Abstract
Purpose
Platinum-based doublet chemotherapy and radiotherapy are the standard treatment option in advanced squamous cell carcinoma patients. However, few agents could be selected for subsequent post-second-line treatment. As a small molecule inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase, apatinib had been proved in advanced gastric cancer. Here, we showed its efficacy and safety in lung squamous cell carcinoma.
Methods
In this retrospective study, 13 advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma patients were enrolled. They received doublet chemotherapy or docetaxel as the first-line treatment. After disease progressed, all patients were administrated apatinib monotherapy (250–425 mg/day) for second-line or fourth-line therapy.
Results
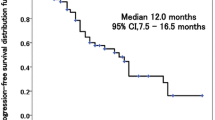
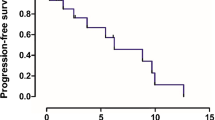
After apatinib monotherapy, two patients achieved partial response, four patients achieved stable disease, and seven patients achieved progression disease. The medium PFS was 3.1 months. The median OS had not yet been reached. The objective remission rate was 15.4% (2/13). The total disease control rate was 46.2% (6/13). The main advert effects were vomiting and hypertension.
Conclusion
Apatinib might be an option as rescue treatment in advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gridelli C, de Marinis F, Cappuzzo F et al (2014) Treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation or ALK gene rearrangement: results of an international expert panel meeting of the Italian Association of Thoracic Oncology. Clin Lung Cancer 15:173–181
Janku F, Garrido-Laguna I, Petruzelka LB et al (2011) Novel therapeutic targets in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 6:1601–1612
Herbst RS, Onn A, Sandler A (2005) Angiogenesis and lung cancer: prognostic and therapeutic implications. J Clin Oncol 23:3243–3256
Goel HL, Mercurio AM (2013) VEGF targets the tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer 13:871–882
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC et al (2006) Paclitaxel–carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 355:2542–2550
Garon EB, Ciuleanu TE, Arrieta O et al (2014) Ramucirumab plus docetaxel versus placebo plus docetaxel for second-line treatment of stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer after disease progression on platinum-based therapy (REVEL): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 384:665–673
de Gramont A, Van Cutsem E, Schmoll HJ et al (2012) Bevacizumab plus oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer (AVANT): a phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 13:1225–1233
Pujade-Lauraine E, Hilpert F, Weber B et al (2014) Bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy for platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer: the AURELIA open-label randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 32:1302–1308
Hu X, Zhang J, Xu B et al (2014) Multicenter phase II study of apatinib, a novel VEGFR inhibitor in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Cancer 135:1961–1969
Li J, Qin S, Xu J et al (2013) Apatinib for chemotherapy-refractory advanced metastatic gastriccancer: results from a randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-arm, phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 31:3219–3225
Ding L, Li QJ, You KY et al (2016) The use of apatinib in treating nonsmall-cell lung cancer: case report and review of literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 95:e3598
Song Z, Yu X, Lou G et al (2017) Salvage treatment with apatinib for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther 10:1821–1825
Xu J, Liu X, Yang S et al (2018) Clinical response to apatinib monotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 14:264–269
Zeng DX, Wang CG, Lei W et al (2017) Efficiency of low dosage apatinib in post-first-line treatment of advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 8:66248–66253
Zeng DX, Wang CG, Huang JA et al (2017) Apatinib in the treatment of advanced lung adenocarcinoma with KRAS mutation. Onco Targets Ther 10:4269–4272
Fang SC, Zhang HT, Zhang YM et al (2017) Apatinib as post second-line therapy in EGFR wild-type and ALK-negative advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 10:447–452
Mi YJ, Liang YJ, Huang HB et al (2010) Apatinib (YN968D1) reverses multidrug resistance by inhibiting the efflux function of multiple ATP-binding cassette transporters. Cancer Res 70:7981–7991
Funding
This study was supported by Jiangsu Province Special Program of Medical Science (BE2016672), Program of Key Talents of Medical Science in Jiangsu Province (QNRC2016745), Clinical Key Speciality Project of China, Clinical Medicine Center of Suzhou (No. SZZX201502), Suzhou Key Laboratory for Respiratory Medicine (No. SZS201617).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Dx., Lei, W., Wang, Cg. et al. Low dosage of apatinib monotherapy as rescue treatment in advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 83, 439–442 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-018-3743-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-018-3743-0