Abstract
Purpose
The present study examined the possible involvement of the lipoxygenase (LOX) pathway in cisplatin (CPT)-induced nephrotoxicity.
Methods
Wistar albino rats were challenged with CPT IP injection (7.5 mg/kg) and were sacrificed after one week. Signs of renal dysfunction, including urea and creatinine clearance levels and renal histological structure, were investigated. Gene and protein expression levels of different LOX pathway enzymes and products, including 5-LOX, 12-LOX, 15-LOX, 5-LOX activating protein (FLAP), leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4 hydrolase), leukotriene C4 synthase (LTC4 synthase), LTB4 receptor, and cysteinyl (cys) LT receptor types 1 and 2, were also determined in the kidneys using real-time PCR and western blotting, respectively. The serum and kidney levels of LTB4 and inflammatory markers were also estimated.
Results
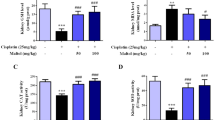
CPT renal toxicity was established as the creatinine and urea clearance levels were significantly reduced, while the serum levels of creatinine and urea were markedly increased. We reported a considerable up-regulation in the mRNA and protein expression levels of 5-LOX, FLAP, 12-LOX, LTA4 hydrolase, LTC4 synthase, LTB4 receptor, and Cys LT receptor types 1 and 2, while 15-LOX expression did not significantly change in the CPT group. Additionally, LTB4 and inflammatory indicators in serum and renal levels were elevated significantly in the CPT group. Histopathological examination clearly showed the nephrotoxic changes in the renal tissues of CPT-challenged animals.
Conclusions
Our findings suggested, for the first time, the participation of LOX enzymes and products in the signaling pathway leading to CPT-associated nephrotoxicity, which could be the foundation stone for combining LOX pathway attenuators with CPT therapy to decrease CPT-associated renal toxicity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Madias NE, Harrington JT (1978) Platinum nephrotoxicity. Am J Med 65(2):307–314. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(78)90825-2
Goldstein RS, Mayor GH (1983) Minireview. The nephrotoxicity of cisplatin. Life Sci 32(7):685–690
Miller RP, Tadagavadi RK, Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2010) Mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins (Basel) 2(11):2490–2518. doi:10.3390/toxins2112490
Conti M, De Giorgi U, Tazzari V, Bezzi F, Baccini C (2004) Clinical pharmacology of intraperitoneal cisplatin-based chemotherapy. J Chemother 16(5):23–25
Townsend DM, Deng M, Zhang L, Lapus MG, Hanigan MH (2003) Metabolism of cisplatin to a nephrotoxin in proximal tubule cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 14(1):1–10
Townsend DM, Hanigan MH (2002) Inhibition of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase or cysteine S-conjugate beta-lyase activity blocks the nephrotoxicity of cisplatin in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 300(1):142–148
Zhang L, Hanigan MH (2003) Role of cysteine S-conjugate beta-lyase in the metabolism of cisplatin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306(3):988–994. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.052225
Reinhold SW, Vitzthum H, Filbeck T, Wolf K, Lattas C, Riegger GA, Kurtz A, Kramer BK (2006) Gene expression of 5-, 12-, and 15-lipoxygenases and leukotriene receptors along the rat nephron. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290(4):F864–872. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00169.2005
Lianos EA, Rahman MA, Dunn MJ (1985) Glomerular arachidonate lipoxygenation in rat nephrotoxic serum nephritis. J Clin Invest 76(4):1355–1359. doi:10.1172/JCI112110
Badr KF (1992) Sepsis-associated renal vasoconstriction: potential targets for future therapy. Am J Kidney Dis 20(3):207–213
Rosenberg B, Vancamp L, Krigas T (1965) Inhibition of cell division in Escherichia coli by electrolysis products from a platinum electrode. Nature 205:698–699
Rosenberg B, VanCamp L, Trosko JE, Mansour VH (1969) Platinum compounds: a new class of potent antitumour agents. Nature 222(5191):385–386
Kociba RJ, Sleight SD (1971) Acute toxicologic and pathologic effects of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (NSC-119875) in the male rat. Cancer Chemother Rep 55(1):1–8
Hartmann JT, Kollmannsberger C, Kanz L, Bokemeyer C (1999) Platinum organ toxicity and possible prevention in patients with testicular cancer. Int J Cancer 83(6):866–869. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19991210)83:6<866:AID-IJC34>3.0.CO;2-9
Santoso JT, Lucci JA 3rd, Coleman RL, Schafer I, Hannigan EV (2003) Saline, mannitol, and furosemide hydration in acute cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a randomized trial. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 52(1):13–18. doi:10.1007/s00280-003-0620-1
