Abstract
Purpose
The relationship between plasma concentration and antitumor activity of gefitinib was assessed in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations.
Patients and methods
Plasma trough levels of gefitinib were measured on days 2 (D2) and 8 (D8) by high-performance liquid chromatography in 31 patients. Plasma concentrations of gefitinib were also measured 10 h after the first administration in 21 of these patients to calculate the elimination half-life of gefitinib.
Results
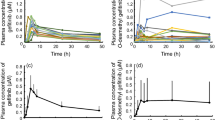
The median trough levels were: 197 ng/ml 10 h from the first administration of gefitinib; 113 ng/ml on D2; and 358 ng/ml on D8. The median D8/D2 ratio was 2.709, and the median elimination half-life was 15.7 h. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 273 days, and the median overall survival (OS) was 933 days. A high D8/D2 ratio was significantly correlated with better PFS, though the plasma trough levels on D2 and D8 were not significantly related to PFS. The elimination half-life was not a significant factor for PFS, but it was significantly correlated with high-grade adverse events. Pharmacokinetic parameters were not significantly correlated with OS.
Conclusions
A high D8/D2 ratio, but not elimination half-life, might be a predictor of better PFS in patients with NSCLC harboring EGFR mutations treated with gefitinib. On the other hand, long elimination half-life was related to high-grade adverse events in these patients.
Clinical Trial Registration UMIN000001066.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K et al (2010) Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 362:2380–2388
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y et al (2010) Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 11:121–128
Zhao YY, Li S, Zhang Y et al (2011) The relationship between drug exposure and clinical outcomes of non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. Med Oncol 28:697–702
Hirano S, Sano K, Takeda Y et al (2012) The pharmacokinetics and long-term therapeutic effects of gefitinib in patients with lung adenocarcinoma harboring the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 39:1501–1506
Nakamura Y, Sano K, Soda H et al (2012) Pharmacokinetics of gefitinib predicts antitumor activity for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 5:1404–1409
Uesugi T, Sano K, Uesawa Y et al (1997) Ion-pair reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of adenine nucleotides and nucleoside using triethylamine as a counterion. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 703:63–74
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Motoshima K, Nakamura Y, Sano K (2013) Phase II trial of erlotinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: additive analysis of pharmacokinetics. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72:1299–1304
Scholler J, Leveque D (2011) Molecular pharmacokinetic determinants of anticancer kinase inhibitors in humans. Oncol Rev 5:77–92
Scheffler M, Di Gion P, Doroshyenko O et al (2011) Clinical pharmacokinetics of tyrosine kinase inhibitors: focus on 4-anilinoquinazolines. Clin Pharmacokinet 50:371–403
Sunaga N, Oriuchi N, Kaira K et al (2008) Usefulness of FDG-PET for early prediction of the response to gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 59:203–210
Authors contribution
K. M. and Y. N. participated in study design and drafted the manuscript. S. S. was responsible for the statistical analysis and data interpretation. K. S., Y. I., K. M., S. T., D. O., H. S., N. T., T. I., H. Y., K. N., M. F., and H. M. collected clinical data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
K. M., Y. N., K. S., S. S., Y. I., K. M., S. T., D. O., H. S., N. T., T. I., H. Y., K. N., M. F., and H. M.: none to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizoguchi, K., Nakamura, Y., Sano, K. et al. Pharmacokinetic parameters of gefitinib predict efficacy and toxicity in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 78, 377–382 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3097-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3097-4