Abstract
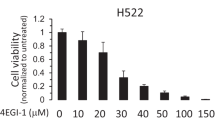
Activated cap-dependent translation promotes cancer by stimulating translation of mRNAs encoding malignancy-promoting proteins. The nucleoside monophosphate Protide, 4Ei-10, undergoes intracellular uptake and conversion by Hint1 to form 7-Cl-Ph-Ethyl-GMP. 7-Cl-Ph-Ethyl-GMP is an analog of cap and inhibits protein translation by binding and sequestering eIF4E thus blocking eIF4E from binding to the mRNA cap. The effects of inhibiting translation initiation by disruption of the eIF4F complex with 4Ei-10 were examined in malignant mesothelioma (MM). In a cell-free assay system, formation of the eIF4F complex was disabled in response to exposure to 4Ei-10. Treatment of MM with 4Ei-10 resulted in decreased cell proliferation, increased sensitivity to pemetrexed and altered expression of malignancy-related proteins. In light of these findings, suppression of translation initiation by small molecule inhibitors like 4Ei-10 alone or in combination with pemetrexed represents an encouraging strategy meriting further evaluation in the treatment of MM.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bitterman PB, Polunovsky VA (2015) eIF4E-mediated translational control of cancer incidence. Biochim Biophys Acta 1849(7):774–780
Gao B (1849) Roux PP (2015) Translational control by oncogenic signaling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta 7:753–765
Pelletier J, Graff J, Ruggero D, Sonenberg N (2015) Targeting the eIF4F translation initiation complex: a critical nexus for cancer development. Cancer Res. 75(2):250–263
Hsieh AC, Ruggero D (2010) Targeting eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16(20):4914–4920
Lu C, Makala L, Wu D, Cai Y (2016) Targeting translation: eIF4E as an emerging anticancer drug target. Expert Rev Mol Med 18:e2
Li S, Jia Y, Jacobson B, McCauley J, Kratzke R, Bitterman PB et al (2013) Treatment of breast and lung cancer cells with a N-7 benzyl guanosine monophosphate tryptamine phosphoramidate pronucleotide (4Ei-1) results in chemosensitization to gemcitabine and induced eIF4E proteasomal degradation. Mol Pharm 10(2):523–531
Chen EZ, Jacobson BA, Patel MR, Okon AM, Li S, Xiong K et al (2014) Small-molecule inhibition of oncogenic eukaryotic protein translation in mesothelioma cells. Invest New Drugs 32(4):598–603
Okon A, Han J, Dawadi S, Demosthenous C, Aldrich CC, Gupta M et al (2017) Anchimerically activated ProTides as inhibitors of cap-dependent translation and inducers of chemosensitization in mantle cell lymphoma. J Med Chem 60(19):8131–8144
Chen X, Kopecky DJ, Mihalic J, Jeffries S, Min X, Heath J et al (2012) Structure-guided design, synthesis, and evaluation of guanine-derived inhibitors of the eIF4E mRNA-cap interaction. J Med Chem 55(8):3837–3851
De A, Jacobson BA, Peterson MS, Jay-Dixon J, Kratzke MG, Sadiq AA et al (2018) 4EGI-1 represses cap-dependent translation and regulates genome-wide translation in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Invest New Drugs 36(2):217–229
Jacobson BA, Thumma SC, Jay-Dixon J, Patel MR, Dubear Kroening K, Kratzke MG et al (2013) Targeting eukaryotic translation in mesothelioma cells with an eIF4E-specific antisense oligonucleotide. PLoS ONE 8(11):e81669
Moerke NJ, Aktas H, Chen H, Cantel S, Reibarkh MY, Fahmy A et al (2007) Small-molecule inhibition of the interaction between the translation initiation factors eIF4E and eIF4G. Cell 128(2):257–267
Jacobson BA, De A, Kratzke MG, Patel MR, Jay-Dixon J, Whitson BA, Sadiq AA, Bitterman PB, Polunovsky VA, Kratzke RA (2009) Activated 4E-BP1 represses tumourigenesis and IGF-I-mediated activation of the eIF4F complex in mesothelioma. Br J Cancer 101(3):424–431