Taguchi T, Nazneen A, Abid MR, Razzaque MS (2005) Cisplatin-associated nephrotoxicity and pathological events. Contrib Nephrol 148:107–121. doi:10.1159/000086055
Kolati SR, Kasala ER, Bodduluru LN, Mahareddy JR, Uppulapu SK, Gogoi R, Barua CC, Lahkar M (2015) BAY 11-7082 ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by attenuating hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative stress and renal inflammation via NF-kappaB pathway. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 39(2):690–699. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2015.01.019
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N, Nugent K (2007) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Am J Med Sci 334(2):115–124. doi:10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31812dfe1e
Nakao A, Watanabe T, Ohishi N, Toda A, Asano K, Taniguchi S, Nosaka K, Noiri E, Suzuki T, Sakai T, Kurokawa K, Shimizu T, Kimura S (1999) Ubiquitous localization of leukotriene A4 hydrolase in the rat nephron. Kidney Int 55(1):100–108. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00257.x
Badr KF (1992) Five-lipoxygenase products in glomerular immune injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 3(4):907–915
Evans JF (2002) Cysteinyl leukotriene receptors. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 68–69:587–597
Wu SH, Bresnahan BA, Lianos EA (1993) Hemodynamic role of arachidonate 12- and 5-lipoxygenases in nephrotoxic serum nephritis. Kidney Int 43(6):1280–1285
Sala A, Folco G (2001) Neutrophils, endothelial cells, and cysteinyl leukotrienes: a new approach to neutrophil-dependent inflammation? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 283(5):1003–1006. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4865
Antonipillai I, Nadler JL, Robin EC, Horton R (1987) The inhibitory role of 12- and 15-lipoxygenase products on renin release. Hypertension 10(1):61–66
Munger KA, Montero A, Fukunaga M, Uda S, Yura T, Imai E, Kaneda Y, Valdivielso JM, Badr KF (1999) Transfection of rat kidney with human 15-lipoxygenase suppresses inflammation and preserves function in experimental glomerulonephritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(23):13375–13380
Huang JT, Welch JS, Ricote M, Binder CJ, Willson TM, Kelly C, Witztum JL, Funk CD, Conrad D, Glass CK (1999) Interleukin-4-dependent production of PPAR-gamma ligands in macrophages by 12/15-lipoxygenase. Nature 400(6742):378–382. doi:10.1038/22572
Samuelsson B, Dahlen SE, Lindgren JA, Rouzer CA, Serhan CN (1987) Leukotrienes and lipoxins: structures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science 237(4819):1171–1176
Rabb H, O’Meara YM, Maderna P, Coleman P, Brady HR (1997) Leukocytes, cell adhesion molecules and ischemic acute renal failure. Kidney Int 51(5):1463–1468
Sasaki M, Hori MT, Hino T, Golub MS, Tuck ML (1997) Elevated 12-lipoxygenase activity in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Am J Hypertens 10(4 Pt 1):371–378
Gonzalez-Nunez D, Sole M, Natarajan R, Poch E (2005) 12-Lipoxygenase metabolism in mouse distal convoluted tubule cells. Kidney Int 67(1):178–186. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00068.x
Montero A, Uda S, Kelavkar U, Yoshimura A, Badr KF, Munger KA (2003) Increased 5-lipoxygenase activating protein in immune-mediated experimental nephritis. J Nephrol 16(5):682–690
Ago H, Okimoto N, Kanaoka Y, Morimoto G, Ukita Y, Saino H, Taiji M, Miyano M (2013) A leukotriene C4 synthase inhibitor with the backbone of 5-(5-methylene-4-oxo-4,5-dihydrothiazol-2-ylamino) isophthalic acid. J Biochem 153(5):421–429. doi:10.1093/jb/mvt007
Noiri E, Yokomizo T, Nakao A, Izumi T, Fujita T, Kimura S, Shimizu T (2000) An in vivo approach showing the chemotactic activity of leukotriene B(4) in acute renal ischemic-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(2):823–828
Patel NS, Cuzzocrea S, Chatterjee PK, Di Paola R, Sautebin L, Britti D, Thiemermann C (2004) Reduction of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in 5-lipoxygenase knockout mice and by the 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor zileuton. Mol Pharmacol 66(2):220–227. doi:10.1124/mol.66.2.220
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the National Plane for Science, Technology and Innovation (MAARIFAH)-King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology-the Kingdome of Saudi Arabia, Award Number (MED894-08-13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alkhamees, O.A., Alroujayee, A.S., Abuohashish, H.M. et al. Possible involvement of the lipoxygenase and leukotriene signaling pathways in cisplatin-mediated renal toxicity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 80, 55–64 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3331-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3331-8