Abstract
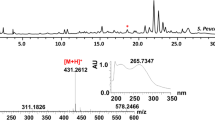
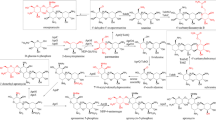
Bitespiramycin (BT), a multi-component antibiotic consisted mainly of 4″-isovalerylspiramycin I, II and III, is produced by Streptomyces spiramyceticus WSJ-1, a recombinant spiramycin-production strain that harbored the 4″-O-acyltransferase gene (ist) from Streptomyces mycarofaciens 1748, which could isovalerylate the 4″-OH of spiramycin. To eliminate the production of components 4″-isovalerylspiramycin II and III, therefore reducing the component complexity of BT, inactivation of the sspA gene, which encodes the 3-O-acyltransferase responsible for the acylation of spiramycin I to spiramycin II and III, was performed in Streptomyces spiramyceticus WSJ-1, by in-frame partial deletion. The resulting strain, Streptomyces spiramyceticus WSJ-2, is a 4″-isovalerylspiramycin-I-producing strain as expected.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shang GD, Dai JL, Wang Y (1999) Construction of a stable bioengineered strain of biotechmycin. Chin J Biotechnol 15(2):171–175
Jin W, Sun C, Jiang W et al (2002) Chemical studies of shengjimycin components. Chin J Antibiot 22(12):705–708
Omura S, Ikeda H, Kitao C (1979) Isolation and properties of spiramycin I 3-hydroxyl acylase from Streptomyces ambofaciens. J Biochem (Tokyo) 86(6):1753–1758
Wu LZ, Ma CY, Wang YG et al (2007) Deletion of spiramycin 3-O-acyltransferase gene from Streptomyces spiramyceticus F21 resulted in the production of spiramycin I as major component. Chin J Biotechnol 23(4):612–617
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K et al (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116(1):43–49
Xu P, Li WJ, Xu LH et al (2003) A microwave-based method for genomic DNA extraction from Actinomycetes. Microbiology (China) 30(4):73–75
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1999) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Tobias K, Bibb MJ, Mark JB et al (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Liu YF, Sun CH, Jin WZ (1997) Isolation and structural identification of shengjimycin A and B, the major components of shengjimycins. Chin J Antibiot 22(5):328–333
Sun CH, Jiang W, Jin WZ et al (2000) Isolation and structure determination of 4″-isovalerylspiramycin I. Chin J Antibiot 25(3):1–4
Shang GD, Dai JL, Wang YG (2001) Construction and physiological studies on a stable bioengineered strain of shengjimycin. J Antibiot 54(1):66–73
Shi XG, Zhong D-F (2003) Analysis of multicomponent in bitespiramycin by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chin Mass Spectrom Soc 24(4):460–463
Liu L, Saevels J, Louis P et al (1999) Interlaboratory study comparing the microbiological potency of spiramycins I, II and III. J Pharm Biomed Anal 20(1–2):217–224
Schauner C, Dary A, Lebrihi A, Leblond P, Decaris B, Germain P (1999) Modulation of lipid metabolism and spiramycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces ambofaciens unstable mutants. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(6):2730–2737
Leblond P, Demuyter P, Moutier L, Laakel M, Decaris B, Simonet JM (1989) Hypervariability, a new phenomenon of genetic instability, related to DNA amplification in Streptomyces ambofaciens. J Bacteriol 171(1):419–423
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by China National High Technology Programme (2006AA02Z230).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Chunyan Ma and Linzhuan Wu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, C., Zhou, H., Li, J. et al. Construction of 4″-Isovalerylspiramycin-I-Producing Strain by In-Frame Partial Deletion of 3-O-Acyltransferase Gene in Streptomyces spiramyceticus WSJ-1, the Bitespiramycin Producer. Curr Microbiol 62, 16–20 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9664-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9664-8