Patel MR, Jacobson BA, De A, Frizelle SP, Janne P, Thumma SC et al (2007) Ras pathway activation in malignant mesothelioma. J Thorac Oncol. 2(9):789–795
Graff JR, Zimmer SG (2003) Translational control and metastatic progression: enhanced activity of the mRNA cap-binding protein eIF-4E selectively enhances translation of metastasis-related mRNAs. Clin Exp Metastasis 20(3):265–273
Sonenberg N, Guertin D, Cleveland D, Trachsel H (1981) Probing the function of the eucaryotic 5' cap structure by using a monoclonal antibody directed against cap-binding proteins. Cell 27(3 Pt 2):563–572
Robichaud N, Sonenberg N, Ruggero D, Schneider RJ (2019) Translational control in cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 11(7):1–16
Willimott S, Wagner SD (2010) Post-transcriptional and post-translational regulation of Bcl2. Biochem Soc Trans 38(6):1571–1575
Jiang S, Tu K, Fu Q, Schmitt DC, Zhou L, Lu N et al (2015) Multifaceted roles of HSF1 in cancer. Tumour Biol 36(7):4923–4931
Wek RC (2018) Role of eIF2α kinases in translational control and adaptation to cellular stress. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 10(7):1–16
Rozpedek W, Pytel D, Mucha B, Leszczynska H, Diehl JA, Majsterek I (2016) The role of the PERK/eIF2alpha/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway in tumor progression during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Curr Mol Med 16(6):533–544
Han J, Back SH, Hur J, Lin YH, Gildersleeve R, Shan J et al (2013) ER-stress-induced transcriptional regulation increases protein synthesis leading to cell death. Nat Cell Biol 15(5):481–490
Bibby AC, Maskell NA (2018) Current treatments and trials in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Clin Respir J 12(7):2161–2169
Kratzke RA (2017) Targeting eukaryotic protein translation in mesothelioma. Transl Lung Cancer Res 6(3):343–349
DeFatta RJ, Nathan CA, De Benedetti A (2000) Antisense RNA to eIF4E suppresses oncogenic properties of a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Laryngoscope 110(6):928–933
Dong K, Wang R, Wang X, Lin F, Shen JJ, Gao P et al (2009) Tumor-specific RNAi targeting eIF4E suppresses tumor growth, induces apoptosis and enhances cisplatin cytotoxicity in human breast carcinoma cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 113(3):443–456
Graff JR, Konicek BW, Vincent TM, Lynch RL, Monteith D, Weir SN et al (2007) Therapeutic suppression of translation initiation factor eIF4E expression reduces tumor growth without toxicity. J Clin Invest 117(9):2638–2648
Thumma SC, Jacobson BA, Patel MR, Konicek BW, Franklin MJ, Jay-Dixon J et al (2015) Antisense oligonucleotide targeting eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E reduces growth and enhances chemosensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther 22(8):396–401
Hong DS, Kurzrock R, Oh Y, Wheler J, Naing A, Brail L et al (2011) A phase 1 dose escalation, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic evaluation of eIF-4E antisense oligonucleotide LY2275796 in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17(20):6582–6591
Duffy AG, Makarova-Rusher OV, Ulahannan SV, Rahma OE, Fioravanti S, Walker M et al (2016) Modulation of tumor eIF4E by antisense inhibition: a phase I/II translational clinical trial of ISIS 183750-an antisense oligonucleotide against eIF4E-in combination with irinotecan in solid tumors and irinotecan-refractory colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 139(7):1648–1657
Chen L, Aktas BH, Wang Y, He X, Sahoo R, Zhang N et al (2012) Tumor suppression by small molecule inhibitors of translation initiation. Oncotarget. 3(8):869–881
De A, Jacobson BA, Peterson MS, Stelzner ME, Jay-Dixon J, Kratzke MG et al (2019) Inhibition of oncogenic cap-dependent translation by 4EGI-1 reduces growth, enhances chemosensitivity and alters genome-wide translation in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 26(5–6):157–165
