogenic, nematophilic bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Int J Syst Bacteriol 29(4):352–360
Utturkar SM, Klingeman DM, Land ML, Schadt CW, Doktycz MJ, Pelletier DA, Brown SD (2014) Evaluation and validation of de novo and hybrid assembly techniques to derive high-quality genome sequences. Bioinformatics 30(19):2709–2716
Webster JM, Chen G, Hu K, Li J (2002) Bacterial metabolites. In: Gaugler R (ed) Entomopathogenic nematology. CAB International, London, pp 35–56
Zang Z, Schwartz S, Wagner L, Miller W (2000) A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J Comput Biol 7(1–2):203–214
Zerbino DR, Birney E (2008) Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res 18(5):821–829
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dreyer, J., Malan, A.P. & Dicks, L.M.T. Three Novel Xenorhabdus–Steinernema Associations and Evidence of Strains of X. khoisanae Switching Between Different Clades. Curr Microbiol 74, 938–942 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1266-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1266-2