Descamps G, Gomez-Bougie P, Tamburini J, Green A, Bouscary D, Maiga S et al (2012) The cap-translation inhibitor 4EGI-1 induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma through Noxa induction. Br J Cancer 106(10):1660–1667
Wu M, Zhang C, Li XJ, Liu Q, Wanggou S (2016) Anti-cancer effect of cap-translation inhibitor 4EGI-1 in human glioma U87 cells: involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress. Cell Physiol Biochem 40(5):1013–1028
Schwarzer A, Holtmann H, Brugman M, Meyer J, Schauerte C, Zuber J et al (2015) Hyperactivation of mTORC1 and mTORC2 by multiple oncogenic events causes addiction to eIF4E-dependent mRNA translation in T-cell leukemia. Oncogene 34(27):3593–3604
Willimott S, Beck D, Ahearne MJ, Adams VC, Wagner SD (2013) Cap-translation inhibitor, 4EGI-1, restores sensitivity to ABT-737 apoptosis through cap-dependent and -independent mechanisms in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 19(12):3212–3223
Assouline S, Culjkovic-Kraljacic B, Bergeron J, Caplan S, Cocolakis E, Lambert C et al (2015) A phase I trial of ribavirin and low-dose cytarabine for the treatment of relapsed and refractory acute myeloid leukemia with elevated eIF4E. Haematologica 100(1):e7–9
Jacobson BA, De A, Kratzke MG, Patel MR, Jay-Dixon J, Whitson BA et al (2009) Activated 4E-BP1 represses tumourigenesis and IGF-I-mediated activation of the eIF4F complex in mesothelioma. Br J Cancer 101(3):424–431
Ramon YCS, Castellvi J, Hummer S, Peg V, Pelletier J, Sonenberg N (2018) Beyond molecular tumor heterogeneity: protein synthesis takes control. Oncogene 37(19):2490–2501
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Harvey Carlson Mesothelioma Research Fund. All authors have read the journal's authorship agreement and the policy on potential conflicts of interest.
Funding
This work was funded in part by the Harvey Carlson Mesothelioma Research Fund of the University of Minnesota.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: Z.A., B.A.J, M.R.P., C.R.W., R.A.K. Performed the experiments: Z.A., B.A.J, M.W.M., N.V.V., G.V.V., S.C. Analyzed the data: Z.A., B.A.J, M.W.M., N.V.V., G.V.V., S.C., M.D., A.M.O., M.R.P., C.R.W., R.A.K. Contributed reagents/materials/analytic tools: M.D., A.M.O., M.R.P., C.R.W., R.A.K. Wrote the main manuscript: Z.A., B.A.J, R.A.K. Wrote subsequent drafts of manuscript: Z.A., B.A.J, M.D., M.R.P., C.R.W., R.A.K. Reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript: Z.A., B.A.J, M.W.M., N.V.V., G.V.V., S.C., M.D., A.M.O., M.R.P., C.R.W., R.A.K.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Zeeshan Ahmad has no conflict of interest, author Blake A. Jacobson has no conflict of interest, author Mitchell W. McDonald has no conflict of interest, author Nicolas Vattendahl Vidal has no conflict of interest, author Gabriel Vattendahl Vidal has no conflict of interest, author Sierra Chen has no conflict of interest, author Maxwell Dillenburg has no conflict of interest, author Aniekan M. Okon has no conflict of interest, author Manish R. Patel has no conflict of interest, author Carston R. Wagner has no conflict of interest, and author Robert A. Kratzke has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
No human subjects were used in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, Z., Jacobson, B.A., McDonald, M.W. et al. Repression of oncogenic cap-mediated translation by 4Ei-10 diminishes proliferation, enhances chemosensitivity and alters expression of malignancy-related proteins in mesothelioma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 85, 425–432 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04029-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04029-9